INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT:
advertisement

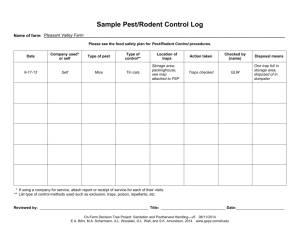
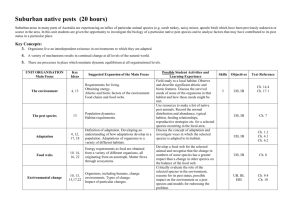
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT: Lecture 1 Introduction to IBE and analyzing the IBE environment (PEST, SWOT, 5 forces, Canalysis) Matevž Rašković Ljubljana, 21. 2. 2012 Expectations THE INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT OF TODAY Global balance of trade? Global FDIs A new FDI trend The rise of China: Exports China: eyeing the no. 1 place China vs. US comparison The rise of the BRIC(S) BRIC(S) as a super power BRIC(S) and Slovenia? Scandinavia represents less than 5 % of EU exports EU-27: > 71 % Germany: > 19 % Italy: > 12 % France: > 8 % Austria: > 8 % Former Soviet Union: < 5 % (Russia < 3 % ) USA: < 2 % Arab markets (without Turkey): < 2 % Turkey: + 1 % Ex-YU: > 14 % (share is slowly declining) Central & South America: < 1 % Mostly Mexico & Brazil) ? China: < 0,5 % (1.34 billion market) India: < 0.5 % (1.1 billion market) Total BRIC: < 4 % (almost 3 billion market) Australia & NZ: < 0,2% Brazil: < 0.2 % (196 million market ) Source: Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia, 2011 World of brands Top brands in 2011 Geographical distribution Top brand changes Top industry changes The impact of the crisis Top companies 2011 And the little ZARA dress you bought last week • Fabric bought in Asia • cut in a factory in Spain • sown by seamstresses in Portugal • printed in Tunisia • and sold in Ljubljana! THE COMPLEXITY OF TODAY http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lUMf7FWGdCw http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sc4HxPxNrZ0&feature=fvw http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nse09-dKATI http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z4gt62uAasE&feature=related MAIN DIFFERENCES: DOMESTIC vs. INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS • Geography & distance • Information (cause & effect) • Additional economic concepts • Culture • Markets- widespread & fragmented • Volumes • Politics • Governments & regulations • Technology THE BASIC APPROACH IN IB Seek & look Spot & target Understand (information) How to do good business? Manage / interact ANALYZING THE IB ENVIRONMENT: AN OVERVIEW WHY IS ANALYSIS IMPORTANT? Ford Pinto ANALYSIS LEVELS • MACRO (COUNTRY) LEVEL: • PEST / PESTL • PORTER’S DIAMOND • SWOT • MEZZO (INDUSTRY) LEVEL: • PORTER’S 5 FORCES • COMPETITIVE POSITIONING • C-ANALYSIS 3 KEY ISSUES: 1. APPLICABILITY & RELEVANCE 2. RISK MITIGATION 3. SUPPORT FOR DECISION-MAKING • MICRO (COMPANY) LEVEL: • INTERNAL COMPANY ANALYSIS (capabilities, resources, etc) • DUE DILLIGENCE EXAMPLE: PORTER’S DIAMOND Which factors are key for your business venture? What drives demand? Decision-making factors Elasticity? Apply the data so it is relevant to your company and line of business! PEST ANALYSIS 1/3 PEST ANALYSIS 2/3 PEST ANALYSIS 3/3 Always ask What? What do I need to know to make a better and informed decision? Why? Why do I need to know this (cause & effect)? Where? Where do I get this information and data? How much? How much resources are needed for this? How? How will I be able to use and apply this info and data in my business processes? PEST: GINI coefficient PEST: example of population structure Variables: Gender Age Education level Literacy Religion Ethnicity Marital status Children Size of family PEST: example quality of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dbqzbxyd9y4 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZpHpz4rTA04 PEST: example CPI (Transparency Int.) http://www.transparency.org/policy_research/surveys_indices/cpi/2010/results Example: Doing Business (World Bank) www.doingbusiness.org 12 pillars of competitiveness World Economic Forum, 2010/20101 EXAMPLE: WEF (Competitiveness) 2 views: 1) Absolute progress and 2) relative progress World Economic Forum, 2010/20101 WEF: Slovenia World Economic Forum, 2010/2011 EXAMPLE: Innovation Scoreboard Pro Inno Europe: 2011. EXAMPLE: Innovation Scoreboard Pro Inno Europe: 2011. EXAMPLE: socio-cultural environment • Hofstede’s indices • PDI • UAI • IND • MAS • LTO • World Values Survey • GLOBE project • Country of origin effect (COO) & consumer ethnocentrism • CET-SCALE (between 17 and 119; i.e. Slovenia: 53.74) • Consumer profiles Schwartz: values Schwartz, 2008/2009. Culture & national character Terracciano et al. (2005): National Character Survey. PORTER’S 5 FORCES (quick recap) EXAMPLE: Slovene retail market PORTER’S 5 FORCES TOOLBOX The bargaining power of suppliers •supplier switching costs •ddifferentiation of inputs •presence of substitute inputs •supplier concentration •threat of forward integration •cost of inputs •importance of volume to supplier The threat of new entrants •barriers to entry •brand equity •switching costs •capital requirements •access to distribution •absolute cost advantages •learning curve advantages •expected retaliation •government policies The bargaining power of customers • bargaining leverage • buyer volume •buyer switching costs •buyer information availability •ability to backward integrate •availability of substitutes •buyer price sensitivity •price of total purchase The intensity of competitive rivalry •number of competitors •rate of industry growth •intermittent industry overcapacity •exit barriers •diversity of competitors •informational complexity The threat of substitutes •brand equity •buyer propensity to substitute •fixed cost allocation •relative price performance •level of ad expense of substitutes •buyer switching costs •perceived level of product differentiation C-ANALYSIS • Doing a profile of your main competitors • SWOT of your main competitors • • • • • • Brand image Positioning Capabilities Competitive advantage Skills Human capital Understanding the value chain Understanding global value chains EXAMPLE: COMPETITIVE POSITIONING Valicon, 2009. EXAMPLE: Gorenje positioning Gorenje, 2008. MARKET SCREEING MODEL: DECIDING WHICH MARKETS TO ENTER WHICH MARKET TO ENTER? WHICH INDUSTRY WHICH SEGMENT? TO ENTER? EXAMPLE: IDEAS Highest per capita BEER consumption in liters Rank Country Consumption 1 Czech Republic 156.9 2 Ireland 131.3 3 Germany 115.8 4 Australia 109.9 5 Austria 108.3 6 United Kingdom 99.0 7 Slovenia 93.3 8 Belgium 93.0 9 Denmark 89.9 10 Finland 85.0 Highest per capita COFFEE consumption in kilograms EXAMPLE: IDEAS Highest per capita GUN ownership in # guns per 100 • 1st USA: 90 guns per 100 people • 2nd Yemen: 61 guns per 100 people • 3rd Finland: 56 guns per 100 people • 4th Switzerland: 46 guns per 100 people • 5th Iraq: 39 guns per 100 people • 6th Serbia: 38 guns per 100 people Top 20 countries in terms of frequency of sex INFORMATION RESOURCES • Alibaba: www.alibaba.com • Transparency international: www.transparency.org • CIA factbook: www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-worldfactbook/ • WTO:http://stat.wto.org/CountryProfile/WSDBCountryPFVie w.aspx?Language=E&Country=SI • World Bank – Doing business: www.doingbusiness.org • Innovation Scoreboard: www.proinno-europe.eu