APUSH Unit 9 Outline 2015 - MPH History - MTS
advertisement

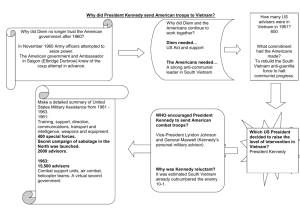
A.P. United States History M . Tw o m e y - S m i t h mtwomeysmith@mph.net Unit 9: World War II and the Cold War: Impacts Home and Abroad Unit Outline 1) ! Mushroom cloud rising over Hiroshima, Japan, August, 1945 2) Diplomacy in the 1930s a) Good Neighbor Policy b) London Economic Conference c) Disarmament d) Isolationism, neutrality legislation e) Japan and Germany f) Appeasement g) Rearmament, Blitzkreig, Lend-Lease h) Atlantic Charter i) Pearl Harbor World War II Organizing for war i) Propaganda ii) Japanese-American internment b) War in Europe, Africa, Pacific c) Diplomacy i) Teheran, Yalta, Potsdam d) End of the war i) Atomic Weapons ii) Transition to peace iii) The rise of the Cold War a) Essential Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What political, social, economic, and cultural events led to World War II? Why was U.S. involvement in WWII delayed? What events led to the rise of the Cold War? Why did the U.S. get involved in places like Korea and Vietnam? What was the social, economic, and political impact of those wars? Learning Objectives At the end of this unit, students should be able to: • • • Identify key reasons the U.S. became involved in overseas wars like WWII, Korea, and Vietnam. Evaluate the successes and failures of those actions. Explain the impact of the Cold War on American culture and politics. 3) Truman and the Cold War Postwar domestic adjustments The Taft-Hartley Act Civil Rights and the election of 1948 Containment Policy i) Truman Doctrine ii) Marshall Plan iii) Berlin Crisis iv) NATO e) Chinese Communist Revolution f) Korea i) MacArthur a) b) c) d) a) b) c) d) Eisenhower and Modern Republicanism McCarthyism Civil Rights movement John Foster Dulles’ foreign Policy Space Race a) b) c) Kennedy and the New Frontier, Johnson and the Great Society Vietnam Cuba and the USSR Civil Rights a) b) c) Kennedy and the New Frontier, Johnson and the Great Society Vietnam Cuba and the USSR Civil Rights 4) 5) 1) Unit 9: World War II and the Cold War: Impacts Home and Abroad USS West Virginia Sinking in Pearl Harbor during air raid, December 7, 1941 ! Terms, People & Concepts Neutrality Acts of 1935, 1937, 1939 Lend-Lease Act Neutrality Act of 1941 Destroyer Deal Atlantic Charter Pearl Harbor Appeasement Conferences: Yalta, Potsdam Operation Overlord (D-Day) Island Hopping Hiroshima Nagasaki Manhattan Project Japanese-American Internment Congress of Racial Equality “Rosie the Riviter” Cold War Containment Brinksmanship Massive retaliation Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan NATO United Nations John Foster Dulles Satellites Peaceful coexistence Flexible response Berlin Airlift Warsaw Pact Arms Race Space Race Central Intelligence Agency Korean War (police action) Suez Crisis Sputnik U-2 Incident Bay of Pigs Cuban Missile Crisis Alliance for Progress Nuclear Test Ban Treaty “hotline” Vietnam War Gulf of Tonkin Incident Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Tet Offensive Paris Peace Accords Henry Kissinger Domino Theory Viet Minh Viet Cong Ho Chi Minh My Lai Massacre Fair Deal Taft-Hartley Act G.I. Bill Full Employment Act McCarthyism Joseph McCarthy Alger Hiss Rosenbergs 22nd Amendment Military-Industrial Complex Interstate Highway Act Desegregation of Armed Forces Brown v. Board of Education Thurgood Marshall Rosa Parks Martin Luther King, Jr. Little Rock Crisis, 1957 School Newsletter Grade Level News Unit 9: World War II and the Cold War: Impacts Home and Abroad Page 3 of 4 Unit 9: AP Exam Essay Questions/ ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS The following questions have been asked as AP Free Response (FRQ) and Document Based Questions (DBQ) on this unit. 1. Analyze the extent to which TWO of the following transformed American society in the 1960s and 1970s: • The Civil Rights movement • The antiwar movement • The women’s movement 2. Analyze the successes and failures of the United States Cold War policy of containment as it developed in TWO of the following regions of the world during the period 1945 to 1975. • East and Southeast Asia • Europe • Latin America • Middle East 3. Compare and contrast United States foreign policy after the First World War and after the Second World War. Consider the periods 1919-1928 and 1945-1950. 4. What were Cold War fears of the American people in the aftermath of the Second World War? How successfully did the administration of President Dwight D. Eisenhower address these fears? Confine your answer to the years 1948-1961. 5. Analyze the success of the United States policy of containment in Asia between 1945 and 1975. 6. “1968 was a turning point for the United States.” To what extent is this an accurate assessment? In your answer, discuss TWO of the following: • National politics • Vietnam War • Civil Rights 7. How do you account for the appeal of McCarthyism in the United States in the era following the Second World War? 8. Analyze the influence of TWO of the following on American-Soviet relations in the decade following the Second World War. • Yalta Conference • Communist Revolution in China • Korean War • McCarthyism 9. To what extent did the decades of the 1950s deserve its reputation as an age of political, social, and cultural conformity? 10. “The United States decision to drop an atomic bomb on Hiroshima was a diplomatic measure calculated to intimidate the Soviet Union in the post-Second World War era rather than strictly a military measure designed to force Japan’s unconditional surrender.” Confine your answer to the years 1939 through 1947. 11. While the Unites States appeared to be dominated by consensus and conformity in the 1950s, some Americans reacted against the status quo. Analyze the critiques of United States society made by TWO of the following. • Youth • Civil Rights Activists • Intellectuals 12. Analyze the ways in which the Vietnam War heightened social, political, and economic tensions in the United States. Focus your answer on the period 1964 to 1975. 13. How did the African-American Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s address the failures of the Reconstruction? 14. Analyze the extent to which TWO of the following transformed American society in the 1960s and 1970s: • The Civil Rights movement • The antiwar movement • The women’s movement A.P. United States History ! Unit 9: World War II and the Cold War: Impacts Home and Abroad Assignments It is expected that you will complete all reading assignments and homework thoroughly and carefully before you come to class. “Norton” refers to the textbook, A People & A Nation. Work to be completed by: March 24 & 25 World War II and the Origins of the Cold War Norton pp. 751-759, 766-793 (skim - do not worry about the military details) March 26 & 27 Cold War Home and Abroad Part I - The New Atomic World, the Korean War and U.S. Soviet Relations under Truman and Eisenhower; 1950s and Cold War Conformist Culture Norton pp. 798-822, 827-849 Primary Source: Truman Doctrine March 30 & 31 Cold War Home and Abroad Part II - Kennedy, Johnson and the Vietnam Quagmire; The 1960s Counterculture and the Protest Movements Norton pp. 859-863, 872-877 Norton pp. 849-855, 877-883 Primary Source: Gulf of Tonkin Agreement Video: Kennedy Speeches April 1 & 2 The Civil Rights and the Great Society Norton pp. 863-872 March 13 & 14 Seminar - Civil Rights Readings TBD April 15 & 16 Unit 11 Exam: DBQ SPRING BREAK READING - Godfrey Hodgson’s America in Our Time Spring Break Movie Assignment - Handout