How to Evaluate Art Elements of Design
advertisement

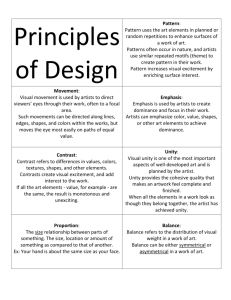
How to Evaluate Art To evaluate you need to consider the craftsmanship (quality), design and aesthetic qualities. The best way to judge these three criteria is to use the Elements and Principles of Design. Elements of Design Color Color consists of hue, value and intensity. Hue is pure and the most intense like the color, red. Value is when white is added to a color like, pink. Intensity refers to the brightness of a color. The Color Wheel is the artists’ tool for understanding and selecting color schemes. The local color of an art work is the dominant color and the reflected color is the color that has been changed because it reflects the colors next to it. example: Femme aux Bras Croisés by Pablo Picasso is a monochromatic painting. Form Form describes volume and mass, or the three-dimensional aspects of objects that take up space. Forms can and should be viewed from many angles. Form is a major part of pottery and Sculpture. example: African sculpture Line Line is a mark made by a pointed tool - brush, pencil, stick, pen, etc - and is often defined as a moving dot. It has length and width and often suggests movement in a drawing or painting. Hiroshige, "The Plum Garden in Kameido" Shape Shape is an area that is contained and has two dimensions, length and width, and can be geometric or organic. Artists add shading to shapes to make them appear to have form. example: Piet Mondrian, Composition II Space Space is a three - dimensional volume that can be empty or filled with objects. It has width, height, and depth. In drawings and paintings space is created by perspective showing the illusion of depth on a two dimensional surface. Aerial perspective uses color in landscapes and cityscapes to show depth and distance. example: Northumberland House in London by Canaletto Texture Texture refers to the surface quality, both simulated and actual, of artwork. example: The Kiss by Ernst Klimt Value Value refers to dark and light. Black is the darkest and white the lightest. High key means the piece has mostly light values. Low keyed means the piece has mostly dark values. example: Francisco de Zurbarán by Saint Rufina Principles of Design The Principles of Design are the concepts that are used to arrange the Elements of Art as in arranging a composition. Balance Balance refers to the distribution of visual weight in a work of art. Balance can be either symmetrical (formal) or asymmetrical in a work of art. Symmetrical balance is a mirror image or equal weight in a composition. Asymmetrical is when there is a larger mass on side than on the other. example: Urhoboan African mask Contrast Contrast refers to differences in values, colors, textures, shapes, and other elements. Contrasts create visual excitement and add interest to the work. example: Portrait of Jan Six, by Rembrandt. Emphasis Emphasis is used by artists to create dominance and focus in art work. Artists can emphasize color, value, shapes, or other art elements to achieve dominance. Emphasis is used to communicate the purpose of an art work. example The Milkmaid by Vermeer Movement Visual movement is used by artists to direct viewers through their work, often to a focal area. Sculptures demonstrate movement as they are viewed in the round. example: The Entombment of Christ by Caravaggio Pattern Pattern uses the art elements in planned or random repetitions to enhance surfaces of paintings or sculptures. Patterns often occur in nature, and artists use similar repeated motifs to create pattern in their work. Many cultures use patterns in their fabric, pottery and more. example: Indonisian Batik Rhythm Rhythm is the repetition of visual movement - colors, shapes, or lines. example: Del porfirismo a la Revolución by David Alfaro Siqueiros Unity Unity provides the cohesive quality that makes an art work look as though they belong together. example : Temeraire by Joseph Turner