Weather and Air Pressure
advertisement

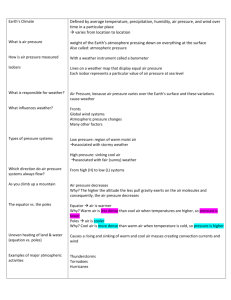
Name _________________________________________ Teacher ___________________________ Weather and Air Pressure Which heats up faster- land or water? Air Pressure The land and water both absorb heat from the Sun, but land heats up much more quickly. That's why your toes stay cool when you walk on grass, but burn on the sidewalk on a hot day! Even though it is invisible, air has mass. Gravity pulls air toward Earth's center, just like us. Air pressure is the weight of air pressing on everything around it. Air presses equally in all directions—up, down, and sideways, not just down on them. Large bodies of water can absorb a lot of heat without changing temperature very much. Ocean temperatures stay fairly constant from day to night and °C from season to season. Rock absorbs heat easily. Its temperature goes up quickly on sunny days and cools off quickly at night. Warm air rises and cold air falls toward Earth’s surface. This creates convection currents in the air that are called winds. Uneven heating of the land and water create temperature differences that make air move. Warm air rises This means that air pressure is greatest near Earth’s surface at sea level and gets lower as you go up in the atmosphere. °C °F 40 100 40 30 30 80 20 20 60 10 0 °F 50 120 50 10 40 0 100 80 60 40 HOT Water Rock & Soil Greatest air pressure The density of air molecules is greatest near Earth’s surface at sea level. Air density gets lower as you go up in the atmosphere. Cool air falls Wind HOT LAND Less air pressure 120 COOL CONVECTION Meteorologists use barometers to measure air pressure. Lower in the atmosphere Higher in the atmosphere or or Colder air near the surface Warmer air near the surface COOL OCEAN Higher density Cold air is more dense than warm air. Air always flows from high pressure areas (denser air) toward areas of lower pressure. This creates winds. Pre s s u re Low High Pressure Air Mass Pressu re Low The same process also happens on a global scale. The equator gets the most direct sunlight, so warm air rises over the equator. Sunlight hits the poles at an angle, so they are cold. Air cools and sinks at the poles. Warm air can hold a lot of water vapor. Air that rises from the carries heat and water vapor to the cooler poles. This helps even out the Earth's temperature. The source of energy for all weather is the Sun, which heats air and water unevenly. re Low P s s u re When the land is hot and the sea is cool, wind blows toward the land. This makes a sea breeze. At night the land cools off, but the sea temperature stays the same. The wind will blow toward the sea, making a land breeze. Lower density GRADE SHOW WHAT YOU KNOW! Weather and Air Pressure 5 DIRECTIONS: Answer these questions without looking at the front page. Check your answers using the key. If any of your answers are incorrect, go back and reread the information about this topic before you take the test again. 1 The diagram below shows a landscape 4 Upper atmosphere Above a continent, a warm air mass slowly passes over a cold air mass. As the warm air begins to cool, clouds form. What will most likely happen next? A Rain will fall. B Hurricanes will form. C Lightning will strike. D Hail will form. 5 Which location on Earth receives the most direct sunlight? A the deserts B Ocean C the equator Where in the diagram would the air pressure be the greatest? A at the beach B on top of the mountain D the Western Hemisphere 6 C at the bottom of the clouds D above Earth’s atmosphere 2 B C water D hailing 7 D metal 3 B pressure from gamma rays hitting the lower atmosphere Polar regions are cold because _. A the Sun's rays reach the poles at a large angle B the Sun's rays fall more directly at the poles C the Sun's rays hit the poles indirectly Air pressure is the result of _. A the weight of the lowest layer of the atmosphere sunny C snowing A rock soil A city has a temperature of 75 °F, with partly cloudy skies. Weather forecasters are predicting that the air pressure and temperature will drop during the day. Which type of weather is most likely for this area in the late afternoon? A rainy Which material is able to absorb a large amount of heat energy without a large increase in temperature? B the South Pole D Both A and C are true. 8 A student wants to measure air pressure. What kind of instrument should he use? C the weight of a column of air pressing down on an area A Hygrometer D All the statements are true C Barometer B Anemometer D Pressurometer 9 The picture below shows a place where air currents will form due to the uneven heating of Earth. 13 Which location has the lowest air pressure? A A B B C C D D A B C D 14 In which direction will air currents most likely move? A straight down over the land B from the land toward the sea C straight up above the sea D from the sea toward the land 10 15 The equator has a hot climate because _. A the Sun's rays reach the equator at a large angle 16 B The molecules in air push in all directions, so the pressure from above is balanced by pressure from the sides and pushing up from below. C Air pressure is repulsed by the magnetic field within your body. D Air pressure is higher near the Earth surface. C D D A student wants to find out whether water will get hotter in the sun than in shade. What kind of instrument should she use? Energy from the Sun heats Earth unevenly, causing _. B air movements that result in changing weather patterns. D the layer of gases that surrounds Earth. A You have the skeleton of a super hero. C A global warming. C the layer of water in the oceans. The column of air above your head and shoulders weighs about as much as a car. Why doesn't the air pressure crush you? B D Thermometer B the layer that contains orbiting space craft. 12 B C Barometer D the Earth has more volcanoes near the equator A the layer in which lithification occurs. A B Anemometer C the Sun's rays hit the equator indirectly The atmosphere is _. A A Hygrometer B the Sun's rays fall more directly at the equator 11 In the diagram above, location has the lowest density of air molecules? C a lack of air movements D the tilt of the Earth's axis 17 What causes convection currents in the Earth's atmosphere? A Uneven heating of the Earth. B air movements that result in changing weather patterns. C a lack of air movements D the tilt of the Earth's axis Warmer air Warmer air Cooler air Cooler air Diagram X Diagram Y 18 Which of the diagrams above shows formation of a sea breeze? A Diagram X. B Diagram Y. C Both diagrams show sea breezes. D Neither diagram shows a sea breeze. 19 Most differences in air pressure are caused by _. A unequal heating of the atmosphere B equal heating of the atmosphere C unequal radiation of the atmosphere D equal tropospheric discombobulations 20 A Which of the diagrams below correctly show how convection currents move in an unevenly heated liquid? A A B B C C D D B C D