Circuits & Devices: Schematic Diagrams & Symbols
advertisement
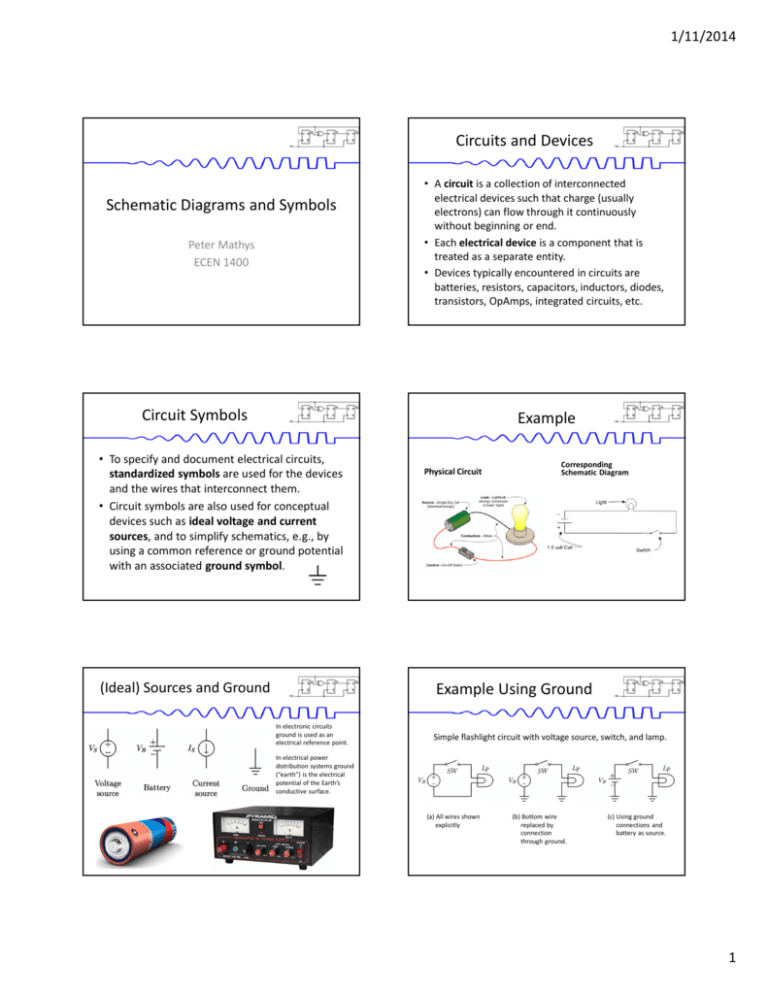
1/11/2014 Circuits and Devices Schematic Diagrams and Symbols Peter Mathys ECEN 1400 • A circuit is a collection of interconnected electrical devices such that charge (usually electrons) can flow through it continuously without beginning or end. • Each electrical device is a component that is treated as a separate entity. • Devices typically encountered in circuits are batteries, resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors, OpAmps, integrated circuits, etc. Circuit Symbols Example • To specify and document electrical circuits, standardized symbols are used for the devices and the wires that interconnect them. • Circuit symbols are also used for conceptual devices such as ideal voltage and current sources, and to simplify schematics, e.g., by using a common reference or ground potential with an associated ground symbol. (Ideal) Sources and Ground Physical Circuit Corresponding Schematic Diagram Example Using Ground In electronic circuits ground is used as an electrical reference point. Simple flashlight circuit with voltage source, switch, and lamp. In electrical power distribution systems ground (“earth”) is the electrical potential of the Earth’s conductive surface. (a) All wires shown explicitly (b) Bottom wire replaced by connection through ground. (c) Using ground connections and battery as source. 1 1/11/2014 Switches Resistors SPDT switch, construction view Standard Values Color Code Standard values for resistors and other components. The most common values are shown in bold on the first line. Lamps and LEDs Diodes Diodes are “oneway streets” for current. 2 1/11/2014 Capacitors Inductors, Transformers Transistors (BJT) Transistors (JFET, MOSFET) BJT: Bipolar Junction Transistor JFET: Junction Field-Effect Transistor MOSFET: Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor Operational Amplifiers Example Switching Regulator: Simple but nontrivial example of a schematic. 3