advanced game theory 2009-2010
advertisement

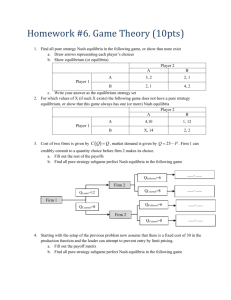
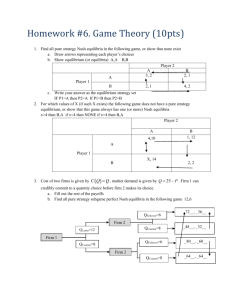
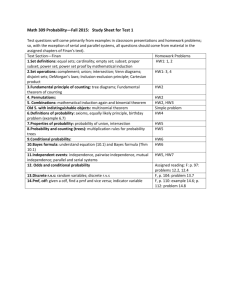
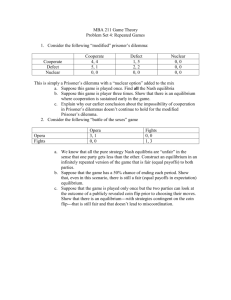
UNIVERSITY OF MILAN – BICOCCA FACULTY OF ECONOMICS ADVANCED GAME THEORY (2009/10) Prof. Mario Gilli PURPOSE: This course is an introduction to advanced topics in game theory. Its objective is to equip the students with tools which are essential to study economics of information and of strategic behaviour and for setting up and solving a wide range of economic problems. COURSE DESCRIPTION: The course consists in the first 32 hours of Game Theory plus other 8 hours, totalizing 40 hours (5 CFU). We begin reviewing game representations. First a game tree is defined, as well as information sets and pure, mixed and behavioral strategies, perfect recall and Kuhn’s theorem. Then we consider Strategic form games and the relation among different ways of modelling strategic Interaction. Thus existence and properties of solutions and of Nash equilibria are discussed. Next Nash equilibria in extensive form games are analysed and refinements proposed. Refinements of Nash equilibria will be discussed considering applications to bargaining, signalling and oligopoly models. Finally we turn to the analysis of dynamic games, covering finitely and infinitely repeated games, the folk theorem for repeated games, subgame perfection, and punishment strategies. STRUCTURE: The lectures will illustrate the main concepts through formal definitions and examples, with a particular attention to the calculus of solutions, some theorems without proof will be discussed in the lectures. There will be problem sets and homework. You are encouraged to form small group to solve homework. The homework will be quite difficult: you are not expected to be able to answer all the questions correctly. Homework are difficult because they are aimed to improve your understanding of the subtle problems of game theory. Because of this characteristics they are done home and in groups so to incentivize discussions and readings among students and talks with the teacher. Clearly this means that they are not a good forecast of the exercises of the final exam, which will be a lot simpler. Your course grade will be based on the homework and on the final exam. Good class participation can improve your evaluation. I expect you to come to class prepared to respond intelligently to questions about the readings and assignments. 1 Textbooks: 1. Jurgen Eichberger, Game Theory for Economists, Academic Press,1993. 2. Martin Osborne and Ariel Rubinstein, A Course in Game Theory, MIT Press, 1994. 3. Lecture notes. OFFICE HOURS: Wednesday 1.30-2.30 p.m. or contact Gilli by email mario.gilli@unimib.it EXAMINATION: The examination consists of two parts: two homework and a written individual examination. • HOMEWORK: the homework will consist in questions, that you have to solve in one or two weeks working in a group. The marks count for 50% of the final mark in Advanced Game Theory. Students that will not be able to follow the lectures can substitute the homework with a written paper. • FINAL EXAM: the final exam will count for 50% of the final mark and it will consist in two questions in one hour and half. • I STRONGLY SUGGEST THE STUDENTS TO TAKE THE EXAM IMMEDIATELY AFTER THE COURSE (December 3rd 2009). On the website of the course (http://dipeco.economia.unimib.it) you will find • all the information relevant for the course • all the slides of the lectures. Moreover it would be extremely useful if you enrol yourself at the following website: http://dipeco.economia.unimib.it/dbs/game/index.asp. putting your name, surname and mail address. LECTURES: The lectures are on Monday from 9.00 to 10.30 am in room U7/12 and Thursday from 9.00 to 10.30 am in room U6/20. CONTENTS: E = Eichberger, Game Theory for Economists; O&R = Osborne and Rubinstein, A Course in Game Theory, O&R1 = Martin Osborne and Ariel Rubinstein, Bargaining and Markets. DETAILLED TIMETABLE OF THE LECTURES L1 L2 L3 Topic of the lecture Models of Games - Extensive Form Games-1 Models of Games - Extensive Form Games-2 Models of Games - Strategic Forms Games Day Chapters 28/9/2009 E, chapter 1 O&R chapters 6 &11 E, chapter 1 O&R chapters 6 &11 1/10/2009 5/10/2009 E, chapter 5 2 L4 Models of Games - Incomplete Information 8/10/2009 HW1 L5 HOMEWORK 1 Solutions for Games in Strategic Form: - Dominance - Bayesian rationality Nash Equilibria in strategic and in extensive form games - Nash Theorem - Properties - Calculations 12/10/2009 12/10/2009 L6 E, chapter 2 O&R chapter 4 E, chapter4 O&R chapter 2 15/10/2009 E, chapter 4 O&R chapter 2 Equilibria in extensive form games Sequential rationality in imperfect information games 19/10/2009 E, chapter 6 O&R chapter 12 E, chapter 6 O&R chapter 12 Refinements of Sequential Equilibria - 1 Refinements of Sequential Equilibria - 2 26/10/2009 HW2 R HW1 L11 L12 HOMEWORK 2 RETURN OF HW1 CORRECTION OF HW1 Sequential Equilibria and signalling games - 1 2/11/2009 2/11/2009 2/11/2009 5/11/2009 L13 Sequential Equilibria and signalling games - 2 Bargaining Theory – 1 9/11/2009 L7 L8 L9 L10 L14 L15 Bargaining Theory - 2 R HW2 RETURN OF HW2 L16 CORRECTION OF HW2 22/10/2009 29/10/2009 E, chapter 7 O&R chapter 12 E, chapter 7 O&R chapter 12 E, chapter 7 Notes 12/11/2009 E, chapter 7 Notes E, chapter ??? 16/11/2009 19/11/2009 19/11/2009 E, Chapter ??? RETURN OF HW2 CORRECTION OF HW2 END OF GAME THEORY COURSE L17 23/11/2009 L18 Repeated Games: - the Folk Theorem Finitely Repeated Games L19 SUMMING UP 30/11/2009 L20 Final exam 26/11/2009 E, chapter 8 O&R chapter 8 E, chapter 8 O&R chapter 8 3/12/2009 3 4