Robert Hooke: • Mid 1600's • English scientist who looked at Cork
advertisement
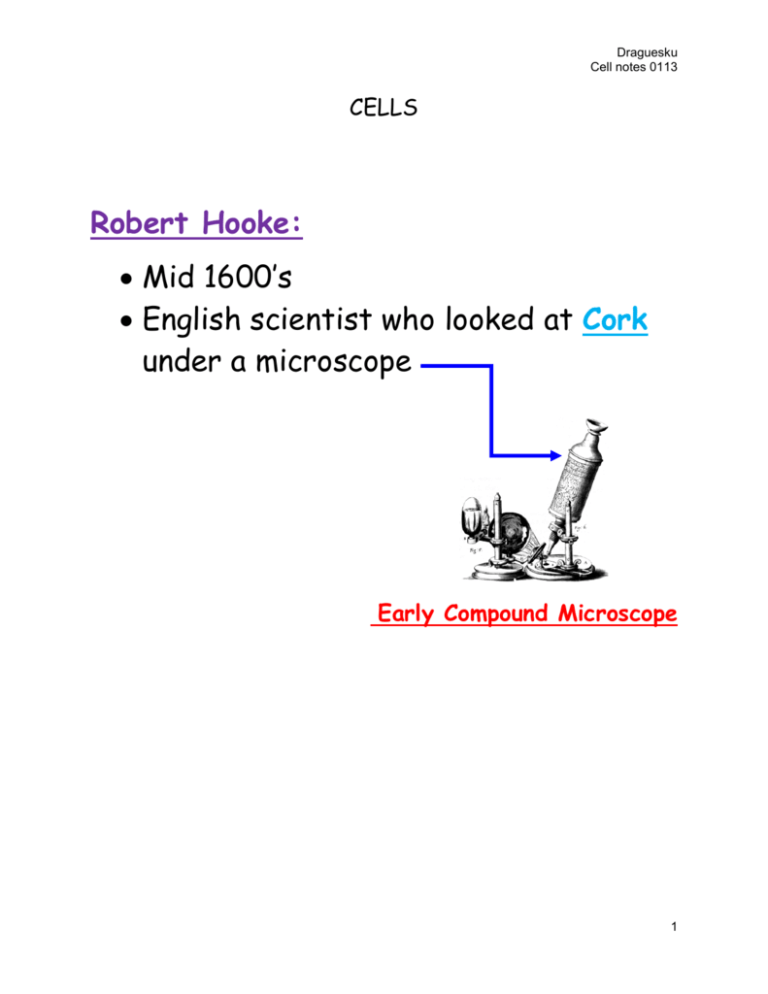
Draguesku Cell notes 0113 CELLS Robert Hooke: Mid 1600’s English scientist who looked at Cork under a microscope Early Compound Microscope 1 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 CORK He described what he saw as a CELL Another scientist: Anton van Leeuwenhoek Dutch Used a microscope and saw LIVING microscopic organisms. He called these “Animicules” He looked at pond water, and the plaque on his teeth 2 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Cells: are the basic unit of life Schleiden: German botanist ALL PLANTS ARE MADE OF CELLS Schwann: German Biologist ALL ANIMALS ARE MADE OF CELLS Virchow: German Physician NEW CELLS COME FROM THE DIVISION OF EXISTING CELLS 3 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 CELL THEORY All living things are composed of cells. All cells come from other cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things Model of a Simple Cell Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm 4 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Cell size and shape varies with function Nerve cell: can transmit nerve signals quickly between distant parts of the animal’s body Red blood Cells (RBC): Very Small so it can fit through the tiniest blood vessels. The “dimple” helps it to fold and bend. 5 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Prokaryotic Cells Very small (2-8 µm) [µm = 10-6m] NO NUCLEUS DNA is coiled in the Nucleoid Region EX: Bacteria Cell Wall: rigid & maintains shape sometimes surrounded by a STICKY capsule Further protects the cell surface Ribosomes: assemble Proteins Flagella: for movement Pili (pilus): attaches to surfaces 6 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Eukaryotic Cells From the Greek: EU = True Karyon =Kernal NUCLEUS Much more complex cell Genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell This type of cell can be in : o Single celled organism Or o Multicellular organism This includes the following Kingdoms: Plants fungi Animals protists 7 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Organelles: Structures within the cell, each with a specific function 8 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 2 MAJOR CELL PARTS Cytoplasm Portion of the cell outside the nucleus Fluid filled region between the nucleus and the plasma (cell) membrane Where are organelles found?? Nucleus Control center of the cell Contains : DNA & Instructions for protein synthesis Also surrounded by nuclear membrane/envelope In the cytoplasm 9 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 NUCLEUS Nuclear Envelope 2 membranes with pores that control the flow of material in and out of the nucleus Chromatin Long fibers of nuclear DNA attached to protein 10 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 During Cell Division chromatin condenses to form CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES carry genetic information Nucleolus: A mass of fibers and granules in the nucleus Ribosomes assembly begins here Inside the nucleus there is DNA synthesis, RNA synthesis and the assembly of the ribosomes 11 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Ribosomes: Small particles of RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) **Synthesis of MEMBRANE PROTEINS Transports proteins and other materials from one place in the cell to another Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) **Lipid synthesis; detoxification in the liver Transports protein and other material through out the cell 12 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Golgi Apparatus (Body) Modify, sort and package proteins for storage or secretion out of the cell Lysosomes: Responsible for digestion: o Of nutrients, o damaged organelles, o destruction of certain cells during Embryonic development. Ex. Tay-Sachs disease results from lysosomes that don’t work properly 13 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Vacuoles: Storage of chemicals, products of digestion Water balance and storage o There is a large central vacuole in plants that keep the plant “plump” Turgor Chloroplasts: Found in plants and protists Convert light energy into chemical energy of SUGARS (Look for the “poker chips”) 14 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Mitochondria: “Mighty Mitochondria” Conversion of chemical energy stored in food to chemical energy of ATP “POWER HOUSE OF THE CELL Fun Facts: Chloroplasts & Mitochondria have their own DNA Mitochondrial folds are called CRISTAE For more surface area Most of your mitochondria is inherited from your MOM! (this has genetic significance) 15 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Cytoskeleton: Includes cilia, flagella, microfilaments, Microtubules*, and centrioles*, *Important in cell division Maintain cell shape, anchorage for organelles, movement of organelles in the cell Cell movement Cell walls (in Plants) 1. Made of CELLULOSE 16 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 The difference between Plant and Animal Cells Plant Animal Cell Wall X Chloroplast X Vacuole One giant Many small Cell Shape More square More circular Centriole X Lysosome X Kingdom Plantae Animalia 17 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 CELL MEMBRANE A thin flexible barrier that surrounds a cell. Made of a lipid bilayer PROTEIN CHANNEL In the membrane there are many proteins with carbohydrates attached o The cell membrane looks like a MOSAIC 18 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 CELL WALL Found in: Plants Algae Fungi Prokaryotes (many) Main function: Support the cell Protect the cell Made of CELLULOSE RIGID 19 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 REGULATING MOVEMENT ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE Some definitions: Solution: A mixture of 2 or more substances Example: Kool-aide and H2O Solute: The substances dissolved in the solutions Example: the Kool-aide powder Concentration (of a solutions): The mass of a solute in a given volume Example: 12 g NaCl in 3 L of H2O= 12g/3L 4g/L 20 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 How do you think the food you eat gets to the cells in your body? (answer in the space below) “Molecule” demonstration Write your observations of what happened after Dr. D. released the “molecules” _____________________ ______________________ _____________________ Why do you think your observations happened? _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 21 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 DIFFUSION: The movement of molecules from an area of HIGH CONCENTRATION to an area of LOW CONCENTRATION across a SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE Molecules move down the Concentration Gradient The difference in concentration of molecules ***Molecules continue to move until EQUILIBRIUM is reached What is the concentration of the molecules on each side of the membrane? 22 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 How much energy is needed to reach EQUALIBRIUM? Works by random particle movement!! Osmosis: The diffusion of H2O molecules through a selectively permeable membrane Definition: membrane that only allows certain substances through. Also called semipermeable 23 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Solute molecules Water molecules move in the direction where there are fewer (lower concentration) of water molecules ***Be careful to look at the number of molecules of H20** Definitions to know Isotonic: The concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside of the cell Hypertonic: Solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell. (number of molecules of solute is higher in the solution) 24 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Hypotonic: Solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell. (number of molecules of solute is lower in the solution) Here’s what happens in the animal cell in solution Isotonic Solution: water in water out NO change In the cell Hypertonic Solution: water out Cell shrinks Hypotonic Solution: water in Cell Bursts 25 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 PLANT CELL: Hypertonic: VACUOLE COLLAPSES Hypotonic: VACUOLE SWELLS Isotonic: NO CHANGE IN VACUOLE 26 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion using Protein channels Fast and specific but still Diffusion PASSIVE TRANSPORT = NO ENERGY 27 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 ACTIVE TRANSPORT Requires ENERGY Usually uses pumps Molecules can be located in cells Move against the CONCENTRATION GRADIENT (Moving from LOW to HIGH) (ACTIVE TRANSPORT VIDEO) http://www.goldiesroom.org/Note%20Packets/06%20Transport/00%20Tr ansport--WHOLE.htm http://www.phschool.com/ web code: cbe-3076 28 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 PHAGOCYTOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS PINOCYTOSIS ACTIVE TRANSPORT EXOCYTOSIS Endocytosis: Take material into the cell by folding and engulfing Vacuole formed inside the cell Two types: 1. Phagocytosis= “cell eating” Cytoplasm surrounds the particle and engulfs it 29 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 2. Pinocytosis = “cell drinking” Liquid filled pockets along the membrane pinch off inside to form vacuoles inside the cell Exocytosis Membrane of the vacuole fuses with the cell membrane and forces its contents out of the cell http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBooktransp.html (video) 30 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 So how large is a cell? The Levels of Cell Organization: Single Cell - smallest structural unit of an organism that is capable of independent function. Example White Blood Cell 31 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Tissue A group of cells that all do the same work Example Muscle Organs: A group of tissues that work together to perform a function Example: Heart, lungs, kidneys A g r o u p o f E 32 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Organ System A group of organs that do a certain job. Examples Circulatory System, Digestion System, Lymphatic System (immune System) Important Point: Cells in an organism may differ in appearance and function, but they all work together to keep the organism alive Unicellular = Single cell These organisms out number multicellular organisms 33 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Multicellular = Many cells Cell specialization: Cells can develop to do different tasks CELL DIVISION 2 MAIN STAGES MITOSIS CELLULAR DIVISION OF BODY CELLS SIMILAR TO ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION CYTOKINESIS DIVISION OF THE CYTOPLASM 34 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 The nuclear material =DNA Starts as chromatin= CONDENSES CHROMOSOME (THICKENS) REPLICATES Chromatin Thread like coils Sister Chromatids 35 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 The human body cell has 46 chromosomes each with 2 Sister Chromatids 36 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 1 HR 2HRs 10 HRS 9 HRS. Interphase: G1, S, G2 Chromosomes copied DNA & Centrioles Replicate(copied) 37 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Begins……………. PROPHASE Chromatin Chromosome Centrioles separate Spindles begin to form ***Nuclear membrane breaks down*** 38 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 METAPHASE Chromosomes line up across the MIDDLE of the cell (equatorial plate) Chromosome connected to spindle fiber at its CENTROMERE 39 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 ANAPHASE Centromeres SPLIT Chromatids SEPARATE each becomes a NEW CHROMOSOME New chromosomes move to the ends Cell stretches SHORTEST PHASE!! LASTS ONLY A FEW MINUTES 40 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 TELOPHASE Nuclear membrane REFORMS Chromosomes lose distinct shape LAST PHASE OF MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS 2 DAUGHTER CELLS are formed Cell membrane pinches off completely 41 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 Mitosis in Plant Cells A CELL PLATE develops and begins by being fused with the cell membrane Then later it will separate from the cell membrane and fuse with the parental cell wall. Now there are 2 daughter cells 42 Draguesku Cell notes 0113 43