The Square Deal Handout
advertisement
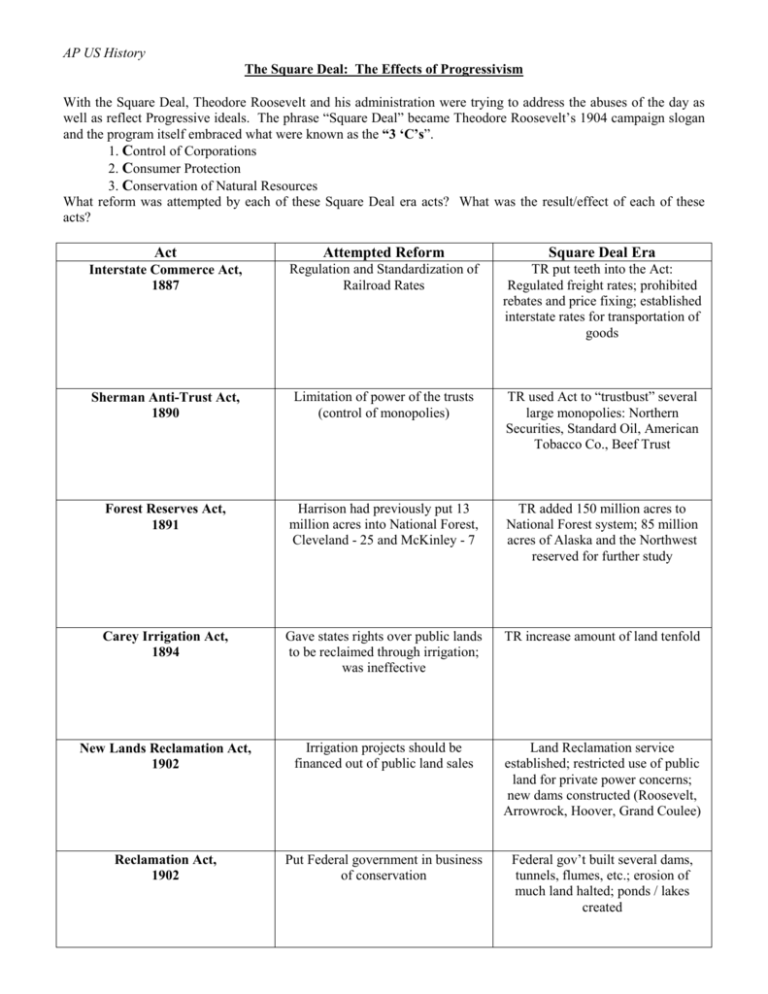
AP US History The Square Deal: The Effects of Progressivism With the Square Deal, Theodore Roosevelt and his administration were trying to address the abuses of the day as well as reflect Progressive ideals. The phrase “Square Deal” became Theodore Roosevelt’s 1904 campaign slogan and the program itself embraced what were known as the “3 ‘C’s”. 1. Control of Corporations 2. Consumer Protection 3. Conservation of Natural Resources What reform was attempted by each of these Square Deal era acts? What was the result/effect of each of these acts? Act Attempted Reform Square Deal Era Interstate Commerce Act, 1887 Regulation and Standardization of Railroad Rates TR put teeth into the Act: Regulated freight rates; prohibited rebates and price fixing; established interstate rates for transportation of goods Sherman Anti-Trust Act, 1890 Limitation of power of the trusts (control of monopolies) TR used Act to “trustbust” several large monopolies: Northern Securities, Standard Oil, American Tobacco Co., Beef Trust Forest Reserves Act, 1891 Harrison had previously put 13 million acres into National Forest, Cleveland - 25 and McKinley - 7 TR added 150 million acres to National Forest system; 85 million acres of Alaska and the Northwest reserved for further study Carey Irrigation Act, 1894 Gave states rights over public lands to be reclaimed through irrigation; was ineffective TR increase amount of land tenfold New Lands Reclamation Act, 1902 Irrigation projects should be financed out of public land sales Land Reclamation service established; restricted use of public land for private power concerns; new dams constructed (Roosevelt, Arrowrock, Hoover, Grand Coulee) Reclamation Act, 1902 Put Federal government in business of conservation Federal gov’t built several dams, tunnels, flumes, etc.; erosion of much land halted; ponds / lakes created Act Attempted Reform Square Deal Era Elkins Act, 1903 Establishment of Dept. of Commerce & Labor; Bureau of Corporations (rebates) TR established uniform labor laws and standards; published freight rates; penalized shipper who received rebates & those who gave them; provided punishment for violators Expediting Act, 1903 Addition of staff to Anti-Trust Division of Justice Department Speeded up judicial consideration of anti-trust cases (corporations cannot delay trials – cases are given precedence) Hepburn Act, 1906 Amendment of ICC Act; put “teeth” into Act Established commission to enforce ICC orders; enforcement of rate regulations; uniform system of bookkeeping; establish normal rates Meat Inspection Act, 1906 All meat sold must be inspected All meat marked by federal inspector and graded; meat industry cleaned up Pure Food and Drug Act, 1906 Extension of federal inspection to all packaged food and drugs Truth in packaging and labeling; medicine as well as food; ingredients must be listed – chemicals and additives included National Monuments Act, 1906 5 new parks established; 50 game refuges; 4 game preserves Flyways protected; natural areas preserved; beautiful areas are now protected; financial gain to states with parks; more areas for recreation Inland Water-Ways Commission, 1907 Called attention to national conservation needs and programs National Conservation Association, 1909 Center established for education and research about conservation in the US Experts gathered to discuss national conservations needs; nat’l index of natural resources established; gov’t regulations established concerning cutting timber on federal land; water and power development; forest fire control; protection established for navigable rivers and inland waterways National Forests Department transferred to Department of Agriculture










