History of Management Therorists

History
of
Management
Therorists
Please find attached a set of flashcards to study the History of Management Theorists.
Fold paper in
half and quiz yourself or go to http://quizlet.com/6273489/history ‐ of ‐ management ‐ theorists ‐ flashcards
If you go to “quizlet”, you can thumb through the flashcards, read them yourself, or click on the loudspeaker icon and they will be read for you.
You can choose to “learn” and quizzes will be developed
for you using the flashcards.
Medical Services Administration represents 12% of the CPMSM exam.
There will probably be at least one question on your exam regarding Theorists of Management.
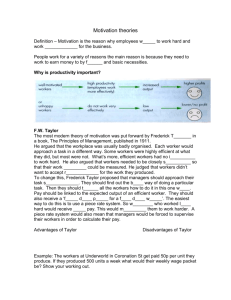
Frederick Taylor
Frederick Taylor is known as the "father of management." Taylor studied work standards and the relationship of productivity to wages.
He emphasized using management practices based on the belief that the individual worker was motivated through financial reward.
Taylor is also credited with the concept that there is "one best way" of doing anything from manual labor to clerical activities
Frank & Lillian Gilbreth
Frank & Lillian Gilbreth expanded the study of Scientific Management by developing techniques and devices to assist employees in performing their jobs more efficiently in the work environment. They were the first to use motion pictures and develop diagrams and work process charts to improve worker productivity and eliminate nonproductive actions.
Max Weber
Max Weber's organization structure included management practices based on the concepts of a clearcut division of labor, chain of command, maintenance of records of administrative decision, delineation of qualification for employment and promotion, and the introduction of measures to prevent unfair employee terminations.
William Leffingwell
Henri Fayol
Mary Parker Follett
Elton Mayo
Known as the "father of office management."
Tried to apply principles of Scientific
Management to clerical activities. Leffingwell proposed "Five Principles of Effective Work."
Plan the work, Schedule the work, Execute the work, Measure the Work, Reward the worker.
Henri Fayol is credited with developing the first comprehensive theory of management.
He identified five basic functions of management: Planning, Organizing,
Commanding, Coordinating, Controlling.
Mary Parker was a Social Reform Critic. She was one of the first to be concerned with human relations and the social responsibilities of management. Once the importance of human relations began to be recognized by management in business, studies on motivation began.
Elton Mayo led a research team from
Harvard to investigate the effects of the physical environment on the output of the worker. The experiments became known as the Hawthorne Experiments. While looking for factors to control to increase productivity, the experiments indicated the emotional needs of the worker had to be addressed in addition to environmental factors under the organization's control.
Abraham Maslow
Douglas McGregor
Frederick Herzberg
William Ouchi
Maslow, a psychologist, theorized that a hierarchy of needs existed for each individual and once needs are satisfied at the lower level, those needs are no longer motivating factors. He identified categories of needs that existed on each level and proposed that individuals were continuously motivated by needs at the next higher level. Maslow's
Hierarchy of Needs included: basic physiological needs, safety, love, recognition and association, self-esteem and selfactualization.
McGregor introduced the concept of the
"dual nature" of people by proposing theories stating that managers supervise workers based on the "dual nature" concept. Theory X stated that people avoided work, had to be threatened, preferred direction and had little ambition on the job. Theory Y stated that employees did enjoy work, preferred selfdirection, desired responsibility and were motivated to succeed on the job.
Frederick Herzberg proposed the Motivation-
Hygiene Theory. Personal growth, job satisfaction, and recognition for work performed are examples of motivation for workers. Hygienic factors, include pay, working conditions, policies, etc., and might be related to productivity. In order to be properly motivated, workers must have job experience that offers recognition, achievement, etc. and also have adequate hygienic factors.
William Ouchi proposed Theory Z
Management which is based on Japanese management practices, that emphasize high productivity, excellent product quality and worker involvement in continuous improvement processes. He adopted some
Japanese concepts, these include: Problem solving groups to improve productivity,
Reducing work hours for all employees to avoid layoffs and Allowing work groups to be more independent in searching for ways to increase productivity.
W. Edwards Deming
Joseph M. Juran
Philip B. Crosby
W Edwards Deming was a founding leader of the Total Quality Management concept. He developed "Fourteen Points." He believed an organization's management should work to create the proper environment for continuous improvement in the quality of the service provided, as well as in the productivity of the employees. Total Quality Management is a process, not just a program.
Dr. Juran was an American management consultant who worked originally with
Deming on Quality Improvement. Juran wrote "Quality Control Handbook" and also worked with the Japanese. His works emphasized the importance of management in the process of continuous quality improvement. He believed issues under management control cause 80% of the quality problems.
Crosby stressed the economic benefits of meeting quality requirements the first time and advocates achieving the goal of Zero
Defects using continuous improvement, where employees pledge to eliminate errors from their work. As part of the technique, employees are rewarded for making suggestions to improve the process.