Exporting, Importing, and Countertrade
advertisement

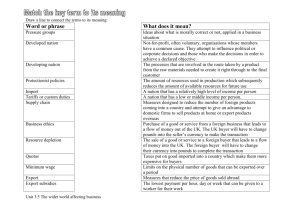
Chapter 16 Exporting, Importing, and Countertrade The Promise And Pitfalls Of Exporting Exporting – great way to increase market size Large firms Proactively seek opportunities Many smaller firms Reactive/wait for the world to come to them Information Sources Most comprehensive government source of export information - U.S. Department of Commerce International Trade Administration and the United States and Foreign Commercial Service http://www.buyusa.gov/home/export.html “International Partner Search” “Franchise Partner Search” “Gold Key” service Organizes events (trade pavilions, catalog shows) to help firms make foreign contacts Small Business Administration can help Local and state governments also provide support Use Caution When Trading If something appears too good to be true, it often is: Check Bureau of Industry & Security (BIS) - Denied Persons List http://www.bis.doc.gov/dpl/default.shtm Direct Selling You export the product - your partner helps you sell it after it arrives there: Sales representative: usually operates on a commission basis within an exclusive territory (next slide has details on agents) Distributor: Merchant who purchases goods from a manufacturer and stocks, services, and resells them to retailers at a profit PREFERRED because they invest in inventory Difference between Agent and Rep Big legal difference between Rep and Agent: BOTH sell product for you in their market, for a commission, but: Representative can NOT make commitments on behalf of your firm (unless authorized) Agent CAN make commitments on behalf of your firm SOLUTION: Have written agreements that define their duties, obligations, responsibilities, limitations, and remuneration Negotiations - What is our style? Handout – Negotiating Style Rate each of the 35 items Handout – Scoring Sheet Your style (strengths/weaknesses/appropriateness) Dodger Dreamer Haggler Competitor Problem Solver Let’s Negotiate: Groups – (6 groups) 17 camels A man, after he died, left 17 camels to his three sons 1/2 to his oldest son, 1/3 to his middle son, 1/9 to youngest Can you figure out how to divide these exactly as directed? They could not figure it out either – They went to a wise negotiator for advice After thinking she said, “See what happens after you take my camel” Now they had 18 camels – oldest took 9, middle took 6 and youngest took 2 – had one left over, so they gave it back to the negotiator In negotiations for long-term – Find the 18th camel Let’s Get Started! Let’s Negotiate: Groups – One is Buyer, One is Seller Buyer: $2 billion company, active in trade, wants a lower price, on-going relationship Seller: $1.5 million company, active in trade, wants higher profits, expand sales, on-going relationship The last transaction (have done business before): 5,000 units @ $200.00 per unit CIF Los Angeles – GPS device Payment: Open Account Net 30 (after invoice – date of shipping) Bubble pack, standard export packing, 1 year warrantee Prepare for negotiation (5 minutes) • Outline what your main points will be (turn in) Negotiate for 5 minutes Results – debrief (write results on paper) Negotiation Strategies Short Film (5 min) Two Questions to ask: 1. What happens to both sides in the event that we don’t agree? (consequences of no agreement) - What are the consequences for both sides? - Clarity on customer’s alternative to us if we don’t reach agreement – know these options better than they do. 2. What are the likely terms in the event we do agree? - What are the likely trades from both sides? - What are all of the factors that come into play? - Where do we have extra wiggle room? Bundling (adjust price and profits) Bundle Up - Adding Value • • • • Value becomes primary buyer motivator Response to competitive pricing Extends life-cycle e.g., computers [combined with software/warranty] Bundle Down - Take Away Value • • • • Price becomes primary buyer motivator “Buy” market share strategy Creates low-cost image e.g., Ikea [knock-down condition/low price] Cost Analysis – Seek lower OVERALL costs Banking Fees Costs related to Standards/Registrations • Costs vs. risks (ISO 90002000) Documentation fees Export/Import processing costs Financing charges Foreign exchange costs (Risks) Freight/ Intermodalism/ Insurance Costs • INCOTERMS Inspection/Lab testing costs Inventory/ carrying costs (up to 1.5%/week) • Fewer larger shipments VS. frequent smaller shipments Legal/contract costs (Risks) Marketing costs Minimum order quantities Production costs • Sample costs • Spare parts allocations (defective goods contact) Special packaging/ private label costs Opportunities to Reduce Costs Adapt Logistics • Product shipping form (KD, SKD) • Adjust frequency of departures • Optimize route sequencing Subassembly in FTZ (Foreign Trade Zones) • Classification (Changes duty rate) • Move labor intensive tasks Alternative Financing Methods Countertrade A range of barter-like agreements that facilitate the trade of goods and services for other goods and services when they cannot be traded for money Used when conventional means of payment are difficult, costly, or nonexistent Example: Computers for “Fertilizer” (Russia) No money – only had . . . Used trading company to facilitate Sold before received as payment Negotiation – Tips (not for the one-time sale) Communicate, communicate, communicate, but focus 1. What happens to both sides in the event that we don’t agree? (consequences of no agreement) 2. What are the likely terms in the event we do agree? Develop solutions BEFORE you meet Offer multiple alternatives Develop them before you begin negotiations Know more about their options than they do Offer if they don’t accept standard terms (if you want long-term) Also attempt to lower overall costs for everyone Look at the details - who can do what most efficiently? Remember who has the power (volume strength) Typical Wish Lists (for the non-professional) Typical Seller Wish List Estimation Rank Item Weight Range (High to Low) 1. Length of contract 40% 1-3 years (longer) 2. Volume 25% 3–1,000 units (more) 3. Price 15% $20–$16 4. Payment terms 10% 30–45 days (shorter) 5. Service 10% 8/5 – 24/7 (less) Typical Buyer Wish List Estimation Rank Item Weight Range (High to Low) 1. Price 40% $14–$18 2. Payment terms 20% 45 - 90 days (longer) 3. Service 20% 12/7 - 24/7 (more) 4. Length of contract 10% 0–2 years (shorter) 5. Volume 10% 1–2,000 units (less) Professional Supplier Selection Professional Buyers’ Needs (in order): 1. Financial stability 2. People 3. Supplier performance 4. Supplier cost reduction ideas 5. Supplier development projects 6. Delivery 7. Quality 8. Product cost (price) 9. Order accuracy 10. Customer support 11. Business relations Let’s Negotiate: Revisited Buyer: $2 billion company, active in trade, wants a lower price, on-going relationship Seller: $1.5 million company, active in trade, wants higher profits, expand sales, on-going relationship The last transaction (have done business before): 5,000 units @ $200.00 per unit CIF Los Angeles – GPS device Payment: Open Account Net 30 (after invoice – date of shipping) Bubble pack, standard export packing, 1 year warrantee Prepare for negotiation (5 minutes) Outline what your main points will be (same paper) Negotiate for 5 minutes Results – debrief (write results on paper) International Sales & Quotation Process 1. Send Initial Correspondence Product Literature Image Brochures/ Corporate background Cover Letter General Price Quotation/ Payment terms 2. Receive Feedback for Additional Information Special Requests Clarifications/ Bargaining 3. Send Out An Individualized Quotation Tie to Purchase Order (P.O.) Establish payment method/ requirements Consider Using Blanket P.O. For Repetitive Purchases (12Month Period) Price and Delivery Schedule Release Schedules Cut Ordering Lead Time Can Obtain Quicker Orders (Not Having to Go Through Purchasing Departments Each Time) Attach Special Sales Agreements (sales contract) 4. Receive P.O. Check sales agreements (contract) Acknowledge/ accept P.O. 5. Send Proforma Invoice Itemize costs/ include validity date Partial shipment/ transshipment allowances Specify documentation/ payment terms 6. Receive Payment/ Payment Arrangement 7. Proceed With Transaction What type of help is available? Video What type of help is available? Video (9 min) Think Globally – Export USA While watching the film please think about this question: How can the U.S. Foreign Commercial Service help a company to enter foreign markets?