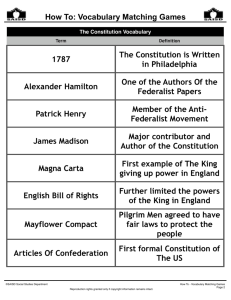
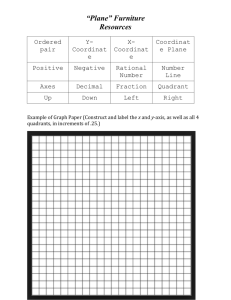
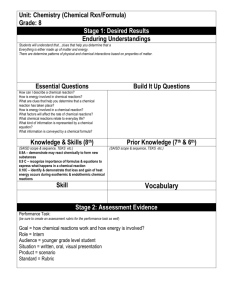
How To Four Quadrants
advertisement
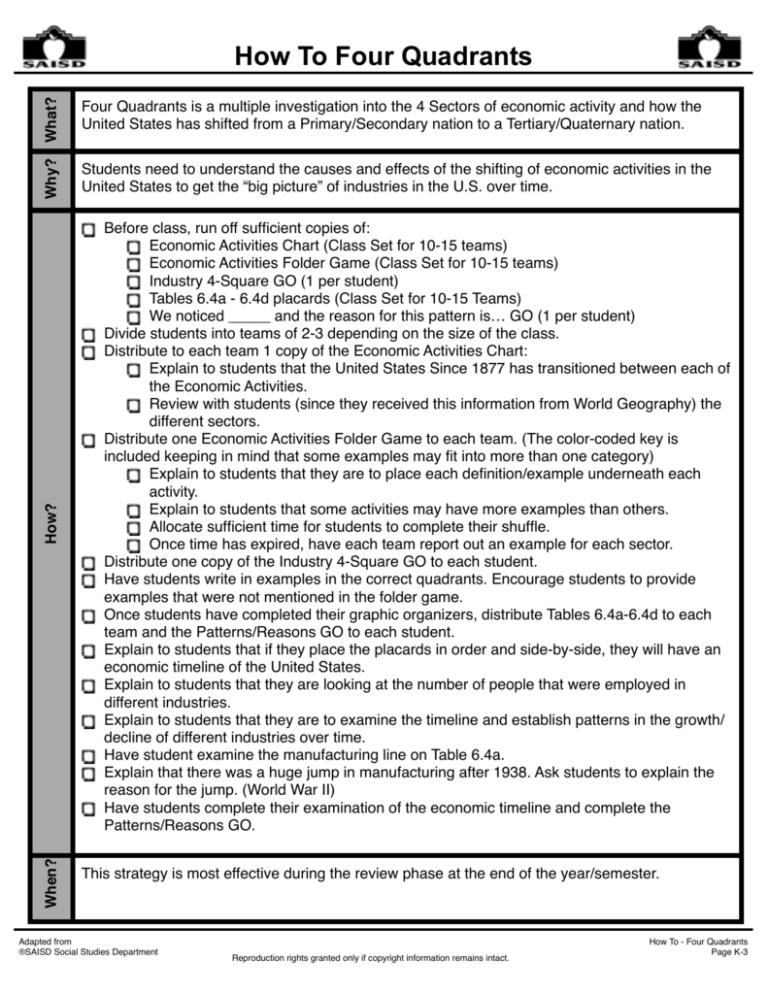
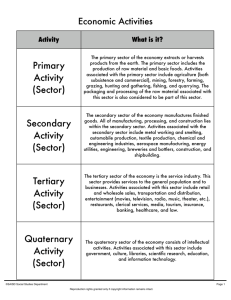
What? Students need to understand the causes and effects of the shifting of economic activities in the United States to get the “big picture” of industries in the U.S. over time. When? How? Four Quadrants is a multiple investigation into the 4 Sectors of economic activity and how the United States has shifted from a Primary/Secondary nation to a Tertiary/Quaternary nation. Why? How To Four Quadrants Before class, run off sufficient copies of: Economic Activities Chart (Class Set for 10-15 teams) Economic Activities Folder Game (Class Set for 10-15 teams) Industry 4-Square GO (1 per student) Tables 6.4a - 6.4d placards (Class Set for 10-15 Teams) We noticed _____ and the reason for this pattern is… GO (1 per student) Divide students into teams of 2-3 depending on the size of the class. Distribute to each team 1 copy of the Economic Activities Chart: Explain to students that the United States Since 1877 has transitioned between each of the Economic Activities. Review with students (since they received this information from World Geography) the different sectors. Distribute one Economic Activities Folder Game to each team. (The color-coded key is included keeping in mind that some examples may fit into more than one category) Explain to students that they are to place each definition/example underneath each activity. Explain to students that some activities may have more examples than others. Allocate sufficient time for students to complete their shuffle. Once time has expired, have each team report out an example for each sector. Distribute one copy of the Industry 4-Square GO to each student. Have students write in examples in the correct quadrants. Encourage students to provide examples that were not mentioned in the folder game. Once students have completed their graphic organizers, distribute Tables 6.4a-6.4d to each team and the Patterns/Reasons GO to each student. Explain to students that if they place the placards in order and side-by-side, they will have an economic timeline of the United States. Explain to students that they are looking at the number of people that were employed in different industries. Explain to students that they are to examine the timeline and establish patterns in the growth/ decline of different industries over time. Have student examine the manufacturing line on Table 6.4a. Explain that there was a huge jump in manufacturing after 1938. Ask students to explain the reason for the jump. (World War II) Have students complete their examination of the economic timeline and complete the Patterns/Reasons GO. This strategy is most effective during the review phase at the end of the year/semester. Adapted from ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-3 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Economic Activities Activity What is it? Primary Activity (Sector) The primary sector of the economy extracts or harvests products from the earth. The primary sector includes the production of raw material and basic foods. Activities associated with the primary sector include agriculture (both subsistence and commercial), mining, forestry, farming, grazing, hunting and gathering, fishing, and quarrying. The packaging and processing of the raw material associated with this sector is also considered to be part of this sector. Secondary Activity (Sector) The secondary sector of the economy manufactures finished goods. All of manufacturing, processing, and construction lies within the secondary sector. Activities associated with the secondary sector include metal working and smelting, automobile production, textile production, chemical and engineering industries, aerospace manufacturing, energy utilities, engineering, breweries and bottlers, construction, and shipbuilding. Tertiary Activity (Sector) The tertiary sector of the economy is the service industry. This sector provides services to the general population and to businesses. Activities associated with this sector include retail and wholesale sales, transportation and distribution, entertainment (movies, television, radio, music, theater, etc.), restaurants, clerical services, media, tourism, insurance, banking, healthcare, and law. Quaternary Activity (Sector) The quaternary sector of the economy consists of intellectual activities. Activities associated with this sector include government, culture, libraries, scientific research, education, and information technology. ®SAISD Social Studies Department Definitions from http://geography.about.com/od/urbaneconomicgeography/a/sectorseconomy.htm Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-4 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Primary Activity (Sector) Production of raw material and basic foods Secondary Activity (Sector) Manufacturing, processing, and construction Tertiary Activity (Sector) Provides services to the general population Quaternary Activity (Sector) Intellectual activities ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-5 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Commercial Agriculture Subsistence Agriculture Mining Hunting and Gathering Fishing More Common in Less Developed Nations Metal Working Automobile Production Textiles Construction More Common Computer in Developing Manufacturing and Newly Industrialized ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-6 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Television Broadcasting Tourism Restaurants Transportation More Common in Newly Industrialized and More Developed Government Teaching Information Technology Libraries More Common in More Developed ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-7 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Television Broadcasting Tourism Restaurants Transportation More Common in Newly Industrialized and More Developed Government Libraries Teaching Information Technology More Common in More Developed Subsistence Agriculture Mining Commercial Agriculture Fishing More Common in Less Developed Nations Hunting and Gathering Automobile Production Textiles Metal Working Computer Manufacturing More Common in Developing and Newly Industrialized Construction Production of raw material and basic foods Primary Activity (Sector) Manufacturing, processing, and construction Secondary Activity (Sector) Provides services to the general population Tertiary Activity (Sector) Intellectual activities Quaternary Activity (Sector) ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-8 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Primary Industry Secondary Industry 4 Industries Tertiary Industry Quaternary Industry ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-9 Transitioning the U.S. Economy A Full-Time and Part-Time Employees by Industry (In Thousands) Farms Manufacturing Retail Services Information 40000 30000 20000 10000 0 1929 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 1938 1939 1940 1941 1942 1943 1944 1945 1946 1947 1948 Data Aggregated from: the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis Information Adapted from the Bureau of Economic Analysis ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-10 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Full-Time and Part-Time Employees by Industry (In Thousands) B Farms Manufacturing Retail Services Information 50000 37500 25000 12500 0 1949 1950 1951 1952 1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 1962 1963 1964 1965 1966 1967 1968 Data Aggregated from: the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis Information Adapted from the Bureau of Economic Analysis ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-11 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Full-Time and Part-Time Employees by Industry (In Thousands) C Farms Manufacturing Retail Services Information 60000 45000 30000 15000 0 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974 1975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 Data Aggregated from: the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis Information Adapted from the Bureau of Economic Analysis ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-12 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Full-Time and Part-Time Employees by Industry (In Thousands) D Farms Manufacturing Retail Services Information 120000 90000 60000 30000 0 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 Data Aggregated from: the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis Information Adapted from the Bureau of Economic Analysis ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-13 Transitioning the U.S. Economy Pattern We noticed _____________________ and the reason for this pattern is… 1 2 3 4 Adapted from ®SAISD Social Studies Department Reproduction rights granted only if copyright information remains intact. How To - Four Quadrants Page K-14