Molecular Structure
advertisement

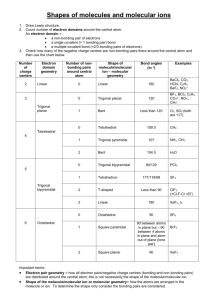
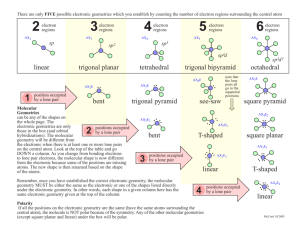
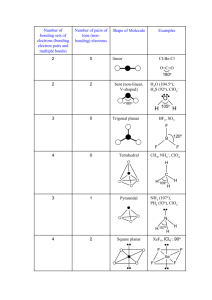
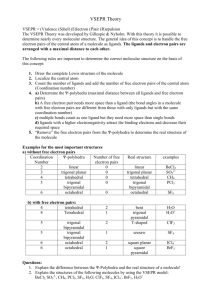
Exercise 12 Illinois Central College CHEMISTRY 130 Laboratory Section: _______ Page 1 Name:___________________________ Molecular Structure Objectives To predict the shapes of molecules based on their Lewis Structures. Background The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) is a model for predicting the shapes of molecules and ions in which valence shell electron pairs are arranged around each atom so that electron pairs are kept as far away from one another as possible, thus minimizing electron pair repulsions. For example, if there are only two electron pairs in the valence shell of an atom, these pairs tend to be on opposite sides of the nucleus. This gives a linear arrangement of electron pairs; that is, the electron pairs mainly occupy regions of space at an angle of 180o to one another. If three electron pairs are in the valence shell, they tend to be arranged in a plane toward the corners of a triangle of equal sides. This arrangement is called trigonal planar, in which the regions of space occupied by the electron pairs are directed at 120o angles to one another. Four electron pairs in the valence shell tend to have a tetrahedral arrangement. The regions of space mainly occupied by the electron pairs are directed at approximately 109.5o angles to one another. In the event that an atom has an "expanded octet", that is, more than four pairs of electrons surrounding it, two more possible shapes arise. Five electron pairs result in a trigonal bipyramid with three "equatorial" pairs at 120o angles to one another and two "axial" positions at 90o angles to the "equator". Six electron pairs results in an octahedral electron arrangement. In this case, each of the electron pairs are directed at 90o angles to one another. The Electron Pair Arrangements just discussed (See Figure 1.) can result in various "Molecular Shapes" depending on how many of the electron pairs are actually used for bonding and how many simply remain as "lone pairs" on the central atom of a molecule. The term 'Molecular Shape' refers to the spatial arrangement of the bonded atoms only (As if the lone pairs on the central atom were simply 'invisible'.) These possible 'Molecular Shapes' for each of the five Electron Pair Arrangements are summarized in Table 1. Number of pairs 2 Linear 3 Trigonal planar 4 Tetrahedral 5 Trigonal bipyramid Figure 1. Electron Pair Arrangements 6 Octahedral Exercise 12 Page 2 Procedure Fill in the Lewis Structures for all of the molecules indicated. SHOW ALL LONE PAIRS ON CENTRAL ATOM AND PERIPHERAL ATOMS. Construct models of all of the molecules or ions shown. HAVE YOUR INSTRUCTOR CHECK YOUR MODELS ONCE YOU HAVE COMPLETED ALL OF THEM. Refer to the color code on your model kit to determine the color used for each element. Note that any trigonal bipyramid must use a brown sphere and octahedral models use a grey sphere. Any lone pairs on the central atom should be represented with a vacant bonding peg as they affect the Electron Pair Arrangement and ultimately, the Molecular Shape. Use the longer flexible bonding pegs to construct any necessary double bonds. Fill in all of the information for each column and for each molecule. EXAMPLE: Number of electron Lewis density Structure _ regions __ .. 4 Species NH3 H N Number of Electron Pair Molecular lone pairs Arrangement Shape on central (Sketch (Sketch Bond atom _ and Name) ___and Name) _ angle(s) .. 1 H H N N H 109.5o H H H tetrahedral H H trigonal pyramid Exercise 12 ELECTRON PAIRS Total Bonding Lone ARRANGEMENT OF PAIRS MOLECULAR SHAPE Page 3 EXAMPLE _________________________________________________________________________ 2 2 0 Linear Linear 3 3 0 Trigonal planar Trigonal planar 2 1 4 0 3 1 Trigonal pyramid 2 2 Bent (or ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Bent(or angular) _________________________________________________________________________ 4 Tetrahedral Tetrahedral angular) _________________________________________________________________________ 5 5 0 Trigonal bipyramid Trigonal bipyramid 4 1 Seesaw 3 2 T-shaped 2 3 Linear _________________________________________________________________________ 6 6 0 Octahedral 5 1 Square pyramid 4 2 Square planar Table 1. Octahedral Exercise 12 Page 4 REPORT SHEET Molecular Structure Species Lewis Structure The central atom is underlined Number of electron density regions Number of lone pairs on central atom Electron pair arrangement (Sketch and Name) Name:________________________ Molecular Shape (Sketch and Name) Bond angle(s) 1. H2S 2. CO2 3. PH3 4. HCN Exercise 12 Page 5 5. CF4 Species 6. SO3 7. XeF2 8. SF4 Exercise 12 Page 6 9. SbCl5 10. ICl5 Lewis Structure Number of electron density regions Number of lone pairs on central atom Electron pair arrangement (Sketch and Name) Molecular Shape (Sketch and Name) Bond angle(s) Exercise 12 Illinois Central College CHEMISTRY 130 Laboratory Section: ______ PRELAB: Exp.12 Page 7 Name:___________________________ Molecular Structure 1. Draw the Lewis Structures for SiF4, SF6, and ICl3. (The central atoms are underlined) Show all of the lone pairs on the central atom and the peripheral atoms. 2. What are the Electron pair arrangements for each of the molecules in #1. SiF4 ____________________ SF6 ___________________ ICl3 ____________________ 3. What are the Molecular Shapes of the molecules in #1. SiF4 ____________________ SF6 ___________________ ICl3 ____________________ 4. Sketch the Molecular Shape for each of the molecules in #1. and indicate the bond angle(s). Exercise 12 Page 8