6.4-Jackson as President PowerPoint
advertisement

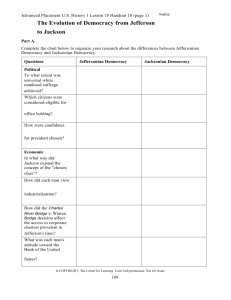
The Age of Jackson: President Jackson and Jacksonian Democracy ESSENTIAL LEARNING OBJECTIVES (ELO): ELO 8.17: Students will identify, describe, and explain the key events, people, and ideas that characterized the Age of Jackson with an emphasis on the expansion of democracy, the role of the Executive Branch, and American Indian relations. LESSON LEARNING OBJECTIVES (TSS): TSS 8.55: Explain the events and impact of the presidency of Andrew Jackson, including the emergence [beginning] of ①Jacksonian Democracy ; his use of the ②spoils system and the ③veto ACTIVITY: Complete Parts 1 and 2 of OneSheet during lecture The Age of Jackson: The Emergence of “Jacksonian Democracy” Background: Andrew Jackson won the presidential election of 1828 convincingly. He carried every state but those in the Northeast corner He won largely in part to his reputation as a selfmade man, war hero, and patriot, but also because he portrayed himself as a common man who promised “equal protection and equal benefits” for all Americans Jackson would for the most part carry through with his promise as president, but not without controversy and challenges Part 1: What was “Jacksonian Democracy”? What was “Jacksonian Democracy”? “Jacksonian Democracy” is a term given to this particular period of American history (1820s-1830s) that saw an expansion of popular democracy This expansion was fueled by the expansion of voting rights to non-propertied and working-class white males It was also encouraged by Jackson’s own personal philosophy that regular citizens of the country should enjoy the benefits of their new found political power and have the opportunities to serve that come along with it. Part 2: What did Jackson do that demonstrated his philosophy or views? What did Jackson do that demonstrated his philosophy or views? Jackson believed that the office of the President was the supreme governmental office and that a strong nation required a strong president; much stronger than the other two branches He vetoed as many bills as the previous six presidents combined and rejected the idea of Judicial Review for the Supreme Court He instituted the “spoils system” or the practice of giving government jobs to his political friends and allies. Though this system would be easily corrupted, it is still (to a smaller extent) in use today The Age of Jackson: President Jackson and Jacksonian Democracy LESSON LEARNING OBJECTIVES (TSS): TSS 8.55: Explain the events and impact of the presidency of Andrew Jackson, including the emergence [beginning] of ①Jacksonian Democracy ; his use of the ②spoils system and the ③veto REVIEW QUESTIONS: 1. 2. Describe Jacksonian Democracy, what fueled it and what characteristics it had. How did Jackson demonstrate his political philosophy in office? ASSIGNMENT: Read The Tariff Debate (328-329)