Principles of Supervision MGT 2220
advertisement

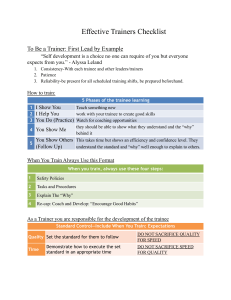
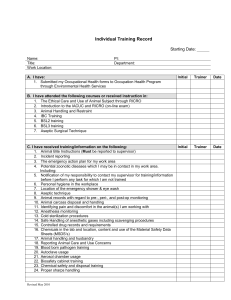
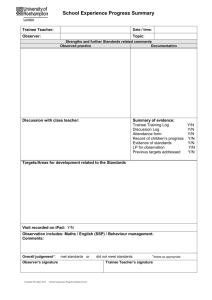
Principles of Supervision MGT 2220 Chapter 16 Providing Orientation & Training Training is important to continuous improvement because of the change that is taking place around us. You need to be aware of change, and you need to be continually growing to adapt to it. Paul Kortier, Plant Training Leader, Libbey Inc. Training = Increasing the skills that will enable employees to better meet the organizations goals. Page 446, Table 16.1 ORIENTATION OF EMPLOYEES Orientation The process of giving new employees the information they need to do their work comfortably, effectively, and efficiently. Benefits; 1. If an employee has to constantly search for explanation of how to do things is not efficient. 2. It reduces the nervousness and uncertainty of the new employee. 3. It encourages new employees to develop a positive attitude. 4. Tours and introductions help the new employee get acquainted with others. 5. These interpersonal aspects of orientation are important to include along with written and technical orientation materials. The supervisor’s role is to manage the “honeymoon period”. Orientation topics; 1. Policies & Procedures. 2. Work hours. 3. Breaks. 4. Location of Company facilities. (Break room, bathrooms, etc.) 5. Procedure for performance appraisals. 6. Time off. 7. Pay increases. 8. Explanation of what the department does. 9. How to perform the job. 10. Explain why this job is important. 11. Checklist, Page 450, Table 16.2. Orientation Methods 1. Employee Handbook is a document outlining policies and procedures. 2. Tour of Facilities. 3. Involvement of co-workers will help the new employee feel welcomed. 4. Follow-up should be provided to encourage questions. They may be overwhelmed in the first week Training 1. Cycle of steps to provide training. 2. Assess needs for training. Determine what is mandatory and create a learning environment. 3. Planning Steps are based on the objectives and performance levels. 4. Implementation is having someone be responsible for carrying out the plan. 5. Evaluation of the result to see if the objectives are met. Types of Training 1. On the Job Training is teaching a job while the trainer and trainee perform the job at the work site. 2. Apprenticeship is training that involves working alongside an experienced person who shows the trainee how to do various tasks of the job. It will have a time frame and pay limits until the trainee is qualified to work alone. 3. Cross Training is using job rotation so that employees learn to perform various jobs. 4. Vestibule Training takes place on equipment set up in a special area off the jobsite. It is a simulation of the real job. 5. Classroom Training is using the classroom setting for off the job training. 6. Computer Based Training is using software to take the place of an instructor. 7. Interactive Media can adjust content on the basis of user responses using video, graphics, animation, etc. 8. Role Playing is a training method in which roles are assigned to participants, who then act out the way they would handle a specific situation. It is an attempt to train for the human element. 9. Basic Skills Training is used to improve skills and keep employees motivated. COACHING TO SUPPORT TRAINING Coaching = Guidance and instruction in how to do a job so that it satisfies performance goals. The supervisor will constantly observe team members. You will identify each employee’s strengths and weaknesses. Encourage the employee to take a personal interest in their skills. Mentoring = Provides guidance, advice, and encouragement through ongoing one-onone work relationship. It is an appropriate way to support the training of an employee that shows great potential. You can use this to navigate issues such as cultural and value expectations. You should be a great listening as you are a sounding board for guiding employees to discover the results of their behavior. EVALUATION OF TRAINING 1. Was the trainer well prepared? 2. Did the trainer communicate clearly and in an interesting manner? 3. Was there visual demonstrations as well as verbal descriptions? 4. Where employees well enough prepared for this level of training? 5. Did employees understand how they would benefit from this training? 6. Did employees have a chance to ask questions? 7. Did employees receive plenty of praise for their progress? Whatever the outcome, training represents a cost to the organization. Consequently, it is worth performing only when it leads to improved performance. Training that does not produce results should be changed or discontinued. Use only training that meets evaluation criteria. Training programs are not an expense but a valuable investment in the organization’s human resources. HOMEWORK Problem Solving Case: Training Call Center Employees, Page 469 & 70. Answer all three questions in detail.