Orbital speed of Earth
advertisement
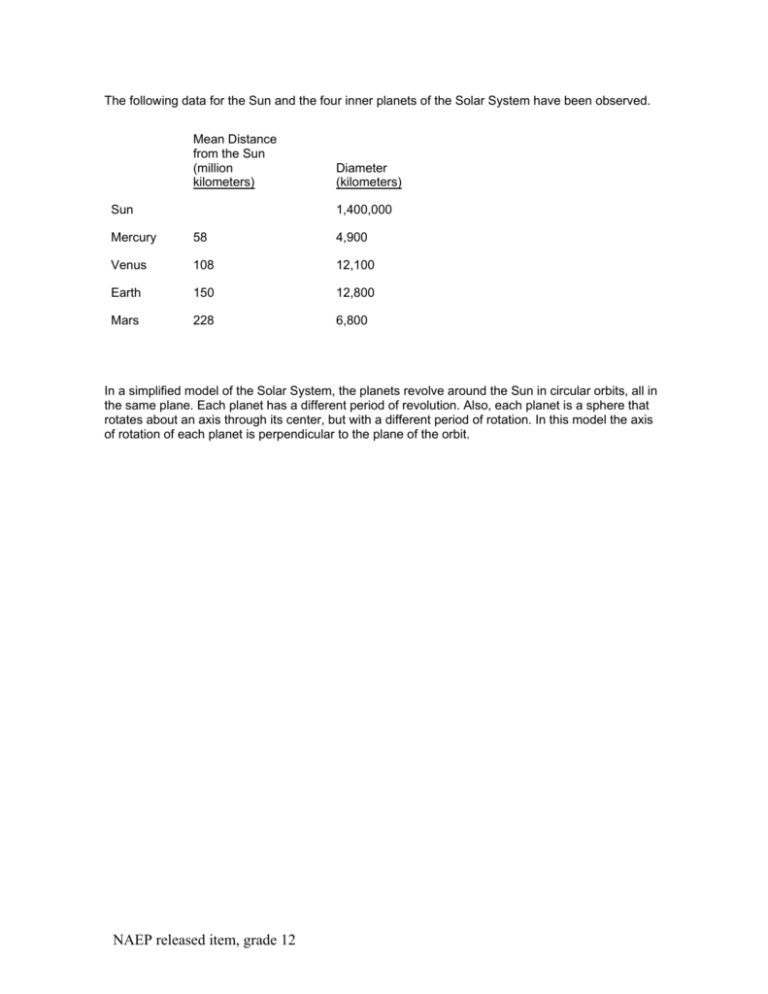
The following data for the Sun and the four inner planets of the Solar System have been observed. Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Sun Diameter (kilometers) 1,400,000 Mercury 58 4,900 Venus 108 12,100 Earth 150 12,800 Mars 228 6,800 In a simplified model of the Solar System, the planets revolve around the Sun in circular orbits, all in the same plane. Each planet has a different period of revolution. Also, each planet is a sphere that rotates about an axis through its center, but with a different period of rotation. In this model the axis of rotation of each planet is perpendicular to the plane of the orbit. NAEP released item, grade 12 1. The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. NAEP released item, grade 12 Scoring Guide Score & Description Complete Student demonstrates an understanding of both speed of an object and the geometry of a circle by describing how to calculate the speed of a planet of known orbital radius and period of revolution. Student response recognizes that speed is distance divided by time, and that in one complete revolution the distance is 2 times the radius of the orbit and time is the period of revolution. The response does not have to provide a numerical calculation. d 2 r 2 (150 x 106 km) 6 v = — = ——— = ———————— = 2.6 x 10 km/day t t 365 days Essential Student response recognizes that the speed is the circumference of the orbit divided by the period of revolution, but does not indicate how to determine the circumference. Partial Student response recognizes only that a speed is distance divided by a time (v = d/t), or equivalently that distance equals speed multiplied by time (d = vt), but indicates neither a correct distance nor time. Response may falsely interpret the radius of the orbit as the distance, or the period of rotation as the period of revolution. Unsatisfactory/Incorrect Student response does not recognize that the estimate involves dividing distance by a time. Complete - Student Response 1 The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. NAEP released item, grade 12 Scorer Comments: Student response states that speed is calculated by dividing distance by time, while recognizing that the distance is represented by the circumference of the orbit, 2 r, and the time - by the length of time it takes to complete one revolution, 365 days. 1 The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. NAEP released item, grade 12 Scorer Comments: Student response consists of a calculation showing that the distance is the circumference of the orbit, 2 r, and the speed v is the distance divided by the length of time it takes to complete one revolution, 365 days. Essential - Student Response 1 The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. Scorer Comments: Student response states that speed is calculated by dividing distance by time, while recognizing that the distance is represented by the circumference of the orbit, and the time - by the length of time it takes to complete one revolution, 365 days. The response neglects to specify how the circumference can be calculated using the data table (d=2 r). 1 The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours NAEP released item, grade 12 Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. Scorer Comments: Student response states that speed is calculated by dividing distance by time, while recognizing that the distance is represented by the circumference of the orbit, and the time - by the length of time it takes to complete one revolution. The response neglects to specify how the circumference can be calculated using the data table (d=2 r). Partial - Student Response 1 The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. NAEP released item, grade 12 Scorer Comments: Student response states that speed is calculated by dividing distance by time, correctly identifies 365 days as the time, but uses the radius of Earth's orbit for the distance instead of its circumference. 1 The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. Scorer Comments: Student response states that speed is calculated by dividing distance (# of km) by the time it takes NAEP released item, grade 12 to complete one revolution, but does not specify that the distance is represented by the circumference of the orbit or how the distance can be calculated using the data table. 1 Unsatisfactory/Incorrect - Student Response The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. Scorer Comments: Student response mentions time and distance, but shows lack of understanding of what the time relates to, and how the variables are related. 1 The table below gives additional information about the planets: their periods of revolution about the Sun and rotation about their axes. Planet Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Period of Revolution (Earth time) Period of Rotation (Earth time) Mercury 58 88 days 59 days Venus 108 225 days 243 days Earth 150 365 days 23.9 hours Mars 228 687 days 24.6 hours Describe how you could best determine, from the data given on page 6, the speed of the Earth in NAEP released item, grade 12 kilometers per day as it moves in its orbit around the Sun. Scorer Comments: Student response mentions time and distance, but shows lack of understanding of what the distance relates to, and how the variables are related. NAEP released item, grade 12 2000 National Performance Results Score Percentage of Students Unsatisfactory/incorrect Partial 49% 13% Essential 5% Complete 4% Omitted Off task 22% 7% Note: • • These results are for public and nonpublic school students. Percentages may not add to 100 due to rounding. The Fields of Science: Earth & Space Sciences (Sub content classification: Earth in Space) Knowing and Doing Science : Practical Reasoning NAEP released item, grade 12 The Fields of Science Earth & Space Sciences This question measures basic knowledge and understanding of the following: Earth in Space • • • • • • • setting of the Earth in the solar system; setting and evolution of the solar system in the universe (not in grade 4); tools and technology that are used to gather information about space; apparent daily motions of the Sun, the Moon, the planets, and the stars; rotation of the Earth about its axis, and the Earth's revolution around the Sun; tilt of the Earth's axis that produces seasonal variations in climate; and earth as a unique member of the solar system that may be approximated in other galaxies in the universe, and that evolved at least 4.5 billion years ago. Knowing and Doing Science Practical Reasoning Practical reasoning probes students' abilities to use and apply science understanding in new, realworld applications. NAEP released item, grade 12






