MUSCLES AND MOVEMENT
advertisement

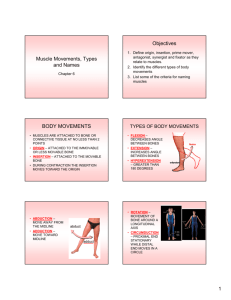
MUSCLES AND MOVEMENT To know the meaning of origin and insertion of a variety of muscles To understand the different muscular movements To be able to develop a mind map on joints and movements. STARTER IN PAIRS IDENIFTY THE TYPE OF MOVEMENTS OCCURING AT EACH JOINT. http://www.wisconline.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=AP 12004 The Origin and Insertion When a muscle contracts, only one bone moves leaving the other stationary. The points at which the tendons are attached to the bone are known as the origin and the insertion. The origin is where the tendon of the muscle joins the stationary bone(s). The insertion is where the tendon of the muscle joins the moving bone(s). Origin The arm is being flexed. Insertion The radius and ulna are the moving bones- INSERTION The humerus and scapular are stationary bones- ORIGIN Antagonistic Muscles Skeletal muscles work across a joint and are attached to the bones by strong cords known as tendons. They work in pairs, each contracting or relaxing in turn to create movement. E.g Biceps brachii and triceps brachii = known as ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLE ACTION. AS one muscle shortens the other one lengthens. Movement of the arm at the elbow Flexion (Bending) of the Arm The muscle doing the work (contracting) and creating the movement is called the agonist or prime mover. The muscle which is relaxing and letting the movement take place is called the antagonist. Agonist or Prime Mover (Biceps contract) Antagonist (Triceps relax) Other muscles support the prime mover (agonist) in creating movement and these are called synergists. Fixtor-the muscle that allows the agonist to work, stabilising the origin. SPINE RECTUS ABDOMINIS Flexion of the trunk Lateral flexion of the trunk ORIGIN: Pelvis INSERTION: Sternum and ribs STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: Crunches Application: sit-ups Cartwheels Pike in diving ERECTOR SPINAE GROUP MOVEMENT: Extension of the trunk Lateral flexion of the trunk ORIGIN: Pelvis INSERTION: Pelvis and lumbar vertebrae STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: back extensions Application: straightening out from a pike rowing Swimming (body position) TRAPEZIUS MOVEMENT- raise the head Pull the shoulders back Raise and drop the scapula Extension of the shoulder ORIGIN- Base of the cranium, 7th cervical vertebrae and all thoracic vertebrae INSERTION- Clavicle and Scapula STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: scaption APPLICATION: rowing Pull shoulders back in throwing Looking up in basketball LATISSIMUS DORSI MOVEMENT: Adduction and extension of the shoulder Internal rotation of the shoulder ORIGIN: Thoracic, Lumbar, sacrum spine and pelvis INSERTION: anterior aspect of Humerus STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: Chin ups APPLICATION: recovery in breaststroke Ten-pin bowling Drawing arm back to punch DELTOID MOVEMENT: Flexion, extension, abduction and rotation of the shoulder ORIGIN: Clavicle and Scapula INSERTION: Humerus STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: Back press APPLICATION: throwing Punching swimming PECTRALIS MAJOR MOVEMENT: Flexion of the shoulder, Adduction of the arm Internal rotation of the shoulder ORIGIN: Clavicle, sternum, 6th rib INSERTION: Humerus STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: Seated rows APPLICATION: Pressups Punching throwing BICEPS BRACHII MOVEMENT: Flexion of the elbow Flexion of the shoulder ORIGIN: Scapula INSERTION: Upper aspect of the radius STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: dumbell curls APPLICATION: biceps curl Rowing Recovery in breaststroke TRICEPS MOVEMENT: Extension of the elbow Extension of the shoulder ORIGIN: Scapula INSERTION: Upper aspect of the ulna STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: tricep dips APPLICATION: karate chop Press-ups punching FLEXOR DIGITORUM MOVEMENT: Flexion of fingers (make a fist) Flexion of wrist ORIGIN: proximal aspect of the radius & ulna INSERTION: fingers Strengthening Exercise: Wrist curls APPLICATION: punching Hold a racquet Wrist ‘dink’ in a set shot (volleyball) EXTENSOR DIGITORUM MOVEMENT: Extension of fingers Extension of wrist ORIGIN: proximal aspect of the radius & ulna INSERTION: fingers STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: reverse wrist curls APPLICATION: karate chop Fend in tackling Set shot in volleyball ILIOPSOAS MOVEMENT: Flexion of the hip ORIGIN: Pelvis and lumbar vertebrae INSERTION: upper Femur STRENGTHENING EXERCISE: Sit ups APPLICATION: kicking Running cycling GLUTEUS MAXIMUS MOVEMENT: Extension, abduction and external rotation of the leg ORIGIN: Pelvis (ilium), sacrum and coccyx INSERTION: Femur (upper third) Strengthening exercises; Bent knee hip extensions APPLICATION: jumping kicking running HIP Movement: Abduction, rotation Muscles: Gluteus medius and minimus Origin: Pelvis Insertion: Femur Strengthening exercises; Floor hip abductions QUADRICEPS 1. 2. 3. 4. Rectus Femoris Vastus Medialis Vastus Laterais Vastus Intermedius (not shown) MOVEMENT: Flexion of the hip Extension of the knee ORIGIN: Pelvis INSERTION: Femur Strengthening exercises: Bent knee hip extensions APPLICATION: jumping kicking running Hamstrings 1. Semitendinsus 2. Biceps femoris 3. semimembranosus MOVEMENT: Extension of the hip Flexion of the knee ORIGIN: Pelvis INSERTION: Femur Strengthening exercises: Bent knee hip extensions APPLICATION: jumping kicking running Gastrocnemius Movement:Knee flexion plantarflexion Origin: femur Insertion: Tarsals (Calcaneus) Strengthening exercises: one leg toe raises APPLICATION: pointing toes Kicking jumping Soleus Movement: Plantarflexion Origin: Proximal aspect of tibia and fibula Insertion: Tarsal (Calcaneus) Strengthening exercises: one leg toe raises APPLICATION: pointing toes Kicking jumping Tibialis Anterior Movement: Dorsiflexion inversion Origin: Tibia Insertion: Tarsals and metatarsals Strengthening exercises; one leg toes raises APPLICATION: passing with the outside of the foot in soccer Kicking (recovery) rowing KNEE KNEE Movement: Flexion, extension Muscles: Hamstring ( biceps femoris, semiteninosus, Semimembranosus Origin: Pelvis, Femur Insertion: Tibia and Fibula Strengthening exercises; Leg curls Knee Knee Movement: Flexion, extension Muscles:Quadriceps (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus Medialis, vastus intermediuus Origin: Pelvis, Femur Insertion: Tibia Strengthening exercises; Dumbbell squats Elbow joint Radioulnar joint Movement: Supination and Pronation Insertion: Radius Origin: Humerus and ulna Strengthening exercises; Dumb bell curls (downward and upward) Elbow joint FLEXION EXTENSION Origin: Scapula Origin: Scapula and humerus Insertion: Radius Insertion: Ulna Agonist; Biceps Antagonist; Triceps Strengthening exercises; Biceps curls and tricep extensions INTERNAL OBLIQUES MOVEMENT: Lateral flexion, rotation ORIGIN: Pelvis INSERTION: Ribs EXTERNAL OBLIQUES MOVEMENT: Flexion ORIGIN: RIBS INSERTION: Pelvis STRENGTHENING EXERCISE; Broomstick twists WRIST EXTENSORS AND FLEXORS Movement: Flexion and Extension Origin: Humerus, radius, ulna Insertion: Carpels, Metacarpels, Phalanges Strengthening exercises; Wrist curls, Reverse wrist curls TYPES OF MUSCULAR CONTRACTION ISOTONIC- the muscle is moving while contracting, it can be divided into concentric and eccentric contractions CONCENTRIC- contractions involve the muscle shortening while contracting e.g biceps brachii in elbow flexion ECCENTRIC- contraction involves muscle lengthening whilst contracting e.g. bicep brachii in elbow extension ISOMETRIC Contractions occur when there is tension on the muscle but NO movement E.G static contractions occur when holding your weight in a stationary position HANDSTAND MUSCLE SHORTENING MUSCLE LENGTHENING ISOKINETIC Contractions cause the muscle to shorten in length and increase in tension whilst working at a constant speed against a variable resistance E.G. running on a treadmill ISOKINETIC MEANS ‘SAME SPEED’