Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
advertisement

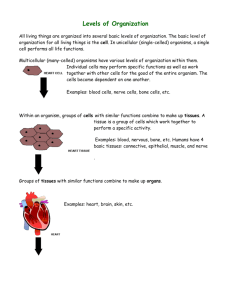
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION (DIVISIONS OF LABOR) DIVISION OF LABOR •An organism’s body divides up the labor into sections depending on the function. •Generalization: A group of cells working together make up tissues, a group of tissues working together make up organs, a group of organs working together make up an organ system, and a group of organ systems working together make up an organism. CELLS •A multi-cellular organism cannot function properly without all of the cells in its body working together. •Each type of cell specializes in performing one particular function. EXAMPLES OF CELLS IN AN ORGANISM Red blood cells: transport oxygen Nerve cell: have nerve fibers to transmit signals Root cell: found in plants that help absorb water from the soil Leaf guard cell: controls water loss FROM CELLS TO TISSUES Group of similar cells that are specialized to perform a particular function. Each type of tissue specializes in performing one particular function. EXAMPLES OF TISSUES •Epithelial tissue: Covering or lining tissue to protect structure beneath it •Muscle tissue: Cause movement •Nerve tissue: Carry messages from one part of body to another •Epidermal tissue: Protects plant against injury and losing too much water •Vascular tissue: Transports materials within a plant FROM TISSUES TO ORGANS Group of specialized tissues that are gathered in a certain part of the body to perform a particular function together ORGAN EXAMPLES HUMAN Skin: protect our innards Lungs: bring oxygen into our body Heart: pumps blood so it can flow through our body Brain: receives and sends messages ORGAN EXAMPLES PLANT Leaves: catch sunlight and perform photosynthesis Stem: transport nutrients and water Roots: absorb water and nutrients for the plant Flowers: reproductive organs of some plants FROM ORGANS TO SYSTEMS Different organs working together to perform a major function in an organism MAIN ORGAN SYSTEMS IN A HUMAN •Nervous System: organizes body response to stimuli •Digestive System: breaks down food into smaller molecules for use by cells for energy •Circulatory System: carries oxygen and food to cells, and removes waste •Respiratory System: provides oxygen to the cells and removes carbon dioxide from the body •Endocrine System: HORMONES, controls growth, development, metabolism and reproduction •Skeletal System: supports body, makes red blood cells •Muscular System: works with skeletal system to cause movement ORGAN SYSTEMS IN A PLANT •Root System: absorbs nutrients and water from the soil to be delivered to the plant •Flower System: preforms reproductive functions FROM SYSTEMS TO ORGANISMS Made up of different systems working effectively in a coordinated manner The Human Body - An organism CELLS TISSUES ORGANS SYSTEMS ORGANISM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z1tVTY7ygus&list=PLncRDtVs7kx PSdDEpDrQCl92-1FT3EaSE