155: 411 Introduction to Biochemical Engineering Web page: sakai
advertisement

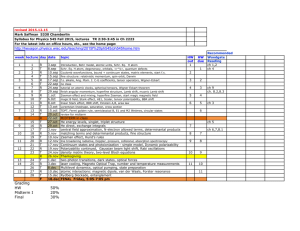
155: 411 Introduction to Biochemical Engineering Web page: sakai.rutgers.edu Lectures: Monday & Wednesday 3:20–4:40 pm, BME 128 Instructor: Ioannis (Yannis) P. Androulakis BME 212 Busch Campus tel: (732) 445-4500 x6212, email: yannis@rci.rutgers.edu Office hours: Open door policy Teaching Assistant: Christopher Papamitrou, tel: (732) 445-5723 email: chrispap@eden.rutgers.edu Course Description: The purpose of this course is to introduce the fundamental principles of biochemical engineering and present a wide spectrum of potential technological applications. Course Objective: Present to the students the fundamentals of biochemical and bioprocess engineering. Discuss recent advances in biotechnology. Discuss technological implications of biochemical engineering in energy and life sciences Textbook (required): Bioprocess Engineering: Basic Concept by M.L. Schuler and F. Kargi, second edition, Prentice Hall, 2002. Class Participation: Students are encouraged to participate in class. Occasional quizzes will also be given. Assessment: Homework assignments: 10%, Two exams: 60%, Two literature review projects: 30% (Engineering micro-organisms for energy production and Treating humans like reactors) Course Content: Week 1 Date Sep. 3 Topic Introduction – Assessment Book Chapter 1-2 2 Sep. 8-10 Enzyme and Enzyme Kinetics 3 3 Sep. 15-17 Enzyme and Enzyme Kinetics 3 4 Sep. 22 How Cells Work 4 Sep. 24 Metabolism 5 5 Sep. 29-Oct. 1 How Cells Grow 6 6 Oct. 6 Oct. 8 Stoichiometry and Product Formation How Cellular information is Altered 7 8 1 6 Oct. 13 Oct. 15 Project #1 Discussion Review 7 Oct. 20 Oct. 22 Exam 1 Special Topics Lecture Notes 8 Oct. 27-29 Special Topics Lecture Notes 9 Nov. 3-5 Special Topics Lecture Notes 10 Nov. 10-12 Special Topics Lecture Notes 11 Nov. 17-19 Nov. 26 No Class – AIChE Conference Happy Thanksgiving! 12 Dec. 1 Dec. 3 Project #2 Discussion Review 13 Dec. 8 Exam 2 Have a great Winter Break! Special topics will be covered by lecture notes and reading material to be distributed in class. 2 ABET Outcomes and Assessment: Program outcomes achieved in this course (a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering; (c) an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs; (e) an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems; and (k) an ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice. The achievement of outcomes (a), (c), (e), and (k) will be assessed in this course as follows: Outcome (a): an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering (1) Assessment test: 1st day of class – same test at the time of the second exam (after the basics have been revisited). The assessment test contains two sections (a) background material; (b) general questions pertaining to the material covered in class. The point of the assessment test is to verify that students improve their understanding by demonstrating that they master the new material, and also that the students made up deficiencies that were identified related to background material (2) Exams – Homeworks : Most of the problems test the ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering in problem solving Outcome (c): an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs Homework problems and course project are designed in an integrative manner that challenges the students to understand the basic elements of synthetic thinking. In particular, the course projects target specific technological questions and requires the students to identify specific design requirements. Outcome (e): an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems Course projects: Course projects are formulated such that the students develop a critical thinking and the ability to synthesize material from diverse sources targeted towards a specific technological question. Outcome (k): an ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice Homework assignments require the use of modeling tools, such as Matlab, as well as preparation of high quality reports 3