Welcome to AP Biology! We have a great deal of material to cover
advertisement

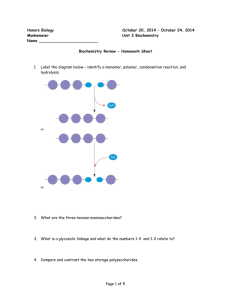
Welcome to AP Biology! We have a great deal of material to cover before the AP Exam beginning with Biochemistry. Your summer assignment is to read Chapters 3, 4, 5, 41 and 42 from your textbook Biology 7th edition, by Campbell and Reece. There are guided reading questions to be completed for chapters 3, 5, 41 and 42. In addition, you will complete a free response (an essay) on the chemical properties of water. The requirements are listed below: 1) Read each of the assigned chapters 2) After reading, complete the self quiz at the end of each chapter. You will turn in your answers to the self quiz questions. Then, answer the guided reading questions for each chapter. Please note – there are no guided reading questions for chapter 4. 3) Complete the free response (essay) on the chemical properties of water (attached). You will need to do independent research to complete this portion of the assignment. Be sure to write this response IN YOUR OWN WORDS! Plagiarized essays will not be graded. This assignment is due on the first day of class. If you have any questions about the assignment, contact me at tamara.averell@dma.k12.de.us or 302 563-0441 Chapter 3 Guided Reading Assignment This chapter is a review from your previous biology class – these concepts are critical and repeated throughout the year. If you have not covered this material previously or need additional assistance with the concepts please schedule time to see me. 1. Why is water considered a polar molecule? 2. For each of the below listed properties of water – briefly define the property and then explain how water’s polar nature and polar covalent bonds contribute to the water special property. Include an example in nature of each property also. a. Cohesion b. Adhesion c. Surface tension d. High specific heat e. Heat of vaporization f. Evaporative cooling 3. What is special about water and density? 4. Define the following terms: a. Solute b. Solvent c. Aqueous solution d. Hydrophilic e. Hydrophobic f. Colloid g. Hydration shell h. Molarity 5. Label the diagram below to demonstrate the dissociation of the water molecule and then relate this diagram to pH. 6. What defines an acid and a base? 7. Why are “apparently” small changes in pH so important in biology? 8. What is a buffer and write and explain the carbonic acid buffer system in human blood – yes we are back to the equation AGAIN! 9. What is acid precipitation and why is it important to living organisms? Chapter 5 Guided Reading Assignment 1. Label the diagram below – identify a monomer, polymer, condensation reaction, and hydrolysis. 2. What are the three hexose monosaccharides? 3. What is a glycosidic linkage and what do the numbers 1-4 and 1-2 relate to? 4. Compare and contrast the two storage polysaccharides. 5. Compare and contrast the two structural polysaccharides. 6. Why are lipids grouped together? 7. What are the building blocks of fats? 8. Contrast saturated and unsaturated fats – how does this relate to the concept that structure and function are linked? 9. Label the molecule below. 10. How would you recognize a basic steroid molecule? 11. List the eight types of proteins and their basic function. 12. What are the names for the monomers and polymers of proteins? 13. Label the diagram below concerning the catalytic cycle of an enzyme - 14. Draw two amino acids – note the amino group, the carboxyl group and the alpha carbon, circle the water molecule to be removed and then note the peptide bond formed when the two are joined. 15. Explain the four levels of protein structure – a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Quaternary 16. How does the characteristics of an amino acid – nonpolar, polar, acidic or basic relate to the issue of tertiary and quaternary structure? 17. What does denaturation mean and why is it important? 18. What are chaperonins and what is their role in protein structure? 19. Describe the technique of x-ray crystallography. 20. What are the roles of nucleic acids? 21. Label the blank diagram below: 22. What is meant by the term that DNA is antiparallel? AP Biology Free Response HW Chapter 5 The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. 1. Compare and contrast the four protein structural configurations – primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. 2. Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins. For each type, describe its role in determining protein structure. You may include diagrams WITH your explanations. Guided Reading Chapter 41 1. Define the following types of feeding mechanisms: a. Suspension b. Substrate c. Fluid d. Bulk 2. Complete the diagram below concerning animal homeostasis and blood sugar regulation. 3. How do hormones regulate appetite in humans? 4. Contrast the terms undernourished, overnourished and malnourished? 5. What are essential amino acids and essential fatty acids? 6. Contrast vitamins and minerals. 7. Define the following terms: a. Ingestion b. Digestion c. Enzymatic hydrolysis d. Absorption e. Elimination 8. Contrast intracellular and extracellular digestion. 9. Label the diagram below of the human digestive system. 10. What are the accessory glands of the digestive system and why are they call “accessory” – are they part of the digestive tract? 11. What is peristalsis? 12. Use the diagram below to label and explain the process of swallowing. 13. What are the three cell types of the gastric glands and what does each of them secrete? 14. Why is it an advantage that pepsin is secreted in its inactive form? 15. Describe the first part of the small intestine – what activity is occurring here? 16. What is bile – is it’s action mechanical or chemical digestion? 17. Complete the chart below – use it as a study guide for the process of enzymatic digestion and the respective enzymes. 18. Explain the roles of the hormones listed below on digestive activity – note whether each are a case of stimulation or inhibition. Why is this level of control an advantage to the organism? a. Enterogastrone b. Gastrin c. Secretin d. Cholecystokinin 19. How does the body control the absorption of nutrients in the small intestine? 20. What is the route for fat absorption? Include the term chylomicrons and the role of bile. 21. What role does the liver play in homeostasis with regard to digestion? 22. What is the major role of the large intestine in the digestive process? 23. Does the appendix have a role in the human body? 24. How can you infer an organism’s diet based on it’s teeth? 25. What general trends are noted in the digestive tracts of herbivores and carnivores? 26. What is different about the ruminant’s digestive system that adapts it to eating a diet of “cellulose”? 27. How do symbiotic interactions impact digestion? Chapter 42 Guided Reading 1. What are the limits to diffusion as a means of transport for living organisms? 2. Compare and contrast open and closed circulatory systems. Be certain focus on advantages of each. 3. Contrast arteries, arterioles, capillaries and venules and veins, 4. Contrast the vertebrate circulatory systems of fish, amphibians, non-avian reptiles and mammals/birds. 5. What is the advantage to double circulation? 6. Write the path of blood through the heart.