UNIDAD EDUCATIVA MONTE TABOR NAZARET
advertisement

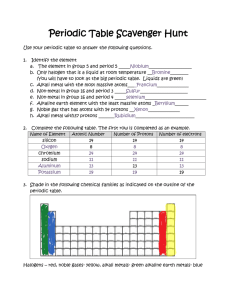
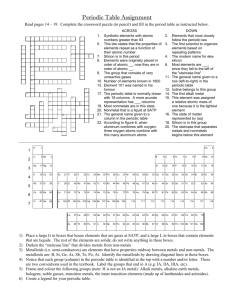
UNIDAD EDUCATIVA MONTE TABOR NAZARET Área de Science Actividades de refuerzo académico I QM 2015 - 2016 NOMBRE: _____________________________ CURSO:_______ FECHA: __________________ Contenido: Caligrafía: Presentación 10 Ortografía: PROFESOR/A: ______________________________ Instrucciones sobre las actividades de refuerzo: Estas actividades de refuerzo académico tienen como objetivo mejorar el desempeño académico de los estudiantes que han obtenido una nota inferior a 7/10 en el examen quimestral y/o en el promedio quimestral, lo cual indica de acuerdo a la escala cualitativa de evaluación que el estudiante está próximo a alcanzar los aprendizajes requeridos o no ha alcanzado los aprendizajes requeridos. La actividad desarrollada debe entregarse al profesor de la asignatura a partir del 19 de octubre en la primera hora de clases de esa asignatura. Se realizará una retroalimentación del trabajo y la calificación corresponderá como lección del primer parcial del segundo quimestre. Semana 1 Chapter Review (Land Biomes) USING KEY TERMS 1. In your own words, write a definition for the following terms: biome and tundra. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2. Use each of the following terms in a separate sentence: intertidal zone, neritic zone, and oceanic zone. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. 3. savanna and desert ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 4. open-water zone and deep-water zone ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 5. marsh and swamp ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS Multiple Choice _____ 6. Trees that lose their leaves in the winter are called a. evergreen trees. c. deciduous trees. b. coniferous trees. d. None of the above _____ 7. In which major ocean zone are plants and animals exposed to air for part of the day? a. intertidal zone c. oceanic zone b. neritic zone d. benthic zone _____ 8. An abiotic factor that affects marine ecosystems is a. the temperature of the water. b. the depth of the water. c. the amount of sunlight that passes through the water. d. All of the above _____ 9. is a marine ecosystem that includes mudflats, sandy beaches, and rocky shores. a. An intertidal area b. Polar ice c. A coral reef d. The Sargasso Sea Short Answer 10. What are seven land biomes? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 11. Explain how a small lake can become a forest. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 12. What are two factors that characterize biomes? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 13. Describe the three zones of a lake. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 14. How do rivers form? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 15. What are three abiotic factors in land biomes? three abiotic factors in marine ecosystems? an abiotic factor in freshwater ecosystems? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ CRITICAL THINKING 16 .Concept Mapping Use the following terms to create a concept map: plants and animals, tropical rain forest, tundra, biomes, permafrost, canopy, desert, and abiotic factors. 17. Making Inferences Plankton use photosynthesis to make their own food. They need sunlight for photosynthesis. Which of the four major ocean zones can support plankton growth? Explain your answer. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 18. Predicting Consequences Wetlands, such as marshes and swamps, play an important role in flood control. Wetlands also help replenish underground water supplies. Predict what might happen if a wetland dries out. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 19. Analyzing Ideas A scientist has a new hypothesis. He or she thinks that savannas and deserts are part of one biome rather than two separate biomes. Based on what you’ve learned, decide if the scientist’s hypothesis is correct. Explain your answer. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 20. Applying Concepts Imagine that you are a scientist. You are studying an area that gets about 100 cm of rain each year. The average summer temperatures are near 30ºC. What biome are you in? What are some plants and animals you will likely encounter? If you stayed in this area for the winter, what kind of preparations might you need to make? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ INTERPRETING GRAPHICS Use the graphs below to answer the questions that follow. 21. Which biome is most likely found in the region described by the graphs above? Explain your answer. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 22. How many centimeters of rain fell in the region during the course of the year? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 23. Which month is the hottest in the region? the coolest in the region? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 24. What is the average monthly precipitation for the month that has the highest average high temperature? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Chapter Review - Intro to Atoms USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. 1. Electrons have a positive charge. ______________________________________________________________ 2. All atoms of the same element contain the same number of neutrons. ______________________________________________________________ 3. Protons have no electrical charge. ______________________________________________________________ 4. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. ______________________________________________________________ 5. The mass number is an average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. ______________________________________________________________ UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS Multiple Choice _____ 6. The discovery of which particle proved that the atom is not indivisible? a. proton c. electron b. neutron d. nucleus _____ 7. How many protons does an atom with an atomic number of 23 and a mass number of 51 have? a. 23 c. 51 b. 28 d. 74 _____ 8. In Rutherford’s gold-foil experiment, Rutherford concluded that the atom is mostly empty space with a small, massive, positively charged center because a. most of the particles passed straight through the foil. b. some particles were slightly deflected. c. a few particles bounced straight back. d. All of the above _____ 9. Which of the following determines the identity of an element? a. atomic number b. mass number c. atomic mass d. overall charge _____10. Isotopes exist because atoms of the same element can have different numbers of a. protons. c. electrons. b. neutrons. d. None of the above Short Answer 11. What force holds electrons in atoms? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 12. In two or three sentences, describe Thomson’s plum-pudding model of the atom. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Math Skills 13. Calculate the atomic mass of gallium, which consists of 60% gallium-69 and 40% gallium-71. Show your work below. 14. Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of zirconium-90 that has no overall charge and an atomic number of 40. Show your work below. CRITICAL THINKING 15. Concept Mapping Use the following terms to create a concept map: atom, nucleus, protons, neutrons, electrons, isotopes, atomic number, and mass number. 16. Analyzing Processes Particle accelerators are devices that speed up charged particles in order to smash them together. Scientists use these devices to make atoms. How can scientists determine whether the atoms formed are a new element or a new isotope of a known element? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 17. Analyzing Ideas John Dalton made a number of statements about atoms that are now known to be incorrect. Why do you think his atomic theory is still found in science textbooks? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 18. Analyzing Methods If scientists had tried to repeat Thomson’s experiment and found that they could not, would Thomson’s conclusion still have been valid? Explain your answer. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Interpreting Graphics Use the diagrams below to answer the questions that follow. 19. Which diagrams represent isotopes of the same element? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 20. What is the atomic number for A? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 21. What is the mass number for B? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Semana 2 Chapter Review – Periodic Table USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. group halogens period alkaline-earth metals alkali metals noble gases 1. Elements in the same vertical column on the periodic table belong to the same ______________________. 2. Elements in the same horizontal row on the periodic table belong to the same ______________________. 3. The most reactive metals are ______________________. 4. Elements that are unreactive are called ______________________. UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS Multiple Choice _____ 5. Mendeleev’s periodic table was useful because it a. showed the elements arranged by atomic number. b. had no empty spaces. c. showed the atomic number of the elements. d. allowed for the prediction of the properties of missing elements. _____ 6. Most nonmetals are a. shiny. b. poor conductors of electric current. c. flattened when hit with a hammer. d. solids at room temperature. _____ 7. Which of the following items is NOT found on the periodic table? a. the atomic number of each element b. the name of each element c. the date that each element was discovered d. the atomic mass of each element _____ 8. Which of the following statements about the periodic table is false? a. There are more metals than nonmetals on the periodic table. b. Atoms of elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer level. c. The elements at the far left of the periodic table are nonmetals. d. Elements are arranged by increasing atomic number. _____ 9. Which of the following statements about alkali metals is true? a. Alkali metals are generally found in their uncombined form. b. Alkali metals are Group 1 elements. c. Alkali metals should be stored underwater. d. Alkali metals are unreactive. _____10. Which of the following statements about elements is true? a. Every element occurs naturally. b. All elements are found in their uncombined form in nature. c. Each element has a unique atomic number. d. All of the elements exist in approximately equal quantities. Short Answer 11. How is Moseley’s basis for arranging the elements different from Mendeleev’s? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 12. How is the periodic table like a calendar? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Math Skills Examine the chart of the percentages of elements in the Earth’s crust below. Then, answer the questions that follow. 13. Excluding the “Other” category, what percentage of the Earth’s crust are alkalimetals? ______________________________________________________________ 14. Excluding the “Other” category, what percentage of the Earth’s crust arealkaline-earth metals? ______________________________________________________________ CRITICAL THINKING 15 . Concept Mapping Use the following terms to create a concept map: periodic table, elements, groups, periods, metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. 16. Forming Hypotheses Why was Mendeleev unable to make any predictions about the noble gas elements? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 17. Identifying Relationships When an element that has 115 protons in its nucleus is synthesized, will it be a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid? Explain your answer. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 18. Applying Concepts Your classmate offers to give you a piece of sodium that he found on a hiking trip. What is your response? Explain. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 19. Applying Concepts Identify each element described below. a. This metal is very reactive, has properties similar to those of magnesium, and is in the same period as bromine. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ b. This nonmetal is in the same group as lead. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ INTERPRETING GRAPHICS 20. Study the diagram below to determine the pattern of the images. Predict the missing image, and draw it. Identify which properties are periodic and which properties are shared within a group. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Chapter Review – Environmental Problems and Solutions USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. conservation biodiversity recycling pollution overpopulation nonrenewable resource renewable resource 1. A(n) ______________________ is a resource that is replaced at a much slower rate than it is used. 2. The presence of too many individuals in a population for available resources is called ______________________. 3. ______________________ is an unwanted change in the environment caused by wastes. 4. The preservation and wise use of natural resources is called ______________________. 5. ______________________ is the number and variety of organisms in an area. UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS Multiple Choice _____ 6. Preventing habitat destruction is important because a. organisms do not live independently of each other. b. protection of habitats is a way to promote biodiversity. c. the balance of nature could be disrupted if habitats were destroyed. d. All of the above _____ 7. Exotic species a. do not affect native species. b. are species that make a home for themselves in a new place. c. are not introduced by human activity. d. do not take over an area. _____ 8. A renewable resource a. is a natural resource that can be replaced as quickly as it is used. b. is a natural resource that takes thousands or millions of years to be replaced. c. includes fossil fuels, such as coal or oil. d. will eventually run out. Short Answer 9. Describe how you can use the three Rs to conserve resources. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 10. What are five kinds of pollutants? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 11. Explain why human population growth has increased. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 12. What are two things that can be done to maintain biodiversity? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 13. List five environmental strategies. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Critical Thinking 14. Concept Mapping Use the following terms to create a concept map: pollution, radioactive wastes, gases, pollutants, CFCs, PCBs, hazardous wastes, chemicals, noise, and garbage. 15 Analyzing Ideas How might deforestation have contributed to the extinction of some species? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 16. Predicting Consequences Imagine that the supply of fossil fuels is going to run out in 50 years. What will happen if people are not prepared when the supply runs out? What might be done to prepare for such an event? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 17. Evaluating Conclusions A scientist thinks that farms should be planted with many different kinds of crops instead of a single crop. Based on what you learned about biodiversity, evaluate the scientist’s conclusion. What problems might this cause? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 18. Applying Concepts Imagine that a new species has moved into a local habitat. The species feeds on some of the same plants that the native species do, but it has no natural predators. Describe what might happen to local habitats as a result. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 19. Making Inferences Many scientists think that forests are nonrenewable resources. Explain why they might have this opinion. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ INTERPRETING GRAPHICS The line graph below shows the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere between 1958 and 1994. Use this graph to answer the questions that follow. 20. What was the concentration of carbon dioxide in parts per million in 1960? in 1994? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 21. What is the average change in carbon dioxide concentration every 4 years? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 22. If the concentration of carbon dioxide continues to change at the rate shown in the graph, what will the concentration be in 2010? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________