N-Vinylformamide - Spezialmonomere
advertisement

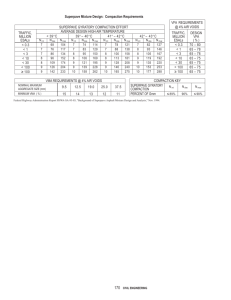
Technical Information TI/ED 1988 e June 2007 Acrylic Monomers and Superabsorbents Page 1 of 3 Supersedes edition dated April 2006 N-Vinylformamide VFA, a multifunctional molecule for manufacturing polymers and for use as a feedstock for syntheses. H N CAS-Nr.: 13162-05-5 EINECS-Nr.: 236-102-9 C3H4ON Molar mass: 71.1 kg/kmol Product specification Assay (HPLC) min. 98.5 % pH value (DIN 19268) min. 4.5, max 8.5 Formamide (HPLC) max. 0.5 % Standard stabilization 25 – 55 ppm Tempo/Tempol he aforementioned data shall constitute the agreed contractual quality of T the product at the time of passing of risk. The data are controlled at regular intervals as part of our quality assurance program. Neither these data nor the properties of product specimens shall imply any legally binding guarantee of certain properties or of fitness for a specific purpose. No liability of ours can be derived therefrom. Other properties Labelling according to Directives see MSDS Appearance Physical form Odour Density at 20 °C Boiling point Viscosity at 0 °C Flash point Ignition temperature Vapour pressure at 20 °C Solubility in water at 20 °C Freezing point colourless – slightly yellow liquid low, product specific 1.017 g/cm3 70 °C/5 hPa 6.5 mPa · s 103 – 105 °C 305 – 315 °C 0.2 mbar perfectly miscible – 8.9 °C O H TI/ED 1988 e June 2007 Page of 3 N-Vinylformamide Applications -Vinylformamide (VFA) is a raw material for homopolymers or copolymers N with acrylamide, acrylonitrile, acrylates or acrylic acid. The polymers are water-soluble and have applications in a number of fields. VFA can be used as a building block to make larger monomers and other compounds. ajor applications are dry and wet strength for paper manufacturing. Other M areas of potential interest are • Reactive Diluent for Radiation Curing • Water treatment • Cosmetics • Specialty chemicals • Surface modification • Superabsorbents • Construction and adhesives • Absorption of pollutants • Petroleum recovery from oil wells Polymers of VFA can be hydrolyzed to form polymers with primary amine functionality. Safety Material Safety Data Sheet has been compiled for Vinylformamide that A contains up-to-date information on all questions relevant to safety. Storage & Handling Suitable materials for storage and piping to avoid corrosion. Suitable conditions of storage. Protect VFA from temperatures of 5 °C and above to prevent exo-thermic reactions. Protect VFA from moisture (e. g. atmospheric moisture) and avoid any contact with acids or bases because of the strongly exothermic hydrolysis. Hydrolysis of VFA monomer leads to increased levels of acetaldehyde. The maximum storage time is 6 month at 4 °C. If VFA is consumed within one month, low temperature storage is not necessary. The maximum ­temperature must be observed. reathing of the storage tank or for Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs) B ­during partial emptying should be handled using a padding regulator (e. g. + 20 mbar) and a gas (e. g. nitrogen) dried to a condensation point of less than – 30 °C. In general, the lower the storage temperature the higher the product quality will be. dequate inhibition is necessary to avoid polymerization in a properly stored A VFA. The standard level of inhibitor in commercially available VFA is 25 to 55 ppm Tempo/Tempol. The standard inhibitor protects against free-radical polymerization. It has no protective effect against hydrolysis caused by acids or bases. Stainless Steel, material numbers: 1.4541, 1.4571 or 1.4139. N-Vinylformamide TI/ED 1988 e June 2007 Page of 3 In addition to the Tempo/Tempol, the presence of dissolved oxygen in the VFA liquid enhances the stabilization. Dissolved oxygen converts carbon centered radicals to oxygen centered radicals, which the Tempo/Tempol can trap to stabilize VFA thereby enhancing the stability margin. The yellowish colour intensifies during this process. An inert atmosphere is preferred in most cases due to the potential intensification of the yellowish colour. Regulation about storage. Water hazard class 1 (in Germany). Recommendation of the supplier: Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place. Protect against temperatures of above 25 °C. Do not store together with acids, bases, ammonia and amines. ADR Transport classification. Not classified as hazardous under transport regulations. Note The data contained in this publication are based on our current knowledge and experience. In view of the many factors that may affect processing and application of our product, these data do not relieve processors from carrying out their own investigations and tests; neither do these data imply any guarantee of certain properties, nor the suitability of the product for a specific purpose. Any descriptions, drawings, photographs, data, pro- portions, weights etc. given herein may change without prior information and do not constitute the agreed contractual quality of the product. It is the responsibility of the recipient of our products to ensure that any proprietary rights and existing laws and legislation are observed. June 2007 BASF Group GBU Acrylic Monomers and Superabsorbents, G-EDG 67056 Ludwigshafen, Germany www.acrylicmonomers.net