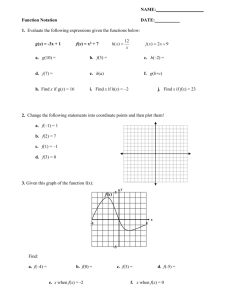
In this essay I will be researching information on vaccination. I will
advertisement

In this essay I will be researching information on vaccination. I will be also finding out how vaccinations controls diseases, what are the responsibilities of the government and other organisations to treat new strains of influenza each year, describing the new microbiological and plant based alternatives to vaccines. Lastly I will be investigating on why does evolution of pesticides resistance in insects and drug resistance in microorganisms have implications for humans. A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity from a particular disease. They also contain the same antigens or parts of antigens that cause the diseases, the antigens in vaccines are either killed or sufficiently weakened. When the antigens are injected into fatty tissues or muscle, vaccine antigens are not strong enough to produce the symptoms and signs of the disease but are strong enough for the immune system to produce antibodies to fight against them. The memory cells that remain prevent reinfection when they encounter that disease in the future. Through vaccinations children develop immunity without suffering for the actual diseases that vaccines prevent. In this diagram you can see the steps in which vaccinations work. All these steps show how new flu strains are developed and what is needed to make new flu strains. To get new flu strains in a step by step process meaning that it takes time to get to the final stage of the process. To get new flu strain all dangerous parts of the HA gene has to be removed scientist then spike the Ha and Na gene from the flu strain 1 into a circular piece of DNA called the plasmids. The next stage is additional plasmids are created using the remaining 6 six genes found in flu strain 2. The third stage scientist do is insert the HA and Na plasmids from strain 1 and the six plasmids carrying genes from strain 2 into cells growing in the laboratory. The fourth stage is the genes in the plasmids instruct the animal cells to make the desired new flu strain. Now the new flu is produced. The expression of antigens in transgenic plants has been increasingly used in the development of experimental vaccines, particularly oriented to the development of edible vaccines. Hence, this technology becomes highly suitable to express immunogenic proteins from pathogens. The government and responsibilities, the DHHS has responsibility for public health policy, for the support of scientific research and development, for surveillance through the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and for collaboration with international health departments and the World Health Organization (WHO) to create an international strategy. The DHS has the lead in the event of emergency response, as in a national disaster such as a bioterrorist attack. These departments work closely with each other and with correlative departments, such as the Department of Defence, which maintains surveillance canters in several remote areas. The use of transgenic plants for the production of viral and bacterial antigens has been frequently reported. This biotechnological strategy has the enormous advantage of not requiring fermentation control systems under strict conditions of bio-safety, which makes this technology particularly attractive for its simplicity and low cost The evolution pesticide resistance insect and drug resistance microorganisms have many implications for humans. Pesticides are there to reduce the number of pests but many insects have become built up a resistance to certain toxics. Rats have become more resistant that they can consume five times of poison before they die. It's a huge problem, but the pests are only following the rules of evolution: the best-adapted survive. Every time chemicals are sprayed on a lawn to kill weeds or ants for example, a few naturally resistant members of the targeted population survive and create a new generation of pests that are poison-resistant. That generation breeds another more-resistant generation; eventually, the pesticide may be rendered ineffective or even kill other wildlife or the very grass it was designed to protect. Bibliography http://www.nature.com/icb/journal/v83/n3/full/icb200531a.html http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vac-gen/howvpd.htm http://creation.com/does-the-acquisition-of-antibiotic-and-pesticide-resistanceprovide-evidence-for-evolution 2) Vaccination How does vaccination control disease? What are the responses of governments and other organisations to the threat of new strains of influenza each year? Describe the new microbiological and plant based alternatives to vaccines Why does the evolution of pesticide resistance in insects and drug resistance in microorganisms have implications for humans?