2009 pre-first class vocabulary math.wps
advertisement

Algebra ½ students should know all of these words, definitions, and formulas. Make flashcards for
and memorize any definitions/formulas you do not already know. Print a copy of 1-66 for your notebook.
Geometry-means “to measure the earth.” Geometry involves measuring shapes.
Angle- two rays that share a common endpoint (vertex).
Perpendicular lines- lines that intersect to form a right angle.
Parallel lines- lines that never intersect.
Similar figures- figures that have the same shape.
Congruent figures- figures that have the same shape and same size.
Intersecting lines- lines that cross at some point.
Plane- is represented by a smooth, flat surface that has no thickness and extends indefinitely in all directions.
~ is the symbol for similar.
Polygon- a simple, closed figure made up of line segments.
Triangle- a polygon with 3 sides.
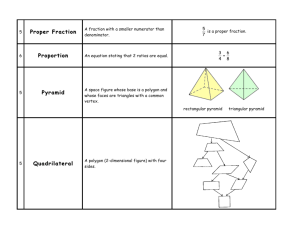
Quadrilateral- a polygon with 4 sides.
Pentagon- a polygon with 5 sides.
Hexagon- a polygon with 6 sides.
Heptagon- a polygon with 7 sides.
Octagon- a polygon with 8 sides.
Vertices- points where the sides of polygons meet.
Parallelogram- a quadrilateral having opposite sides parallel.
Rectangle- a quadrilateral having opposite sides parallel and 4 right angles.
Right angle- a 90 degree angle.
Straight angle- a 180 degree angle (a straight line).
Square- a quadrilateral having opposite sides parallel and 4 right angles and all sides equal.
Rhombus- a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and all sides equal.
Trapezoid- a quadrilateral with only one pair of parallel sides.
Acute angle- an angle of less than 90 degrees.
Obtuse angle- an angle of more than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees.
Isosceles triangle- a triangle having 2 sides =.
Scalene triangle- a triangle having no sides =.
Equilateral triangle- a triangle having all 3 sides =.
Sum- the answer to an addition problem.
Difference- the answer to a subtraction problem.
Product- the answer to a multiplication problem.
Quotient- the answer to a division problem.
Proper fraction- a fraction representing a number less than one. ( like ½ , 3/4 , 6/9 , etc.)
Improper fraction- a fraction representing a number more than one. (like 6/3, 3/2, 8/3, etc.)
Addends- the numbers being added.
Factors- the numbers being multiplied.
Prime number- a whole number greater than 1 whose only whole number factors are 1 & itself.
Composite number- a whole number greater than 1 which is not prime.
Numerator- the top number of a fraction.
Denominator- the bottom number of a fraction.
Equivalent fractions- fractions which have the same value.
Perimeter- the distance around a polygon.
A number is divisible by 2 if- it ends in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8.
A number is divisible by 10 if- it ends in 0.
A number is divisible by 5 if- it ends in 0 or 5.
A number is divisible by 3 if- the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. (For 27, 2+7=9 and 9 is div. by 3).
1 foot = 12 inches
1 yard = 3 feet
1mile = 5,280 feet
1meter = 100 centimeters (just like 1dollar = 100 cents)
1kilometer = 1000 meters (just like Y2K = the year 2000)
Mode- the number that appears the most often
Median- the middle number
Mean- the average
Area of a triangle = ½ bh (b is base and h is height)
Area of a rectangle = bh
Area of a parallelogram = bh
Ratio- a comparison of two numbers.
Rate- a ratio.
Equivalent equations - equations having the same solution.
The product of any number and its reciprocal is ? .
(Answer: one)
The only number which does not have a reciprocal is ? .
(Answer: zero)
Dividing by 2 is the same as multiplying by ? .
(Answer: ½ )
Be sure that you know perfectly all the ADD FACTS up through 9 + 9 = 18. (Ex. 7+8=15, etc.)
66.
Be sure that you know perfectly all the MULTIPLICATION TABLES through 12x12=144.
Algebra 1 students should know all of the above Algebra ½ terms plus the following Algebra 1
items. Make flashcards for and memorize any definitions/formulas that you do not already know.
2 points determine a
Line
3 noncollinear points determine a
plane
A half-line
Ray
2 rays joined at a common vertex
angle
An angle more than 180 and less than 360 Reflex angle
Angles which share a common vertex and a common side and do not overlap
adjacent angles
2 angles whose sum is 90 degrees
complementary angles
2 angles whose sum is 180 degrees
supplementary angles
2 opposite angles formed by intersecting lines
vertical angles
The distance of a number from the origin
absolute value
Changing the order of the addends does not change the sum commutative property of addition
Changing the grouping of the addends does not change the sum
associative property of addition
The perimeter of a circle
circumference
Area of a circle
Pi are square
Area of a rectangle
A=bh
Area of a triangle
A=1/2 bh
The base and height are always ___ to each other
perpendicular
Volume of a cylinder
V=(area of the base)h
Volume of a cone (or pyramid)
V=1/3(area of the base)h
Volume of a sphere
V=2/3(area of the base)h
A part of a circle is an
arc
Area of a wedge of a circle
sector
A segment that connects 2 points on a circle
chord
A closed figure made of line segments joined at the end points only
polygon
A polygon with all sides congruent and all angles congruent
regular polygon
Consecutive integers
N, N+1, N+2, ...
Consecutive odd integers
N, N+2, N+4, ...
Consecutive even integers
N, N+2, N+4,...
The number under the radical sign is called the
radicand
Equations containing variables are called
Conditional equations
Equation having the same solutions are called
equivalent equations
Opposite
Additive inverse
Reciprocal
Multiplicative inverse
The product of any number and its reciprocal is
one
The sum of any number and its opposite is
Zero
Scientific Notation a method of writing a number as a product of a decimal number and a power of 10
Concave Polygon
a polygon in which at least one interior angle; has a measure greater than 180
Order of Operations
PEMDAS
Least Common Multiple
the smallest whole number into which several other whole numbers will divide
evenly
Counting Numbers
{1, 2, 3, ...}
Whole Numbers
{0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
Integers
{...-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
Geometry Students should know all of the above Algebra ½ and Algebra 1 terms plus the following
terms. Make flashcards for and memorize and terms that you do not already know. (You should remember
terms 1- 30 below from Algebra 1.) Geometry Students need to pick up a Geometry book from me ASAP
in order to complete the pre-first class assignment. (Cost is $25 rental for the year.)
Monomial
a polynomial of one term
Binomial
a polynomial of 2 terms
Trinomial
a polynomial of 3 terms
Relation
a pairing that matches each element of the domain with one or more images in the range
Function
a pairing that matches each element of the domain with only one image in the range
Subtraction the inverse operation of addition
Division
the inverse operation of multiplication
Squaring
the inverse operation of taking the square root
Domain
The set of permissible replacement values for the independent variable of a function. X’s
Range
the set of permissible replacement values for the dependent variable of a function. Y’s
Direct Variation
y = kx
Inverse Variation
y = k/x
Hypotenuse the side opposite the right angle in a right triangle
Legs
the 2 sides which form the right angle in a right triangle
Set
a collection of objects
Cube
a 3-dimensional geometric figure whose 6 faces are identical squares
Pythagorean Theorem ?
Exponential Growth Formula ?
Can you find the formulas for #’s 17 - 24 ?
Interest Compounded Annually Formula
?
If so, write the formula next to the definition.
Area of a Kite Formula
?
The Slope Formula ?
The distance between 2 points formula
?
Surface Area of a Cone
?
Volume Formula of a Sphere
?
i = prt
interest = principal x rate x time (The simple interest formula)
y = mx + b
slope-intercept formula of a line (m = slope and b = y intercept)
Rational Number
any number which can be written as a fraction
Irrational Number
any number which is both non-terminating and non-repeating
Null Set
the set that has no members (Also called the Empty Set)
Postulate
a statement that is assumed to be true without proof. (Also called an Axiom)
* Geometry students, pre-read pages 3 - 21 and be ready for a quiz over the definitions,
postulates, and theorems in sections 1-1, 1-2, 1-3, and 1-4.
Algebra 2 students should know all of the above Algebra ½, Algebra 1, and Geometry terms. Make
flashcards for and memorize any that you do not already know.
Advanced Math 1 students should know all of the above Algebra ½ , Algebra 1, and Geometry
terms, plus the following Algebra 2 terms. Make flashcards for and memorize any that you do not
already know.
An operation which undoes another operation
inverse operation
Of 2 or more terms, the product of all prime factors common to every term, each to the highest power that it
occurs in all terms
G.C.F.
Write each factor the most it appears in anyone factorization to get the ___
L.C.D.
A first-degree polynomial equation in one or more variables.
Monomial
The set of all images of the elements of the domain of a function. (the Y s)
range
A line whose 2 endpoints are on the circle
Chord
The set of numbers made of the Rationals plus the Irrationals
Reals
2 nonadjacent angles formed by 2 intersecting lines (they re always equal)
vertical angles
A line that intersects a circle at only one point
tangent
For any 2 Real numbers a and b, exactly one of the following is true: a < b,a =b ,or a >b. Trichotomy Law
A polynomial of 2 terms is a ___.
Binomial
The sum of any number and its additive inverse is ___.
Zero
A statement accepted as true without proof is a/an ___. (Also called a postulate)
Axiom
A number of the form a + bi , where a and b are Real numbers and i is the imaginary part. Complex number
A line segment (in a polygon) that connects any 2 nonconsecutive vertices
diagonal
A property that states a ( b + c ) = ab + ac.
Distributive Property
A mapping between 2 sets with no same 1st elements
Function
If a radius is perpendicular to a chord, then it ____ the chord.
Bisects
THE FORMULA FOR THE FOLLOWING IS:
Area of a trapezoid: ½ (base 1 + base 2)h; Area of a sector of a circle: Fraction of the area of a circle;
Length of an arc of a circle: Fraction of the circumference; Slope: Rise divided by Run.
The logarithm is the ___.
Exponent
The antilogarithm is the ___.
Number or Argument
A ___ is an ordered arrangement.
Permutation
Tools for construction are the ___ and the straight edge.
Compass
In the quadratic formula, b 4ac is called the ___.
Discriminant
When b -- 4ac is a negative number, the equation has 2 complex solutions which are __.
Conjugates
Give an equation for a
circle: Area=pi are squared; parabola: y=a(x-h)squared + k; ellipse: (for example) 2xsquared+3ysquared=7;
hyperbola: (for example) 2xsquared – 3ysquared=7
Write the product (or factorization): ( a + b ) squared= ?; ( a - b )squared=?; ( a + b )cubed =?;
(a-b)cubed=?
An equation that equates 2 ratios is a ___.
Proportion
Changing the order of the addends does not change the sum is the ___ property.
Commutative Property
Changing the grouping of the addend does not change the sum is the ___ property.
Associative Property
The ___ is the additive inverse.
Opposite
The ___ is the multiplicative inverse.
Reciprocal
Area formula of any quadrilateral that has diagonals which are perpendicular to each other.
A=½dd
Permissible replacement values for the independent variable. How far to the left & right
Domain
The formula for the distance between 2 points (on a plane) is ___.
d=square root of the sum of legs squared
The ___ numbers are both non-terminating and non-repeating.
Irrational Numbers
The ___numbers are numbers which can be written in the form of a/b, where b does not equal 0. Rational Nos.
A line that intersects (touches) a circle at only one point is a ___.
Tangent
An assertion that can be proved is a ___.
Theorem
A quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction.
Vector
Two triangles that have the same angles.
Similar triangles
A polygon whose interior angles are equal and whose sides are equal.
Regular polygon
A line that intersects a circle at 2 points.
Secant
Advanced Math 2 students should know all of the above Algebra ½ , Algebra 1, Geometry,
Algebra 2, and the following Advanced Math 1 terms . Make flashcards for and memorize any that you
do not already know. (Consult the Index of your book to find pages of the definitions and formulas not listed.)
Distance formula
Midpoint formula
Natural Log implies base ___
e
Common Log implies base ___
10
Law of Sines
Law of Cosines
An ordered arrangement is a ___
Radians = ___
Length of an arc =____
Radius x Radian
Perpendicular lines have ___ slopes.
Opposite reciprocal
Double – Intercept Form
Parallel lines have ___slopes.
Same
If f( ) = x and g( ) = x, the 2 functions are ___ functions.
Inverse
csc A = ____
Permutation (linear) = ___
Circular permutation = ___
Distinguishable permutation = ___
Combination = ___
Area of a sector of a circle = ___
Area of a segment = ___
If f(x) = f(-x) for all x in the domain, we say the function is ___
even
The graphs of ___ functions are symmetric about the origin.
Odd
DeMoivre’s theorem states that ?
sin squared + cos squared
= ____
1 + cot squared = ____
tan sfquared + 1 = ____
Area formula of a trapezoid
Oblique cylinders are cylinders whose bases are not ____ to the sides.
Perpendicular
The formula to find the longest diagonal in a box.
___ reasoning is the process of using a rule once it has been formulated and applying it to specifics. Deductive
____reasoning is the process of trying to find a rule, a general rule, as a result of observing information and
data from specifics.
Inductive
___ numbers are real numbers that can be written as fractions of integers.
Rational
___numbers are real numbers that are both 1) non-terminating and 2)non-repeating.
Irrational
The quadratic formula
Equation of a circle
Equation of a hyperbola
Equation of a parabola
Equation of a line
Equation of an ellipse
Direct variation formula
Inverse variation formula
Factor a squared + b squared
We cannot use replacements for x that indicate division by ___
Zero
Or require that we take square roots of ___ numbers.
Negative
If a graph on the coordinate plane passes the ___ ___ test, then it is a function.
Vertical line
If a graph on the coordinate plane passes the ___ ___ test too, then it is a non-to-one function. Horizontal line
tan 45 = ___, tan 180 = ___, tan 0 =___, sin 0 = ___, sin 270 = ___, cos 90 = ___, cos 90
If the resultant is ?
The equilibrant is ? .
___ is the statistic used to get a feel for how much the measurements are spread out.
Standard deviation
The standard deviation = ?
The square root of the variance
To get the ___ of a list of data, subtract the smallest score from the largest.
Range
The length of the ___ of the triangle (formed when we graph a complex number) is called the absolute value of
the complex number.
Hypotenuse
Example of Rectangular form of a vector
Example of Polar form of a vector
Example of Rectangular form of a complex number
Example of Polar form of a complex number






![7th Grade [Pre-Algebra] Math Vocabulary](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006617991_1-76ce0e26cff8b794b821343c050f71cb-300x300.png)