Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
advertisement

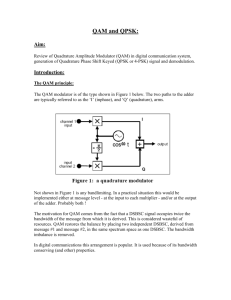
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Roshni A Chaudhari ME EC What is QAM? Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals or two digital bit streams, by changing amplitude of two carrier waves, using the amplitude shift keying (ASK) digital modulation scheme, or amplitude modulation scheme for analog modulation. Analog QAM The QAM is similar to DSB-SC but sends two message signals over the same spectrum. One of this message signal say m1(t) is sent in phase, i.e by multiplying it with and the other message signal, m2(t) is sent in quadrature by multiplying it with and finally adding these two signals. A QAM signal represented as QAM Transmitter QAM Receiver The Demodulation uses coherent detection i.e multiplication by carrier and then baseband low pass filtering. If is multiplied with we get back and if we multiplied with we get back. There is serious problem with QAM demodulation if local oscillator has some phase error, this gives cochannel interference. QAM Constellation In M-ary PSK modulation, amplitude of transmitted signal was constrained to remain constant, there by yielding a circular constellation. By allowing the amplitude to also vary with the phase we obtain QAM, so constellation consist of a squre lattice of a signal points. Constellation diagram of 16-ary QAM QAM bits per symbol The advantage of using QAM is that it is a higher order form of modulation and as a result it is able to carry more bits of information per symbol. By selecting a higher order format of QAM, the data rate of a link can be increased. Modulation Bits per symbol Symbol rate BPSK 1 1*bit rate QPSK 2 ½*bit rate 8PSK 3 1/3*bit rate 16QAM 4 ¼*bit rate 32QAM 5 1/5*bit rate 64QAM 6 1/6*bit rate QAM noise margin While higher order modulation rates are able to offer much faster data rates and higher levels of spectral efficiency for the radio communications system, this comes at a price. The higher order modulation schemes are considerably less resilient to noise and interference. As a result of this, many radio communications systems now use dynamic adaptive modulation techniques. They sense the channel conditions and adapt the modulation scheme to obtain the highest data rate for the given conditions. Bandwidth and Power efficiency The power spectrum and bandwidth efficiency of QAM modulation is identical to M-ary PSK modulation In terms of power efficiency QAM is superior to Mary PSK. Bandwidth and Power efficiency(cont…) QAM advantages and disadvantages QAM increase the efficiency of transmission for radio communications systems by utilising both amplitude and phase variations. It has a number of drawbacks. The first is that it is more susceptible to noise. Receivers for use with phase or frequency modulation are both able to use limiting amplifiers that are able to remove any amplitude noise and thereby improve the noise reliance. This is not the case with QAM. The second limitation is also associated with the amplitude component of the signal. When a phase or frequency modulated signal is amplified in a radio transmitter, there is no need to use linear amplifiers, whereas when using QAM that contains an amplitude component, linearity must be maintained. Unfortunately linear amplifiers are less efficient and consume more power, and this makes them less attractive for mobile applications. Almost always requires a highly stable local oscillator In the optical domain this is very expensive Applications of QAM Used in bandwidth-limited applications Modems: telephones have 3kHz bandwidth, excellent SNR (20dB) => M-ary QAM Cellular Telephones: Bandwidth is at a premium, very expensive (However, POWER QAM is used in analog color television to multiplex the chrominance signals, which carry the information about the color. Digital satellite television transmission also applies QAM. References John G. Proakis, Masoud Salehi, Communications Systems Engineering, Prentice Hall 1994 Principles of communication systems by taub and schilling Modern digital and analog communication system by B.P.Lathi