Body Cells vs. Sex Cells - Manhasset Public Schools
advertisement

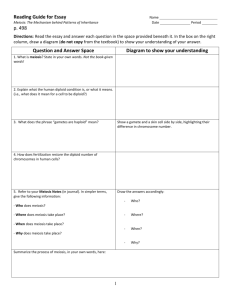
LE22­Meiosis Body Cells vs. Sex Cells: Body Cells (somatic) Examples: # of chromosomes: Type of cell division: Sex Cells (gametes) Examples: # of chromosomes: Type of cell division: LE22­Meiosis *Review: Prophase • replicated chromosomes are visible • centrioles begin to move to opposite poles • spindle fiber begins to form Metaphase • sister chromatids line up at the center of the cell • sister chromatids separate from each other Anaphase • each chromatid reaches the "poles" of the cell Telephase • new nuclear membrane forms *Label each phase and describe what is happening. *Is this an animal cell or plant cell? How can you tell? What would the difference be? LE22­Meiosis Mitosis http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm Why is DNA replicated only once before meiosis even though there are two rounds of cell division? 2N (23 pairs) DNA Replication 4N (23 tetradsdouble pairs) Meiosis I (1st cell division) 2N (23 pairs) 2N (23 pairs) Meiosis II (2nd cell division) N (23) N (23) N (23) N (23) LE22­Meiosis Meiosis in Gonad (sex organ) Homologous Chromosomes 2n Sister Chromatids Replicated Homologous Chromosomes Centromere Tetrad Crossing Over 1st Meiotic Division Disjunction of Homologous Chromosomes 2nd Meiotic Division Gametes LE22­Meiosis Meiosis http://www.cellsalive.com/meiosis.htm LE22­Meiosis What is Meiosis? haploid diploid haploid, reproductive cells: sperm and egg (gametes) 2 Reproductive organs Spermatogenesis (testes) ­ making sperm 2n(diploid) 4 n(monoploid/haploid) cells 46 46 23 46 23 23 23 LE22­Meiosis Oogenesis (ovaries) ­ making egg cells 4 n (monoploid/haploid) cells* 2n (diploid) (only 1 egg) 46 46 23 46 23 23 23 Polar bodies (disintegrate) Egg (ovum) Create a venn diagram on the back of your sheet to compare mitosis and meiosis. LE22­Meiosis LE22­Meiosis LE22­Meiosis Question Sheet LE22­Meiosis LE22­Meiosis LE22­Meiosis LE22­Meiosis LE22­Meiosis