aGOnist - VitaAPPsych
advertisement

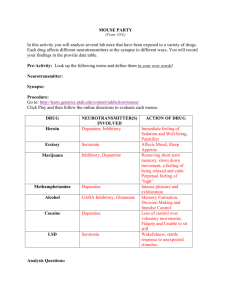
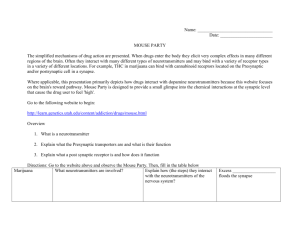
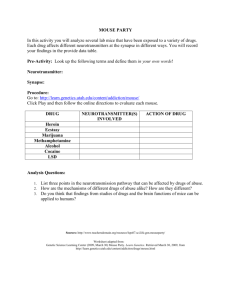
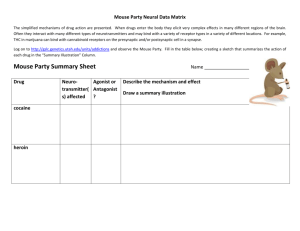
PMHS AP PSYCH Name______________________________ AIM: To understand, summarize the mechanism of action of major psychoactive drugs aGOnist – MORE neurotransmitters a) close reuptake channel b) mimic or pretend to be the neurotransmitter anTAGonist – FEWER neurotransmitters a) block receptors or dendrites b) prevent neurotransmitters from being released Stimulants: Drugs that EXCITE neural activity and speed up body functions Drug Significant AGOnist or Neurotransmitters or AnTAGonist – why? ions Cocaine Mouse Party Mechanism of action - PBS Amphetamine or Methamphetamine Mouse Party Ecstasy or MDMA (methylenedioxymethamphetamine) Mouse Party *note: Ecstasy also considered a mild hallucinogen Hallucinogens: Drugs that DISTORT perception and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input. Also known as “psychedelic or “mind manifesting” Drug Significant AGOnist or Neurotransmitters or AnTAGonist – why? ions LSD or acid (lysergic acid diethylamide) Mouse Party Marijuana Mouse Party Depressants: Drugs that CALM neural activity and slow body functions Significant AGOnist or Drug Neurotransmitters or AnTAGonist – why? ions Barbiturates (tranquilizers) Mechanism of action Alcohol Mouse Party Mechanism of action - PBS Opiates or analgesics “pain reducers” – heroin, opium, morphine, methadone Mouse Party Mechanism of action – PBS *note: There are many FDA approved prescription “pain reducers” that are currently being abused like Oxycontin and Vicodin and a newly approved drug, as of Oct 25, 2013 Zohydro Practice Classification Drug names (try to rewrite without looking at notes) Stimulants Depressants Hallucinogens Neurotransmitters or ions Cerebral Commando video game Review sleep stages Study for Monday’s test