Java Database Connectivity
advertisement
jonkv@ida
JDBC 1: What is it?
2
2003-01-16
jonkv@ida
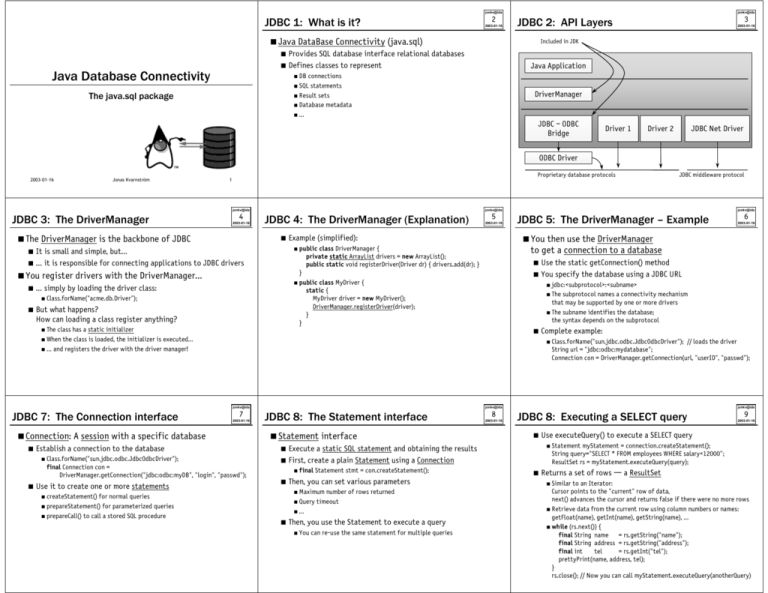
JDBC 2: API Layers
Java DataBase Connectivity (java.sql)
■
■
Java Database Connectivity
3
2003-01-16
Included in JDK
Provides SQL database interface relational databases
Defines classes to represent
Java Application
DB
connections
SQL statements
Result sets
Database metadata
…
The java.sql package
DriverManager
JDBC – ODBC
Bridge
Driver 1
Driver 2
JDBC Net Driver
ODBC Driver
2003-01-16
Jonas Kvarnström
Proprietary database protocols
1
jonkv@ida
JDBC 3: The DriverManager
4
2003-01-16
The DriverManager is the backbone of JDBC
■
■
jonkv@ida
JDBC 4: The DriverManager (Explanation)
■
■
}
public class MyDriver {
static {
MyDriver driver = new MyDriver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
}
}
… simply by loading the driver class:
But what happens?
How can loading a class register anything?
jonkv@ida
JDBC 5: The DriverManager – Example
■
The
subprotocol names a connectivity mechanism
that may be supported by one or more drivers
The subname identifies the database;
the syntax depends on the subprotocol
class has a static initializer
the class is loaded, the initializer is executed…
… and registers the driver with the driver manager!
■
When
// loads the driver
String url = "jdbc:odbc:mydatabase";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "userID", "passwd");
7
2003-01-16
Connection: A session with a specific database
Establish a connection to the database
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
final Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:myDB", "login", "passwd");
■
Use it to create one or more statements
for normal queries
prepareStatement() for parameterized queries
prepareCall() to call a stored SQL procedure
Complete example:
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
jonkv@ida
■
Use the static getConnection() method
You specify the database using a JDBC URL
jdbc:<subprotocol>:<subname>
The
JDBC 7: The Connection interface
6
2003-01-16
You then use the DriverManager
to get a connection to a database
Example (simplified):
class DriverManager {
private static ArrayList drivers = new ArrayList();
public static void registerDriver(Driver dr) { drivers.add(dr); }
Class.forName("acme.db.Driver");
■
5
2003-01-16
public
It is small and simple, but…
… it is responsible for connecting applications to JDBC drivers
You register drivers with the DriverManager…
■
JDBC middleware protocol
jonkv@ida
JDBC 8: The Statement interface
Statement interface
■
Execute a static SQL statement and obtaining the results
First, create a plain Statement using a Connection
■
Then, you can set various parameters
■
final
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
Maximum
number of rows returned
Query timeout
…
createStatement()
■
Then, you use the Statement to execute a query
You
can re-use the same statement for multiple queries
8
2003-01-16
jonkv@ida
JDBC 8: Executing a SELECT query
■
9
2003-01-16
Use executeQuery() to execute a SELECT query
Statement
myStatement = connection.createStatement();
String query="SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary<12000";
ResultSet rs = myStatement.executeQuery(query);
■
Returns a set of rows — a ResultSet
Similar
to an Iterator:
Cursor points to the "current" row of data,
next() advances the cursor and returns false if there were no more rows
Retrieve data from the current row using column numbers or names:
getFloat(name), getInt(name), getString(name), …
while (rs.next()) {
final String name = rs.getString("name");
final String address = rs.getString("address");
final int
tel
= rs.getInt("tel");
prettyPrint(name, address, tel);
}
rs.close(); // Now you can call myStatement.executeQuery(anotherQuery)
jonkv@ida
JDBC 9: Statement / executeUpdate()
■
10
2003-01-16
jonkv@ida
JDBC 10: {Prepared,Callable}Statement
UPDATE,
INSERT, CREATE TABLE, …
These queries return the number of changed rows
Statement myStatement = connection.createStatement();
■
■
Used for calling stored procedures
jonkv@ida
13
2003-01-16
DatabaseMetaData: Information about the database
DatabaseMetaData dbmd = con.getMetaData();
DatabaseMetaData is a large interface that lets you find out
jonkv@ida
JDBC 14: Repetition
■
final Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:myDB", "login", "passwd");
■
Send it an SQL statement
final
Statement stmt
final String
query
final ResultSet rs
■
jonkv@ida
Useful Links
■
JDBC home page
■
JDBC section of the JDK documentation
■
The Java Tutorial on JDBC
= con.createStatement();
= "SELECT name, address, tel FROM Employees";
= stmt.executeQuery(query);
■
Java Developer Connection Articles on JDBC
Process the results
■
Examplets
while
(rs.next()) {
final String name = rs.getString("name");
final String address = rs.getString("address");
final int
tel
= rs.getInt("tel");
prettyPrint(name, address, tel);
Column
count, column names, types
table a column belongs to, whether an int is signed. …
… and so on
Which
}
15
2003-01-16
http://java.sun.com/products/jdbc/index.html
Establish a connection to the database
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
ResultSetMetaData: Information about a result set
ResultSetMetadata rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
ResultSetMetadata lets you find out
14
2003-01-16
Repetition:
What
■
String q = "UPDATE employees SET salary = ? WHERE name = ?";
PreparedStatement stmt = con.prepareStatement(q);
stmt.setInt(1, 15000); stmt.setString(2, "John Doe");
stmt.executeUpdate();
stmt.setInt(1, 17000); stmt.setString(2, "Jane Doe");
stmt.executeUpdate();
con.commit(); // or con.rollback();
con.setAutoCommit(true);
Parameters are marked by question marks
CallableStatement extends PreparedStatement
■
■
Turn this off to handle transactions
con.setAutoCommit(false);
q = "UPDATE employees SET salary = ? WHERE name = ?";
PreparedStatement stmt = con.prepareStatement(q);
stmt.setInt(1, 15000); stmt.setString(2, "John Doe");
stmt.executeUpdate();
stmt.setInt(1, 17000); stmt.setString(2, "Jane Doe");
stmt.executeUpdate();
"UPDATE employees " +
"SET salary = salary * 1.10 " +
"WHERE salary < 12500";
int changed = myStatement.executeUpdate(update2);
System.out.println(changed + " rows changed.");
tables are available
What stored procedures are available
The maximum number of tables in a GROUP BY clause
… and so on (around 150 methods)
■
String
String update2 =
12
2003-01-16
Connections are normally in auto-commit mode
Used for queries that are executed many times
varying parameters
The query can be pre-compiled, increasing performance
"INSERT INTO employees " +
"VALUES ('John Doe', 37, 12400)";
myStatement.executeUpdate(update);
■
jonkv@ida
JDBC 11: Transactions
With
String update =
■
2003-01-16
PreparedStatement extends Statement
Use executeUpdate() to execute update queries
JDBC 12: Metadata
11
http://java.sun.com/j2se1.4/docs/guide/jdbc/
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/jdbc/index.html
http://developer.java.sun.com/developer/technicalArticles/Database/
http://javaalmanac.com/egs/java.sql/pkg.html