Chlorophyll
advertisement

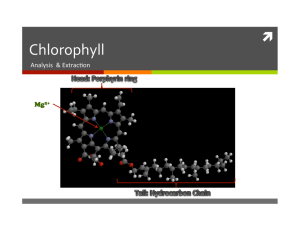
ì Chlorophyll Analysis & Extrac/on Chlorophyll a Week 1 Experiment Summary ì Absorbance (A) Measurements ì Fluorescence (F) Measurements & Coloring Standard Food ì λmax Comparisons ì Beer’s Law to find ε Standard ì Standards by Serial Dilu/on ì Calibra/on Curve (similar to BL Plot) 750 nm 400 nm 430 nm 630 nm Yellow & Blue 480 nm 590 nm 560 nm ì Sketch blue food coloring’s ì Sketch yellow food coloring’s absorp/on spectrum: Absorbance Absorbance absorp/on spectrum: 400 750 Wavelength (nm) 400 750 Wavelength (nm) Why are plants green? ì Plants contain chlorophyll, which is green. ì Sketch chlorophyll’s absorp/on spectrum: Absorbance 750 nm 400 nm 400 750 Wavelength (nm) 630 nm 430 nm 590 nm 480 nm 560 nm Stoke’s Shift ì What is the rela/onship between the fluorescence and absorp/on spectra of the same chemical? Energy LUMO hνa hνe HOMO ì The spectrometer used in lab has 2 excita<on wavelengths: 405 nm & 500 nm. Which should be used? Concentration Units (ppm) ì If an aqueous solu/on is 6.0% (pph) by mass NaCl, what is the concentra/on of the solu/on in Molarity? ì 6.0 g NaCl x 1 mol NaCl x 1.0 g H2O x 103 mL = 1.0 M 100 g H2O 58.44 g 1 mL 1L ì If an aqueous solu/on is 6.0 ppm by mass NaCl, what is the concentra/on of the solu/on in Molarity? ì 6.0 g NaCl x 1 mol NaCl x 1.0 g H2O x 103 mL = 1.0 x 10-­‐4 M 106 g H2O 58.44 g 1 mL 1L ì What assump/on was made in this calcula/on? Vwater = Vsoln Fluorescence Calibration Curve ì Chlorophyll stock solu/on: 6.0 ppm. Create 5 standard solu/ons, each ½ the concentra/on of the solu/on before it. Direc<ons: Add 2.0 mL the chlorophyll stock/standard solu/on to a 10 mL graduated cylinder, then add 2 mL of heptane. ì What does a fluorescence calibra/on curve will look like? Week 2 Experiment Summary ì Spinach Extrac/on ì Grind w/ acetone, add heptane, then water. Separate layers & add MgSO4 to heptane layer ì TLC of Extract ì Developing Chamber ì Rf Calcula/on ì Absorbance & Fluorescence Measurement of Extract ì Determina/on of [Chlorophyll] from A & F data Which of the following is false? A. Electronega/vity is an atom’s ability to ahract shared electrons to itself. B. A bond dipole arises when a electronega/vity difference exists between two atoms. C. A significant bond dipole exists between C-­‐H in heptane. D. CCl4 has a molecular dipole. Intermolecular Forces ì Dipole-­‐Dipole Forces ì electrosta/c ahrac/on between the par/ally posi/ve & nega/ve ends of polar molecules ì Hydrogen Bonding ì dipole-­‐dipole forces for polar molecules with hydrogen atoms bound to oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine atoms. ì Dispersion Forces ì Transitory dipole forma/on: random e-­‐ shij results in δ+ & δ-­‐ ends of a molecule/atom ì Disturbing other molecules/ atoms to form more transitory dipoles & weak electrosta/c ahrac/on Which of the following is false? A. Hydrogen bonding occurs between molecules containing C-­‐H bonds. B. Dipole Dipole forces exist between water molecules. C. Dispersion Forces exist between acetone molecules. D. Intermolecular forces between nonpolar molecules decrease with molecular weight. What chemicals are in ì Chlorophyll a & b ì Pheophy/n a & b ì Xanthophylls ? Extraction / Separatory Funnels ì How do you use a separatory (sep) funnel? ì What is the iden/ty of the layers? ì Which layer contains “ ”? ì What is MgSO4 used for? Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) ì What is the TLC process? ì Developing Chamber ì Prep & Spot Plate ì Develop Plate ì Measure Rf = xorigintocpd xorigintofront What are the Rfs for A, B, & C? Does the size of plate maHer? 3 Classes of “Chemicals” Silica SiO2 ì Phase? Sta1onary ì Polarity? POLAR Si-­‐O-­‐H (silanol) groups on outside of silica par/cles Eluent Analyte ì Phase? Mobile ì Defini/on? Mixture of 2 or more chemicals to be separated ì Polarity? NONPOLAR to intermed. polar Eluent use wrt polarity? in order of ñpolarity Use order of these eluents? acetone, CH3(CH2)4CH3, CH2Cl2, CH3CH2OCH2CH3 ì Polarity? NONPOLAR to intermediate polar How does TLC separate these chemicals? By Polarity… ì Is A polar, intermediate polar, or nonpolar? ì Which chemical is the most strongly adsorbed to the silica plate? What can be said about its polarity? ì Which eluent is most likely responsible for the separa/on seen to the right: pure acetone, 1:1 mix of acetone & heptane, pure heptane? A B C D What is [Chlorophyll a] in ? ì Remember: The extract is a mix of compounds… the standard only contains chlorophyll! Use the data from week 1 to find [chlorophyll a]: ì from Absorbance… at 2 λs… Beer’s Law Eqn: A = εCl low & high ì from Fluorescence… Calibra1on Curve ì Which method is beHer to calculate concentra<on?