View Revision Note
advertisement
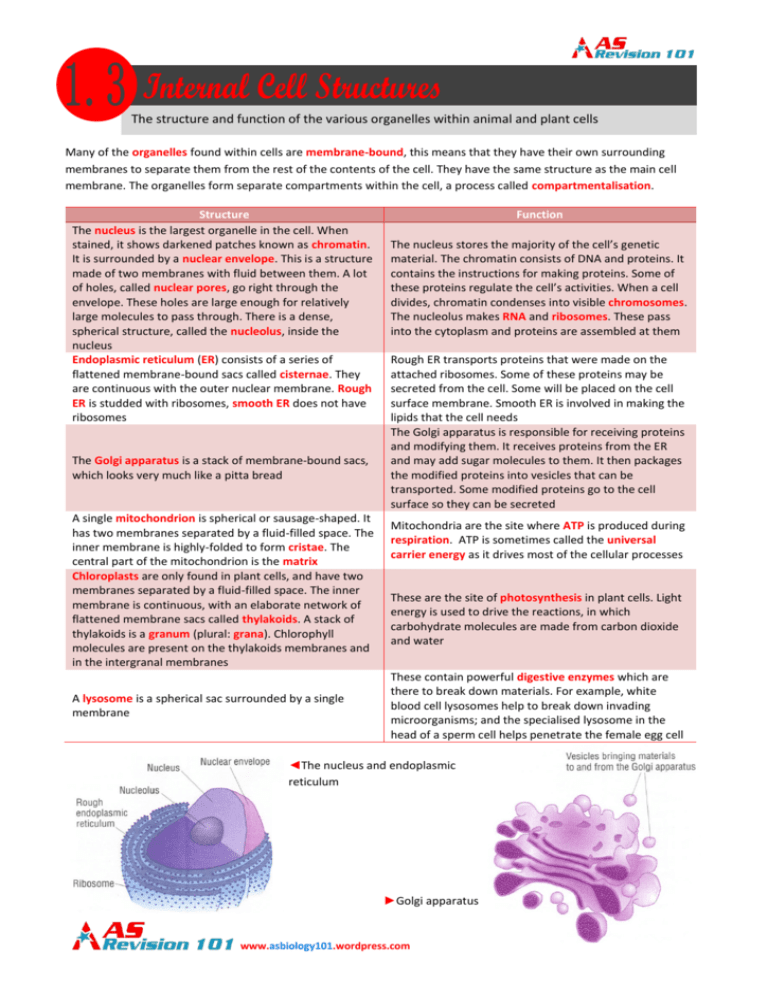
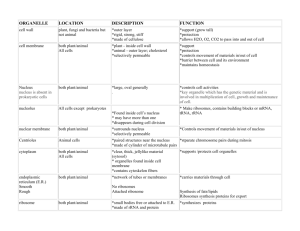
The structure and function of the various organelles within animal and plant cells Many of the organelles found within cells are membrane-bound, this means that they have their own surrounding membranes to separate them from the rest of the contents of the cell. They have the same structure as the main cell membrane. The organelles form separate compartments within the cell, a process called compartmentalisation. Structure The nucleus is the largest organelle in the cell. When stained, it shows darkened patches known as chromatin. It is surrounded by a nuclear envelope. This is a structure made of two membranes with fluid between them. A lot of holes, called nuclear pores, go right through the envelope. These holes are large enough for relatively large molecules to pass through. There is a dense, spherical structure, called the nucleolus, inside the nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) consists of a series of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae. They are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes, smooth ER does not have ribosomes The Golgi apparatus is a stack of membrane-bound sacs, which looks very much like a pitta bread A single mitochondrion is spherical or sausage-shaped. It has two membranes separated by a fluid-filled space. The inner membrane is highly-folded to form cristae. The central part of the mitochondrion is the matrix Chloroplasts are only found in plant cells, and have two membranes separated by a fluid-filled space. The inner membrane is continuous, with an elaborate network of flattened membrane sacs called thylakoids. A stack of thylakoids is a granum (plural: grana). Chlorophyll molecules are present on the thylakoids membranes and in the intergranal membranes A lysosome is a spherical sac surrounded by a single membrane Function The nucleus stores the majority of the cell’s genetic material. The chromatin consists of DNA and proteins. It contains the instructions for making proteins. Some of these proteins regulate the cell’s activities. When a cell divides, chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. The nucleolus makes RNA and ribosomes. These pass into the cytoplasm and proteins are assembled at them Rough ER transports proteins that were made on the attached ribosomes. Some of these proteins may be secreted from the cell. Some will be placed on the cell surface membrane. Smooth ER is involved in making the lipids that the cell needs The Golgi apparatus is responsible for receiving proteins and modifying them. It receives proteins from the ER and may add sugar molecules to them. It then packages the modified proteins into vesicles that can be transported. Some modified proteins go to the cell surface so they can be secreted Mitochondria are the site where ATP is produced during respiration. ATP is sometimes called the universal carrier energy as it drives most of the cellular processes These are the site of photosynthesis in plant cells. Light energy is used to drive the reactions, in which carbohydrate molecules are made from carbon dioxide and water These contain powerful digestive enzymes which are there to break down materials. For example, white blood cell lysosomes help to break down invading microorganisms; and the specialised lysosome in the head of a sperm cell helps penetrate the female egg cell ◄The nucleus and endoplasmic reticulum ►Golgi apparatus www.asbiology101.wordpress.com ◄Mitochondrion ► Chloroplast There are some organelles which are non membrane-bound… Structure A ribosome is a tiny organelle that consists of two subunits. They can be found in the cytoplasm or attached to the ER making rough ER Centrioles are small tubes of protein fibres (microtubules) which are present only in animal cells and cells of some protoctists. They are found in a pair next to the nucleus Function Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis in the cell (where new proteins are made). They act as an assembly line where coded information (mRNA) from the nucleus is used to assemble proteins from amino acids These are used in cell division, they form fibres known as spindle which move the chromosomes during nuclear division www.asbiology101.wordpress.com