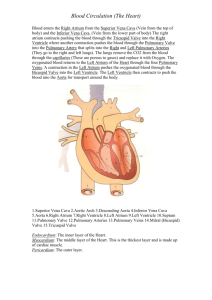
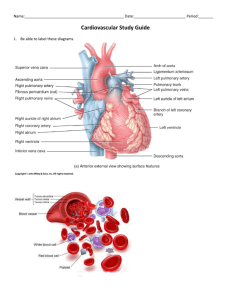
Biology 12 - The Heart & Circulatory System
advertisement
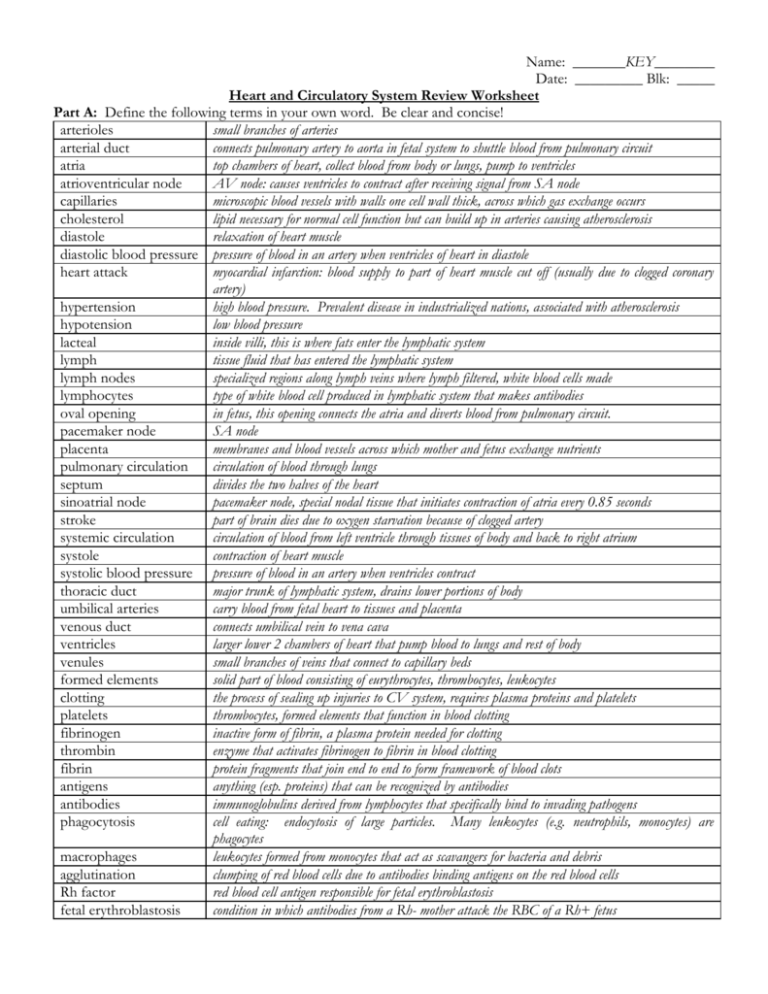
Name: _______KEY________ Date: _________ Blk: _____ Heart and Circulatory System Review Worksheet Part A: Define the following terms in your own word. Be clear and concise! arterioles small branches of arteries arterial duct connects pulmonary artery to aorta in fetal system to shuttle blood from pulmonary circuit atria top chambers of heart, collect blood from body or lungs, pump to ventricles atrioventricular node AV node: causes ventricles to contract after receiving signal from SA node capillaries microscopic blood vessels with walls one cell wall thick, across which gas exchange occurs cholesterol lipid necessary for normal cell function but can build up in arteries causing atherosclerosis diastole relaxation of heart muscle diastolic blood pressure pressure of blood in an artery when ventricles of heart in diastole heart attack myocardial infarction: blood supply to part of heart muscle cut off (usually due to clogged coronary artery) hypertension high blood pressure. Prevalent disease in industrialized nations, associated with atherosclerosis hypotension low blood pressure lacteal inside villi, this is where fats enter the lymphatic system lymph tissue fluid that has entered the lymphatic system lymph nodes specialized regions along lymph veins where lymph filtered, white blood cells made lymphocytes type of white blood cell produced in lymphatic system that makes antibodies oval opening in fetus, this opening connects the atria and diverts blood from pulmonary circuit. pacemaker node SA node placenta membranes and blood vessels across which mother and fetus exchange nutrients pulmonary circulation circulation of blood through lungs septum divides the two halves of the heart sinoatrial node pacemaker node, special nodal tissue that initiates contraction of atria every 0.85 seconds stroke part of brain dies due to oxygen starvation because of clogged artery systemic circulation circulation of blood from left ventricle through tissues of body and back to right atrium systole contraction of heart muscle systolic blood pressure pressure of blood in an artery when ventricles contract thoracic duct major trunk of lymphatic system, drains lower portions of body umbilical arteries carry blood from fetal heart to tissues and placenta venous duct connects umbilical vein to vena cava ventricles larger lower 2 chambers of heart that pump blood to lungs and rest of body venules small branches of veins that connect to capillary beds formed elements solid part of blood consisting of eurythrocytes, thrombocytes, leukocytes clotting the process of sealing up injuries to CV system, requires plasma proteins and platelets platelets thrombocytes, formed elements that function in blood clotting fibrinogen inactive form of fibrin, a plasma protein needed for clotting thrombin enzyme that activates fibrinogen to fibrin in blood clotting fibrin protein fragments that join end to end to form framework of blood clots antigens anything (esp. proteins) that can be recognized by antibodies antibodies immunoglobulins derived from lymphocytes that specifically bind to invading pathogens phagocytosis cell eating: endocytosis of large particles. Many leukocytes (e.g. neutrophils, monocytes) are phagocytes macrophages leukocytes formed from monocytes that act as scavangers for bacteria and debris agglutination clumping of red blood cells due to antibodies binding antigens on the red blood cells Rh factor red blood cell antigen responsible for fetal erythroblastosis fetal erythroblastosis condition in which antibodies from a Rh- mother attack the RBC of a Rh+ fetus blood liquid connective tissue consisting of plasma and formed elements that transports wastes, nutrients, gases Part B - Short Answers 1. The major systemic artery in the body is the aorta. 2. The systemic system begins with the left ventricle of the heart and ends with the right atrium of the heart. 3. Contraction of the heart is called systole; just following contraction, blood pressure is at it highest. 4. The SA node is often called the pacemaker. 5. The first wave in an electrocardiogram occurs during the contraction of the atria; the second occurs during the contraction of the ventricles. 6. A vein is a blood vessel that takes blood to the heart. 7. Movement of blood in the veins is aided by skeletal muscle contraction. 8. Capillaries are tiny vessels with very thin walls, facilitating the exchange of molecules. 9. The lymph vessels begin in the tissues and eventually join the subclavian veins. 10. Two dietary components that may contribute to the medical condition hypertension are salt and cholesterol. 11. A stroke occurs when brain cells are denied oxygen. 12. Label the parts of the circulatory system in this diagram below: 9 1. 1 2. 10 3. 2 4. 11 5. 3 6. 12 7. 4 13 5 14 15 6 7 13. 16 8 superior vena cava aorta SA node right atrium AV node inferior vena cava tricuspic valve/right atrioventicular valve 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. right ventricle pulmonary artery left pulomonary vein left atrium bicuspid valve/left atrioventricular valve 13. 14. 15. 16. aortic semilunar valve left ventricle septum pulomary semilunar valve Match the structures in the key to the statements below: ARTERY/VEIN/CAPILLARY i. has the thickest walls: artery ii. has valves: vein iii. has the greatest total cross-sectional area: capillary iv. v. vi. takes blood away from the heart: artery takes blood to the heart: vein exchanges carbon dioxide and oxygen with tissues: capillary 14. The heart beats about 70 times a minute. What actually happens is that the sinoatrial node initiates the contraction of the atria(chambers). The nervous stimulus is picked up by the atrioventicular node, and this initiates the contraction of the ventricles(chambers). When the chambers are not actually contracting, they are relaxing. Contraction is termed systole, and resting is termed diastole. 15. When the atria contracts, this forces the blood through the atrioventricular valves into the ventricles. The closing of these valves is the lub sound. Next the ventricles contract and force the blood into the arteries. Now the semilunar valves close, and this is the DUPP sound. A heart murmur is caused by leaky valves. 16. The path of blood through the heart. Starting with vena cava, list the structures in order through which blood flows. Use the parts in the column on the left. Structures Correct Order Structures Correct Order 1. aorta 1. vena cava 8. pulmonary veins 8. pulmonary veins 2. bicuspid valve 2. right atrium 9. right atrium 9. left atrium 3. left atrium 3. tricuspid valve 10. right ventricle 10. bicuspid valve 4. left ventricle 4. right ventricle 11. semilunar valve 11. left ventricle 5. lungs 5. pulmonary semilunar 12. tricuspid valve 12. semiilunar valve valve 6. pulmonary artery 6. pulmonary artery 13. vena cava 13. aorta 7. pulmonary 7. lung semilunar valve 17. Of what significance is each of the following in an electrocardiogram like the one on the right? i. P wave: atria systole ii. iii. 18. R QRS wave: ventricular systole T wave: ventricular recover Trace the path of blood from: i. the left ventricle to the legs: left ventricle, aorta, iliac arteries, legs ii. the legs to the right atrium: iliac veins, vena cava, right atrium iii. the aorta to the liver: aorta, mesenteric artery, intestine, hepatic portal vein, liver iv. the liver to the vena cava: liver, hepatic vein, vena cava T P Q S 19. Label the indicated parts of the fetal heart at right: Arterial Duct Oval Opening 20. List the four structural differences between the fetal circulatory system and the adult, as well as the function of each difference. Name Function Oval opening Bypass fetal lung by blood going from the right atrium to the left atrium. Arterial duct Bypass fetal lung by blood going from the pulmonary artery to the aorota. Umbilical artery/vein Delivers oxygen and nutrients from the mother to the fetus Venous due Bypass fetal liver and connects the umbilical vein with the inferior vena cava 21. There are only two types of lymph vessels, the lymph capillaries and the lymph veins. 22. Mix and match the correct term for each description on the left. O 1. largest artery F 2. returns tissue fluid to the circulatory system A 3. prevent blood from flowing in the wrong direction E 4. vessel transporting blood through kidneys G 5. vessel transporting blood through legs K 6. localized swelling due to excess tissue fluid M 7. supply blood to the heart C 8. the highest arterial pressure L 9. the lowest arterial pressure H 10. condition of high blood pressure N 11. "hardening of the arteries" B 12. a stationary clot along an arterial wall K 13. a dislodged, moving thrombus D 14. when a portion of the brain dies due to a lack of oxygen P 15. chest pain (including pain in the left arm) I 16. occurs when circulation to part of the heart is blocked 23. If you press a finger down on a prominent vein, say, on the back of your hand and then slide the finger distally to a new pressure point closer to the fingers, would you expect the section of vein you just moved along to refill with blood? Suppose you had moved the finger proximally toward the upper arm? In the first case, blood would have to flow backward in the vein to refill the section you emptied; however, the valves in the vein prevent backflow, and the vein should remain empty or refill only slowly. In the second case, the emptied section of vein would be quickly refilled by blood traveling toward the heart. 24. Explain how the blood that right now is arriving at your fingertips will get back to your heart. What will drive its movement? It will move from capillary beds to small venules, then to larger venules and then through radial veins, 25. The smallest of the white cells is the lymphocyte, which has a mononucleus and makes antibodies. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P valves thrombus systolic blood pressure stroke renal lymphatic system iliac hypertension heart attack embolism edema diastolic blood pressure coronary arteries atherosclerosis aorta angina pectoris 26. Oxygen is transported about the body in combination with hemoglobin. 27. At the arterial side of a capillary, blood pressure aids the passage of water out of the blood. At the venous side, osmotic pressure brings about the passage of water into the blood. 28. Small organic molecules such as glucose are transported in the plasma portion of blood. 29. Blood clotting is dependent on both a formed element, platelets, and two proteins in the blood, fibrinogen and thrombin. 30. White cells are divided into the agranulocytes and the granulocytes; the latter have granules in the cytoplasm. 31. Antibodies are protein molecules, which combine with antigens. 32. Neutrophils function by phagocytizing bacteria. 33. Blood type AB has A and B antigens on the red cells and no antibodies in the plasma. 34. An Rh-negative woman may form anitbodies that destroy her Rh-postivite baby's red cells. 35. Fill in the following table: PlasmaConstituent Water Plasma Proteins a. Albumin b. Fibrinogen c. Globulins Gases a. Oxygen b. CO2 Nutrients: Fats, glucose, amino acids, etc. Salts Wastes Hormones, vitamins etc. Function Maintains blood volume and transports molecules All maintain blood osmotic pressure & pH transport clotting Fight infection Source Absorbed from large intestine cellulart respiration End product of metabolism food for cells lungs tissues Absorbed from intestinal villi Maintain blood osmotic pressure/pH, aid metabolism end products of metabolism aid metabolism Absorbed from intestinal villi liver liver lymphocytes tissues varied 36. Life cycle of red blood cells: The red cells, scientifically called erythrocytes, are made in the red bone marrow. Upon maturation, they are small, biconcave disks that lack a nucleus, but they are filled with the complex protein called hemoglobin, which transports oxygen about the body. After about 120 days, the red cells are destroyed in liver or spleen. 37. Life cycle of white cells: Most white cells, scientifically called leukocytes, are made in the bone marrow, but lymphocytes are also made in the lymph nodes. White cells are divided into two types, the agranulocytes and the granulocytes. Leukocytes with many-lobed nuclei are called polymorphonuclear. 38. Fill in the following table with the contrasting word or phrase: Neutrophil polymorphonuclear mononuclear Lymphocyte granular phagocytic made in red bone marrow agranular makes anitbodies made in lymphoid tissue 39. The two ways that white cells fight infection are: a. phagocytizing invaders b. making antibodies against foreign antigens 40. The capillaries are the most important part of the circulatory system because exhcnage occurs at the capillaries 41. Blood clotting: These are the reactions that occur when blood clots. Put a check beside those substances that are always present in the blood. Put an X beside those substances that arise after blood begins the process of clotting. Put a star beside those substances that act as enzymes. Underline the words that indicate the actual clot. platelets thromboblastin X, prothrombin thrombin X, fibrinogen X fibrin threads 42. Blood typing is based on antigen-antibody reaction, which takes place when an antigen is brought into contact with an antibody of the same type letter. The antigen-antibody reaction causes clumping or agglutination of the red cells. In the plasma, the antibodies present will not be of the same type letter as the antigen. Why not? because agglutination would occur 43. Fill in the following table: Blood Type of Antigen A B AB O Antibody Can Receive From Can Donate To b a a,b A,O B,O A,B,AB,O O A,AB B,AB AB A,B,AB,O 44. Which combination can lead to fetal erythroblastosis? Rh negative mother and Rh postivie father. 45. Filling the missing steps in the following diagram of blood clotting. Injured tissues and platelets release Prothombin Activator (an enzyme) (vitamin K required for the production of Prothombin) Prothrombin Activator catalyzes the conversion of Prothrombin to Thrombin. (Ca++ is necessary for this step) Prothrombin Activator + Ca++ Thrombin Prothrombin Thrombin is an enzyme that acts like a pair of scissors, cutting short amino acid ends off Fibrinogen molecules Fibrinogen Fibrin Fragments join together end to end to form long fibers. Fibrin fibers form the framework of the clot. Fibrin Fragment