Cardiac Cycle
advertisement

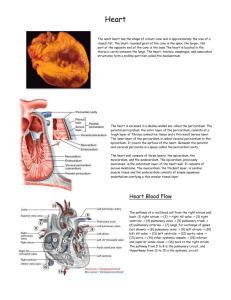
Cardiac Cycle • 1 complete contraction and relaxation of the heart • Diastole - the time during which cardiac muscle relaxes. • Systole - the time in which cardiac muscle is contracting. – Atrial systole – Atrial diastole – Ventricle systole – Ventricle diastole – Quiescent period Animation of Cardiac cycle • http:// www.getbodysmart.co m/ap/ circulatorysystem/ heart/ mechanicalevents/ cardiaccycle/ tutorial.html Electrical conduction in the Heart SA node (sinoatrial node) AV node (atrioventricular node) Bundles of His Purkinje Fibers Animation of transmission of signal http://www.lifehugger.com/pic/ 1801/ Normal_ECG_wave_Animation • Sinoatrial node (SA node) - main pacemaker of the heart • in the right atrium (near the entry of the superior vena cava) • Atrioventricular node (AV node) - found near the floor of rt. Atrium • Note of interest: • The AV node – delays the transmission of action potentials slightly, – allowing the atria to complete their contraction before the ventricles begin their contraction. Electrocardiogram (ECG) • Composite of all action potentials of myocardial cells • detected, amplified and recorded by electrodes on arms, legs and chest ECG • P wave - atrial systole – SA node fires – occurs right before atria contract • QRS complex - atrial diastole and ventricles systole – atrial diastole (signal obscured) – AV node fires, occurs right before ventricles contract • T wave - ventricles diastole – ventricular repolarization (get ready to fire again, refill with blood) Animation of ECG http://www.getbodysmart.com/ ap2/circulatorysystem/heart/ electricalevents/ecg/tutorial.html Normal Electrocardiogram (ECG) Electrical Activity of Myocardium 1)atria begin to depolarize 2) atria depolarize 3)ventricles begin to depolarize at apex; atria repolarize 4)ventricles depolarize 5) ventricles begin to repolarize at apex 6) ventricles repolarize Summary of cycle - animation http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/ dci/Diseases/hhw/ hhw_electrical.html Diagnostic Value of ECG • 1. 2. 3. 4. Invaluable for diagnosing abnormalities in: conduction pathways MI heart enlargement electrolyte and hormone imbalances ECGs, Normal & Abnormal No P waves ECGs, Abnormal Arrhythmia: conduction failure at AV node No pumping action occurs Heart Sounds • Auscultation - listening to sounds made by body 1. First heart sound (S1), • • louder and longer “lubb”, occurs with closure of AV valves 2. Second heart sound (S2), • • softer and sharper “dupp” occurs with closure of semilunar valves Unbalanced Ventricular Output Unbalanced Ventricular Output Cycle of a Heartbeat: 1. Atrial Systole: - atria contract - blood is forced into the ventricles • P wave occurs right before this 2. Ventricular Systole - ventricles contract • blood is forced into the pulmonary artery and aorta 3. Atrial Diastole • Occurs during ventricular systole • Atria refill with blood and muscles “relax” • 2 and 3 occur during the QRS wave 4. Ventricular diastole • Ventricles fill with blood from atria • T wave occurs