Ch. 5 - The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
advertisement

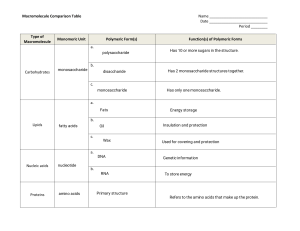
Campbell Chapter 5 - The Structure and Function of Macromolecules 1. Outline the difference between dehydration and hydrolysis reactions 2. How are both reactions important to many biological molecules? 3. To what do the terms monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide refer? What do all three have in common? 4. State the general molecular formula for a monosaccharide. 5. Write the straight chain and ring structural formulas for alpha glucose and number the carbons. 6. List the important differences between amylose, amylopectin, and glycogen. Where would each be found? 7. Compare the primary structure of amylose with that of cellulose. How do they differ in their secondary structure (glycosidic linkages)? What are the dietary implications of the difference? 8. What is it that makes cellulose strong? 9. Name the components needed to build a triglyceride. 10. What reaction is used to join the components? 11. What feature of the composition of a triglyceride makes it hydrophobic? 12. Distinguish between an oil and a fat and between a saturated fat, an unsaturated fat, and a polyunsaturated fat. Where are saturated fats more common? unsaturated fats? 13. Describe the general structure of phospholipids, and explain their arrangement into membranes. 14. Why are phospholipids amphipathic? 15. List the special uses of steroids. How do steroids differ structurally from other lipids? 16. What are six significant uses for protein? State some examples. 17. Carefully define the term protein. How is a protein different from a polypeptide? 18. What do all amino acids have in common? How do they differ? 19. Amino acids are grouped into three general categories. What are they? 20. What is the process which links two amino acids together? Describe the reaction. 21. Describe the four levels of organization possible in a protein, and explain what forces are involved at each level. What must a protein have in order to have a quaternary structure? Adapted From: KVHS Biology - Kevin Gallant Rothesay, N.B. 22. What is denaturation? How or when may it occur? What does a protein lose when it becomes denatured? 23. Identify, with a drawing, the three monomers found in a nucleotide. 24. What is the difference between a purine and a pyrimidine? 25. How are purines and pyrimidines linked in a double helix? Which ones attach to which? Adapted From: KVHS Biology - Kevin Gallant Rothesay, N.B.