Motivation theories.doc
advertisement
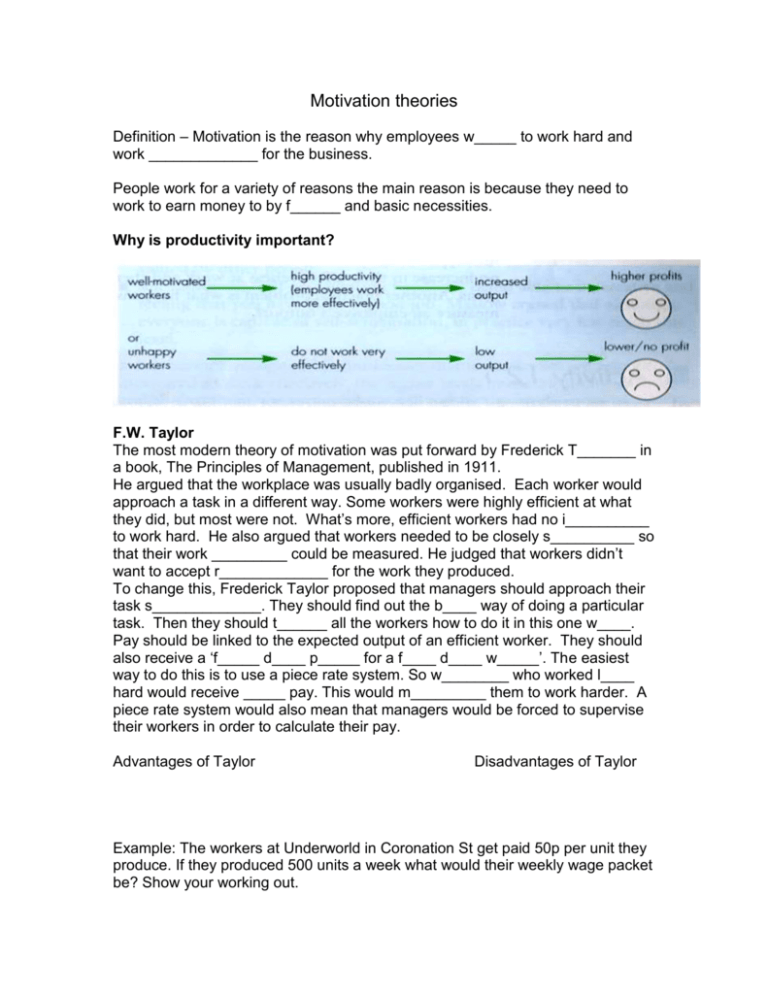
Motivation theories Definition – Motivation is the reason why employees w_____ to work hard and work _____________ for the business. People work for a variety of reasons the main reason is because they need to work to earn money to by f______ and basic necessities. Why is productivity important? F.W. Taylor The most modern theory of motivation was put forward by Frederick T_______ in a book, The Principles of Management, published in 1911. He argued that the workplace was usually badly organised. Each worker would approach a task in a different way. Some workers were highly efficient at what they did, but most were not. What’s more, efficient workers had no i__________ to work hard. He also argued that workers needed to be closely s__________ so that their work _________ could be measured. He judged that workers didn’t want to accept r_____________ for the work they produced. To change this, Frederick Taylor proposed that managers should approach their task s_____________. They should find out the b____ way of doing a particular task. Then they should t______ all the workers how to do it in this one w____. Pay should be linked to the expected output of an efficient worker. They should also receive a ‘f_____ d____ p_____ for a f____ d____ w_____’. The easiest way to do this is to use a piece rate system. So w________ who worked l____ hard would receive _____ pay. This would m_________ them to work harder. A piece rate system would also mean that managers would be forced to supervise their workers in order to calculate their pay. Advantages of Taylor Disadvantages of Taylor Example: The workers at Underworld in Coronation St get paid 50p per unit they produce. If they produced 500 units a week what would their weekly wage packet be? Show your working out. The human relations school of thought A different view of motivation emerged from an e_____________ carried out between 1927 and 1932 at the Hawthorne Plant in C________. The researchers initially believed in Taylor’s scientific management theories. Over a five year period, changes were made in lighting, heating, incentive schemes, rest p______ and hours of work. Each time a change was made, output rose. This was true even when conditions of work were put back to how they were at the s_____ of the experiment. Elton M_____ reported on this experiment. He concluded that output was rising because of the a___________ that was being given to the w__________. This motivated the workers to work more p_________. The rising productivity due to the attention paid to workers came to be known as the H________ e________. McGregor Douglas McGregor published his research findings in 1960. He identified two types of managers – those who believe in Theory __ and those who believe in Theory __. Managers who believe in Theory X think that the willingness to work is mainly influenced by external factors, such as pay schemes which pay more if more output is produced. These managers think people are naturally l____ and have to be motivated, pushed and urged to work. Managers who believe in Theory Y think that motivation is basically an internal factor. Most people want to do a g____ day’s work but need a favourable environment in which to do it. Maslow Abraham Maslow studied employee motivation. His ideas were published in 1954 where he proposed a hierarchy of needs, shown in the diagram below. It has become recognised by businesses that if employees are going to be motivated to work efficiently, the higher levels in the hierarchy must be available to them i.e. money alone will not be the single route to increased productivity as was thought by T________. Evidence for the higherarchy can be seen from people who are unemployed, in that they very often lose their self-respect and self-e_______ and they do not have the feeling of belonging to society, which often comes from working. Maslow also suggested that each level in the hierarchy mush be achieved before an employee can be m___________ by the next level. For example, once s_______ needs are met, this will no longer motivate the employee, but the opportunity to gain the respect of fellow workers and gain esteem could motivate someone to work effectively. Managers must identify the l______ of the hierarchy a particular job provides and then look for ways of allowing the employees to benefit from the next level up the hierarchy.. Herzberg: hygiene or motivation? Frederick herzberg was an American psychologist whose research in the 1950’s led to his t___-f________ theory. They are factors which lead to Job dissatisfaction – known as hygiene factors Job satisfaction – known as motivators. Job enlargement and job enrichment The work of researchers such as Maslow and Herzberg has led to ideas that workers’ jobs could be made more satisfying through: job enlargement – instead of a worker doing one small task every day, they would be able to do a variety of tasks. This would make the work less monotonous and boring; Job e___________ – where workers are given some opportunities to choose how to complete a particular job of work, usually working in a team.











