Vitamin Flash Cards.indd
advertisement

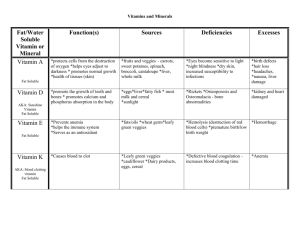
Vitamin Vitamin Vitamin Vitamin A D E K Fat Soluble Fat Soluble Fat Soluble Fat Soluble Vitamin Vitamin Vitamin Vitamin B1 B2 B3 B6 Thiamin Water Soluble Riboflavin Water Soluble Niacin Water Soluble Water Soluble Biotin & Vitamin Pantothenic C Acid Vitamin B12 Folate Calcium Chloride Phosphorus Potassium & Sulphur Water Soluble Major Mineral Water Soluble Water Soluble Major Mineral Water Soluble Major Mineral Major Mineral Sodium Major Mineral Iodine Iron Zinc Trace Mineral Trace Mineral Trace Mineral Function: K stands for “Klot” (clot), helps blood to clot, aids in bone formation Precursor: Intestinal bacteria Source: dark, leafy vegs., cabbage family Function: Antioxidant aka: tocopherol (so is Vitamin C) Protects cell membranes, nerve development, & WBC’s Source: Vegetable oils Function: Converts AA’s to needed cells; regulates glucose, critical to CNS in fetus Deficiency: dermatitis, anemia, heart disease Source: Potatoes, veggies, liver, bananas Function: All cells use for energy release from fats, carbs, and AA’s, made from AA tryptophan Defieciency: Pellagra Toxicity: Liver damage, ulcers, vision loss. Source: White meats: chicken, tuna, pork; cereal, potatoes Function: aka ascorbic acid; antioxidant, enhances immune response, promotes collagen. Deficiency: Scurvy Sources: citrus fruits, veggies, fruits 60mg/day is normal Function: All cells use for energy release from fats, carbs, important coenzymes Source: widespread in foods Function: principle positive Function: 2nd most abunion found inside cells, major dant mineral in body; role in fluid & electrolyte bal- 85% found combined with ance, critical for maintenance calcium. Provides buffers of heart beat. for ph balance, part of DNA Dehydration leads to & RNA of new cells, & potassium loss, energy metabolism. may cause death. Source: protein Source: found in all fresh foods (lost in processing). Function: Does it All: Assists enzymes in all cells, makes heme, disposes of free radicals, makes part of cells genetic material, affects behavior and learning, assists immune function and wound healing, & MORE! Source: meat, shellfish, poultry, grains, legumes. Function: Every living cell (plant & animal) contains iron. Part of two proteins: hemoglobin and myoglobin, essential in blood production, helps deliver ox. to tissues. Deficiency: anemia Source: green leafy veggies, clams, enriched cereal, tofu, beef Function: Bone integrity, functions as hormone, Precursor: The Sun! & cholesterol Deficiency: Rickets, osteomalacia -Most toxic of all vitaminsSource: The Sun! & Milk products Function: Vision, immunity Precursor: Beta Carotene AKA: Retinol Deficiency: Blindness, night blindness Toxicity: Very dangerous Function: All cells use for energy release from fats, carbs, very similar to Thiamin Source: mostly from milk and milk by products, leafy veggies, whole grain breads, a little from meat Function: All cells use for energy release from fats, carbs. Also benefits nerve cells and muscle tissue Deficiency: Beri-Beri, Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome Source: grains, meats, veggies, fruits Function: aka: folacin, folic acid. Required to make all new cells; synthesizes DNA Deficiencies: neural tube defects during childbearing years, anemia Source: “Foliage”, green, leafy veggies, liver, legumes. Function: Helps folate make RBC’s, sheath for nerve fibers, needs “intrinsic factor” from the gut for absorption Source: Only from animals, may be stored up to 5 years. Function: Chloride: essential to acid-base balance, part of stomach acid: hydrochloric acid, source: salt (sodium chloride). Body’s major negative ion in & outside of cells. Function: Most abundant mineral, 99% in bones, combines with phosphorus to form bones: “calcium phosphate”. Bone will release calcium into blood when needed. Source: milk & byproducts, broccoli, sardines Deficiency: osteoporosis Sulphur: helps protein to assume shape Function: Part of thyroxine, helps regulate basal metabolic rate. Deficiency: Goiter. In pregnant women: Cretinism (severe retardation) Source: iodized salt, seafood Function: Chief ion used to maintain fluid balance outside of cells, maintains ph balance, muscle contractions, and nerve transmission. Shaker only accounts for 15% of our salt intake; the rest is found in processed foods. Magnesium Major Mineral Copper Trace Mineral Selennium Fluoride Chromium Trace Mineral Water Trace Mineral Electrolytes Trace Mineral