Ch 1 - Major Objectives - biology - branches of biology

Ch 1 - Major Objectives
- biology
- branches of biology
- the cell theory
- development of cell theory - significant events / contributions by different scientists
- biogenesis vs abiogenesis (spontaneous generation)
- experiments performed and how they supported / disproved abiogenesis
Redi, Needham, Spallanzani, Pasteur
- Fathers of Medicine, Biology, and Microscopy - contributions made for which they’re considered “Fathers”
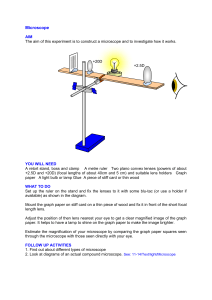
- microscope history of microscope (within development of cell theory) parts of compound light microscope and their functions differences between types of microscopes (source, type of image, specimen, cost, image quality)
Compound light microscope dissecting/stereo microscope
- essential tasks of living cells
- prokaryotic cells vs eukaryotic cells transmission electron microscope scanning electron microscope
- structures of cells cell membrane, cytoplasm, protoplasm organelles: description + function for each; nickname for those that have them cytoskeleton: components, functions of each component
- cilia vs flagella
- animal cells vs plant cells
- label parts of plant, animal (eukaryotes), and bacterial cell (prokaryote)
A FEW SUGGESTIONS TO CONSIDER AS YOU STUDY:
Make some study tools like those we’ve been speaking about as you get new material.
Spend a few minutes each day reviewing using those study tools or going back over the notes, etc.
Go through your notes and list important names + terms so you can test yourself quickly (Recognition).
Review your notes, questions in the textbook, diagrams in your notes.
Make up questions for yourself the way you think I might ask them and answer them.
Rewrite your notes in shorter form.
Use colored pens or markers to color code your notes.
Print off similar diagrams, but different enough to transfer your recognition skills to practice labeling them!
Sketch the experiments to keep straight which scientist did what study and what they proved/disproved.
Get together with someone if you are auditory so you can share / ask each other questions / discuss.
Teach someone else - sibling, parent/guardian, pet, friend
Record your notes or answers to questions and listen to them while driving on bus, going to sleep etc.
Jot down a little poem or song to help you remember order, lists, etc.
If you’re kinesthetic, run your finger along your notes / study tools as you read over them / study.
Use a squishy ball, gum, or some other tactile activity to keep you focused as you study!
Make study tools that you can move around / manipulate (ex.Cards to flip; labels to move+ stick on diagram)
(460-359 BCE)
(384 - 322 BCE)
(130 - 200CE)
1268
1590
1620's
1665
*1666, 74, 83
1668
1748 shortly after
1809
1831
1838
1839
1845
1846-47
1856
1858
1860
THE ROAD TO THE CELL THEORY
Hippocrates----------------------- Father of Medicine
Aristotle------------------------- - Father of Biology (started many branches)
- started studies of embryology (chick dev) taxonomy (classified plants & animals)
Anatomy (dissected ~ 50 animals)
Physiology (how cow’s stomach worked)
Galen------------------------------ Greatest Medical Thinker of Ancient World
- traced circulation, brain & nerves, healing ~ infection
- supported by church so hard to disprove
Roger Bacon--------------------- first recorded reference to eyeglasses
Janssen & Zacharias------------ first compound microscope (2 lenses)
William Harvey----------------- suggested maggots hatched from eggs but no proof
- disproved many of Galen’s theory
Robert Hooke------------------- used the word “cells” to describe compartments/rooms
he saw when viewing cork (inner lining of tree bark)
Anton van Leeuenhoek--------- Father of Microscopy
- dev powerful simple (1 lens) microscopes (500 +)
- saw “animalcules” in water, then later in plaque
- first to observe bacteria, sperm, blood cells
- brought microscopic world to awareness of scientists
Francesco Redi------------------ experiment: 2 jars, 1 with lid, 1 without; meat in each
- demonstrated maggots appear only if flies land on meat
- disproves spontaneous generation but no one believed
John Needham------------------ experiment: 2 jars, 1 with lid 1 without; broth in each
- boiled to “kill” living things; both grew living things
- resurgence in spontaneous generation theory
Lazzaro Spallanzani------------ skeptical, so repeated Needham’s expt; boiled longer
- boiling longer killed them; nothing grew over time
- disproved spontaneous generation theory
- others argued - no “air” the vital principal necessary
Jane Haldimand----------------- referred to cells, cellular tissue, cellular system in texts
Robert Brown-------------------- observed and named “nucleus” - dark region inside
Matthias Jacob Schleiden------ “all plants are made of cells”
Theodor Schwann--------------- “all animals are made of cells”
Alexander Carl Henrich Braun -“the cell is the basic unit of life”
Jugo von Mohl------------------- protoplasm is living substance of cell;
William Henry Perkin----------- invented purple dye used for staining slides
Rudolph Virchow---------------- Wherever a cells exists, the must be a preexisting cell.
Louis Pasteur--------------------- experiment: swan neck flask; boiled broth
- caught microorganisms + dust in neck of flask
- air (vital principle) still permitted in
- boiled broth; no living things grew
- tipped so in contact with microorganisms + dust
- microorganisms grew
- final proof that living things come from living things