Marketing Flash Cards
advertisement
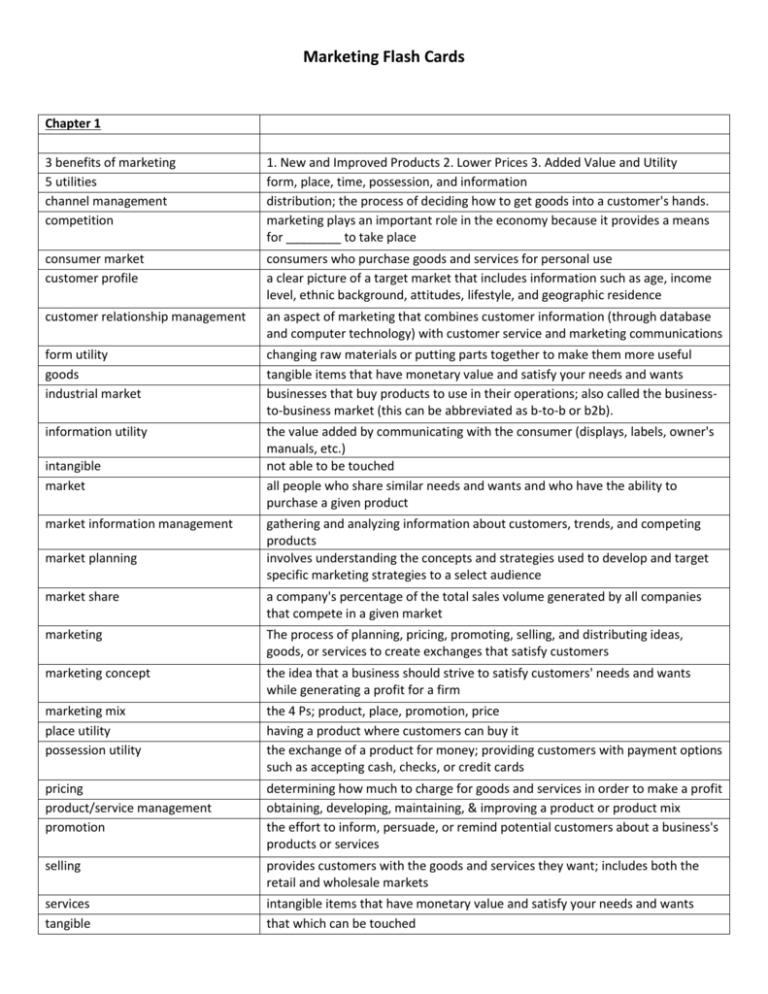
Marketing Flash Cards Chapter 1 3 benefits of marketing 5 utilities channel management competition 1. New and Improved Products 2. Lower Prices 3. Added Value and Utility form, place, time, possession, and information distribution; the process of deciding how to get goods into a customer's hands. marketing plays an important role in the economy because it provides a means for ________ to take place consumer market customer profile consumers who purchase goods and services for personal use a clear picture of a target market that includes information such as age, income level, ethnic background, attitudes, lifestyle, and geographic residence customer relationship management an aspect of marketing that combines customer information (through database and computer technology) with customer service and marketing communications form utility goods industrial market changing raw materials or putting parts together to make them more useful tangible items that have monetary value and satisfy your needs and wants businesses that buy products to use in their operations; also called the businessto-business market (this can be abbreviated as b-to-b or b2b). information utility the value added by communicating with the consumer (displays, labels, owner's manuals, etc.) not able to be touched all people who share similar needs and wants and who have the ability to purchase a given product intangible market market information management market planning gathering and analyzing information about customers, trends, and competing products involves understanding the concepts and strategies used to develop and target specific marketing strategies to a select audience market share a company's percentage of the total sales volume generated by all companies that compete in a given market marketing The process of planning, pricing, promoting, selling, and distributing ideas, goods, or services to create exchanges that satisfy customers marketing concept the idea that a business should strive to satisfy customers' needs and wants while generating a profit for a firm marketing mix place utility possession utility the 4 Ps; product, place, promotion, price having a product where customers can buy it the exchange of a product for money; providing customers with payment options such as accepting cash, checks, or credit cards pricing product/service management promotion determining how much to charge for goods and services in order to make a profit obtaining, developing, maintaining, & improving a product or product mix the effort to inform, persuade, or remind potential customers about a business's products or services selling provides customers with the goods and services they want; includes both the retail and wholesale markets services tangible intangible items that have monetary value and satisfy your needs and wants that which can be touched target market time utility utility a group of consumers identified for a specific marketing program having a product available at a certain time of year or a convenient time of day added value; the attributes of a product or service that make it capable of satisfying consumers' wants and needs Chapter 2 All Eyes On Me Everywhere I Go (demographic factors) behavioral factors company analysis company, customer, and competition competitive position customer analysis demographics discretionary income disposable income economic factors Age, Education, Occupatin, Maritial Status, Ethnic Background, Income, Gender Segmenting the market based on _____________ involves looking at the benefits desired by consumers, shopping patterns, and usage rate. (For example, many people, regardless of their socio-economic status, desire luxury merchandise). The part of a company's internal analysis about what the company does well and what areas are week (including review of staff, the company's financial situation, production capabilities, and each aspect of the marketing mix) The internal analysis centers are these; the three Cs A company's strengths and weaknesses when compared to its competitors, based on factors such as market share, core competencies, or reputatation. The part of a company's internal analysis about customers' buying habits (including understanding who the customers are, what, when, where and how much do they buy, how satisfied is each customer segment, etc.) Refer to statistics that describe a population in terms of personal characteristics such as age, gender, income, marital status, ethnic background, education, and occupation. Money left after paying for basic living necessities such as food, shelter and clothing. (Money available to spend on luxury or premium items). Money left over after taking out taxes (your net income), this money is spent on basic needs such as food, shelter and clothing. External factors such as the unemployment rate, inflation, retail sales figures, productivity, and consumer confidence. environmental scan executive summary external factors geographics Internal factors market segmentation marketing plan marketing strategy mass marketing niche marketing Personal Selling political factors psychographics sales forecast situation analysis Part of a company's external analysis that includes four types of factors: political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological (sometimes referred to to with the acronym PEST). A brief overview of the entire marketing plan; it briefly addresses each topic in the plan and gives an explanation of the costs involved in implementing the plan. Opportunities and Threats are both _________ that affect business operation. Refers to segmentation of the market based on where people live. Strengths and weaknesses are both ___________ that affect business operations The process of classifying people who form a given market into even smaller groups is called __________________. A formal, written document that directs a company's activities for a specific period of time. It details analysis and research efforts and provides a roadmap for how a product will enter the market, be advertised, and sold. Part of a marketing plan that identifies target markets and sets marketing mix choices that focus on those markets. Involves using a single marketing strategy to reach all customers. The current trend in marketing markets are narrowed down and defined with extreme precision (as opposed to mass marketing). any form of direct contact between a salesperson and a customer. External factors that involve government involvement in business operations, such as changes in laws and regulations. Involves grouping people with similar lifestyles, as well as shared attitudes, values, and opinions. The projection of probable, future sales in units or dollars. The study of the internal and external factors that affect marketing strategies. The information from a company's SWOT analysis and from the environmental scan becomes the basis for this portion of the marketing plan. socio-cultural factors SWOT SWOT analysis technological factors The 80/20 rule Chapter 12 Business-to-business selling Cold canvassing Consultative selling Customer Benefits Emotional Motive Endless chain method Extensive decision making Feature-benefit selling Limited decision making Pre-approach Product features Prospect Rational Motive External factors that analyze customers and potential customers. This covers changes in all demographic factors, such as age, income, occupation, and marital status, as well as pychographic factors, such as lifestyle and attitudes. The acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats The process of analyzing everthing that can foster the business's success and make it fail External factors that may threat one industry or company, but provide an opportunity for others (such as digital photography). Means that 80 percent of a company's sales are generated by 20 percent of its loyal customers. may take place in a manufacturer's or wholesaler's showroom (inside sales) or a customer's place of business (outside sales). It is up to the salesperson to make contact with the customer. Potential customers are selected at random, such as by going door-to-door or selecting names from a telephone directory. Providing solutions to customers' problems by finding products that meet their needs. The advantages or personal satisfaction a customer will get from a good or service. A feeling experienced by a customer through association with a product. When salespeople ask previous customers for names of potential customers. Used when there has been little or no previous experience with an item. Matching the characteristics of a product to a customer's needs and wants. When a person buys goods and services that he or she has purchased before but not regularly. The preparation for the face-to-face encounter with potential customers. Basic, physical, or extended attributes of a product or purchase. a potential customer. A conscious, logical reason for a purchase. (dependability, time or monetary savings, health, etc.) Referrals Routine decision making Sales Quotas Telemarketing The names of other people who might buy the product. When a person needs little information about a product. Dollar or unit sales goals set for the sales staff to achieve in a specified period of time. The process of selling over the telephone.











