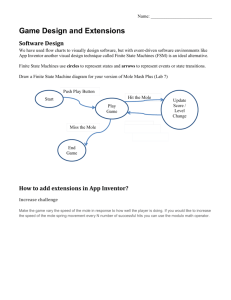
1-Mole Flow Chart.cwk (WP)
advertisement

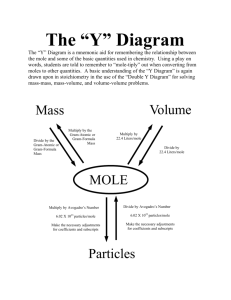
Chemistry Mole Flow Chart Conversion Factors Particles/Atoms/Molecules 6.02 x 1023 1 Mole 6.02 x 102 3atoms -OR6.02 x 102 3atoms 1 Mole Conversion Factors 1 Mole Atomic/molecular Wt. -ORAtomic/Molecular Wt. 1 Mole 1 Mole Conversion Factors 1 Mole 22.4 dm3 -OR22.4 dm3 1 Mole Mass (grams) atomic mass or molecular mass from periodic table Volume Of A Gas 22.4 dm3 Activity Series Chart Metals Most Active Non-Metals Name Symbol Name Symbol Lithium Potassium Barium Strontium Calcium Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Manganese Zinc Iron Cadmium Cobalt Nickel Tin Lead Hydrogen Copper Silver Mercury Gold Li K Ba Sr Ca Na Mg Al Mn Zn Fe Cd Co Ni Sn Pb H Cu Ag Hg Au Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine F Cl Br I Least Active *** Elements CANNOT replace anything ABOVE them. The reaction DOES NOT OCCUR in this situation. Chemistry Gas Laws Cheat Sheet Boyle’s Law P1V1 = P2V2 P1 = P2V2 V1 = P2V2 V1 P1 V2= P1V1 P2 P2 = P1V1 V2 Combined Gas Law Charles’ Law V1 = V2 T1 V1 = V2T1 T2 T1 = V1T2 V2 V2= V1T2 T1 T2 = V2T1 V1 Graham’s Law P1V1 = P2V2 T1 T2 P1 = P2V2T1 T2V1 P2 = P1V1T2 T1V2 V1 = P2V2T1 T2P1 V2= P1V1T2 T1P2 T1= P1V1T2 P2V2 T2= P2V2T1 P1V1 V1 = M2 V2 M1 ______ diffuses ______ times as fast as _____. General Conversions STP = OoC (273 K), 101.3 kPa 101.3 kPa = 760 mm Hg = 760 torrs = 1 atm = 14.69 lbs/in2 1 kPa = 7.5 torrs 1 kPa = 7.5 mm Hg 1 torr = 1 mm Hg PSI = T2 lbs/in2 (Gas X ) (#) (Gas Y) Temperature Conversions T K = ToC + 273 ToC = TK - 273 ToF = 1.80 (ToC ) +32 ToC= ToF - 32 1.80 Ion Charge Sheet Binary Fixed Charge Symbol H Li Na (+) K Rb Cs Ag Be Mg Ca Sr (+2) Ba Ra Zn Ni (+3) Al Name hydrogen lithium sodium potassium rubidium cesium silver beryllium magnesium calcium strontium barium radium zinc nickel aluminum (-) (-2) (-3) (-4) Symbol H F Cl Br I O S Se Te N P As B C Name hydride fluoride chloride bromide iodide oxide sulfide selenide telluride nitride phosphide arsenide boron carbon Variable Charged Metals (Stock system) copper(I) copper(II) iron(II) iron(III) tin(II) Common Name cuprous cupric ferrous ferric stannous Sn4+ Cr2 + tin(IV) chromium(II) Cr3+ Mn2 + Mn3+ chromium(III) manganese(II) manganese(III) Symbol Cu+ Cu2 + Fe2 + Fe3+ Sn2 + Hg2 + Pb2 + Pb4+ Co2 + (Stock system) mercury(I) mercury(II) lead(II) lead(IV) cobalt (II) Common Name mercurous mercuric plumbous plumbic cobaltous stannic chromous Co3+ Au+ cobalt (III) gold(I) cobaltic aurous chromic manganous manganic Au3+ gold(III) auric Symbol Hg2 2 + Co2 + Symbols and Charges for Polyatomic Ions (+) (-) Formula Name Formula + NH4 ammonium Hg2 Mercury (I) or Mercurous nitrate nitrite cyanide hypoiodite iodate periodate permanganate amide thiocyanate ClO4 ClO3 ClO2 ClO BrO BrO3 OH ReO4 perchlorate chlorate chlorite hypochlorite hypobromite bromate hydroxide Perhennate HS HCO3 HC2 O4 hydrogen sulfide hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) hydrogen oxalate (binoxalate) H2 PO4 dihydrogen phosphate HPO4 C4H4O6 SiO3 S2O3 SeO4 SiF6 hydrogen phosphate tartrate silicate thiosulfate selenate hexafluorosilicate NO3 NO2 CN IO IO3 IO4 MnO4 NH2 SCN HSO3 HSO4 C2 H3O2 hydrogen sulfite (bisulfite) hydrogen sulfate (bisulfate) acetate (CH3COO-) O2 CO3 SO4 SO3 (-2) C2O4 B4O7 CrO4 Cr2O7 peroxide carbonate sulfate sulfite oxalate tetraborate chromate dichromate PO4 2+ Name phosphate (-3) PO3 AsO3 phosphite arsenite AsO4 BO3 arsenate borate Greek Prefixes 1 mono 2 di 3 tri 4 tetra 5 penta 6 hexa 7 hepta 8 octa 9 nona 10 deca Diatomic Molecules N2 , O2 , H2 , Cl2 , Br2 , I2 , F2 The Modern Periodic Table of the Elements 1 18 Hydrogen H 1.01 2.1 2 Lithium Beryllium 3 4 Li Be 6.94 1.0 Sodium Element name Average relative masses are 2001 values, rounded to two decimal places. 1 1.5 Mercury Symbol 2 Atomic # 80 All average masses are to be treated as measured quantities, and subject to significant figure rules. Do not round them further when performing calculations. 9.01 Helium He Hg 200.59 Avg. Mass 14 15 16 17 Boron Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Fluorine 5 6 7 8 9 10 B C N O F Ne 10.81 1.9 Electronegativity 12.01 2.0 Magnesium 4.00 13 Aluminum 14.01 2.5 16.00 3.0 19.00 3.5 Silicon Phosphorus Sulfur --Neon 20.18 4.0 Chlorine --Argon 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar 22.99 24.31 26.98 28.09 30.97 32.07 35.45 39.95 Krypton 0.9 1.2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1.5 1.8 2.1 2.5 3.0 --- Potassium Calcium Scandium Titanium Vanadium Chromium Manganese Iron Cobalt Nickel Copper Zinc Gallium Germanium Arsenic Selenium Bromine 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 40.08 44.96 47.88 50.94 52.00 54.94 55.85 58.93 58.69 63.55 65.39 69.72 72.61 74.92 78.96 79.90 83.80 Rubidium Strontium Yttrium Zirconium Niobium Technetium Ruthenium Rhodium Palladium Silver Cadmium Indium Tin Antimony Tellurium Iodine Xenon 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe 85.47 87.62 88.91 91.22 92.91 95.94 (98) 101.07 102.91 106.42 107.87 112.41 114.82 118.71 121.76 127.60 126.90 131.29 Cesium Barium Lutetium Hafnium Tantalum Tungsten Rhenium Osmium Iridium Platinum Gold Mercury Thallium Lead Bismuth Polonium Astatine Radon K 39.10 0.8 0.8 1.0 1.0 55 56 Cs Ba 132.91 137.33 Francium Radium 87 88 Fr Ra 0.7 (223) 0.7 1.3 1.2 57-70 * 0.9 (226) 1.8 1.9 1.8 2.2 1.8 2.2 1.8 2.2 1.9 1.9 1.6 1.7 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.8 2.0 1.9 2.4 2.1 2.8 2.5 3.0 2.6 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn 174.97 178.49 180.95 183.84 186.21 190.23 192.22 195.08 196.97 200.59 204.38 207.20 208.98 (209) (210) Ytterbium 1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.4 1.9 1.8 1.8 Rutherfordium Dubnium Seaborgium Bohrium Hassium Meitnerium Ununnilum Unununium Ununbium 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 114 Lr Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Uun Uuu Uub Uuq (262) (261) --- (262) --- (263) --- (262) --- --- (265) (266) --- (271) --- (272) --- 2.0 Ununquadium (277) --- 1.9 (289) --- --- Lanthanum Cerium Praseodymium Neodymium Promethium Samarium Europium Gadolinium Terbium Dysprosium Holmium Erbium Thulium 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb 138.91 140.12 140.91 144.24 (145) 150.36 151.97 157.25 158.93 162.50 164.93 167.26 168.93 173.04 Actinium Thorium Protactinium Uranium Neptunium Plutonium Americium Curium Berkelium Californium Einsteinium Fermium 1.1 **actinides Molybdenum 1.5 Hf 0.9 *lanthanides 1.6 1.6 71 Lawrencium ** 1.4 1.6 Lu 1.1 89-102 1.5 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.2 1.1 1.2 1.1 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.3 Mendelevium 1.1 Nobelium 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 Ac Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No (227) 232.04 231.04 238.03 (237) (244) (243) (247) (247) (251) (252) (257) (258) (259) 1.1 1.3 1.5 1.4 1.4 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 2.2 (222) 2.4 Solubility Table To Be Used With Double Replacement Reactions Table Of Solubility In Water KEY CHART S = soluble in water PHASE (aq) I = insoluble in water (s) P = slightly soluble in water (s) - = compound does not exist General Rules Of Solubility 1.) All ammonium, potassium and sodium compounds are soluble in water (aq). 2.) All acetates, chlorates and nitrates are soluble in water (aq). 3.) All chlorides are soluble in water except those of silver, mercurous and lead. 4.) All sulfates are soluble in water except those of barium, lead, calcium, strontium and silver which are only slightly soluble (s). 5.) Carbonates, phosphates, oxides, silicates, sulfides and sulfates are generally insoluble (s) with the exceptions of those of ammonium, potassium and sodium. 6.) All hydroxides are insoluble except those of ammonium, potassium, sodium, barium, calcium and strontium. Those of barium , calcium, and strontium are only slightly soluble in water (s). 7.) All acids are soluble (aq). 8.) HOH is water (H2 O) and it is a LIQUID (l) (s) Solutions Chemistry Conversions & Equations Equations Molarity = Moles Of Solute Liter Of Solution Liters Of Solution = Moles Of Solute Molarity Moles Of Solute = Liter Of Solution Moles Of Solute = grams of solute molar mass of solute x Molarity ***molar mass = formula mass Grams Of Solute = molar mass of solute x moles of solute Liter Of Solution = ml of solution 1000 Conversions 1000 ml = 1 liter 1 cm3 = 1 ml 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3 = 1 liter Acid Base Titrations VaNa = VbNb Va = volume of acid Na = normality of acid Vb = volume of base Nb = normality of base Va = VbNb Na Na = VbNb Va Nb = VaNa Vb 1 Vb = VaNa Nb STOICHIOMETRY COEFFICIENT MOLE BRIDGE Given Substance Flow Chart Atoms Find Substance Flow Chart Atoms Given To Find Mole Bridge 6.02 x 1023 6.02 x 1023 1 Mole Mass (grams) atomic mass or formula mass 1 Mole Volume Of A Gas 22.4 dm3 Balanced Equation Coefficients Mass (grams) atomic mass or formula mass Volume Of A Gas 22.4 dm3