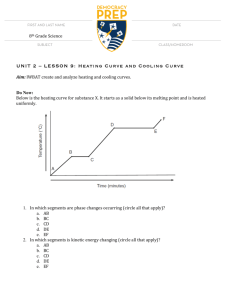
Heating curve for Ethanol
advertisement

Temperature, heat, and phases Physical science Period: Name: Date: AVERAGE kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in a substance. How does the internal energy of 0°C water compare to 0°C ice? How do you know? Because melting is an endothermic process, the ice had to take in energy to become a liquid (partially break bonds of attraction) and thus 0°C water has more internal energy than 0°C ice 1. What is temperature related to (don’t say how hot something is): 2. 3. Which has the greater the average kinetic energy of the molecules, 0°C liquid water, or 0°C ice? How do you Since temperature is related to the average kinetic energy of the particles, and they have the same temperature, they must have the same average kinetic energy. know? 4. Which has the greater the average potential energy of the molecules, 0°C liquid water, or 0°C ice? How do Since water has more internal energy, but the kinetic energy is the same between the particles, the potential energy must be greater. Why can water boil at a lower temperature when the atmospheric pressure is lower? Boiling occurs when the vapor pressure in a fluid matches the atmospheric pressure outside the fluid, if the atmospheric pressure is reduced, the vapor pressure can be lower, meaning the fluid will start boiling at a lower temperature you know? 5. Below is the heating curve for ethanol, use this to answer questions 6-10 Heating curve for Ethanol 200 Temperature (degrees C) 150 vaporization 100 gas 50 0 -50 0 -100 -150 -200 -250 200 liquid 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 melting solid Heat absorbed by 1 g of Ethanol (J) 6. List the following at the appropriate places on the graph: solid, liquid, gas, melting, vaporization -105 to -125 (-114.3°C) What is the approximate boiling point of ethanol? 65 to 85 (78.4°C) What state of matter is the ethanol in at: -150°C solid -100°C liquid 0°C liquid 50°C liquid 100°C gas 7. What is the approximate melting point of ethanol? 8. 9. 10. Which takes more energy, converting 1 g of ethanol from solid to liquid, or from liquid to gas? Why is that? It takes more energy to change 1 g of ethanol from a liquid to a gas than it does to change it from a solid to a liquid, because going from a solid to a liquid, the molecules are still in contact, so the attractive forces are still present, whereas in going from a liquid to a gas, the attractive forces of molecules have to be completely overcome, requiring much more energy. The following is a temperature vs. time graph for a substance that was a solid, was heated, and then the heat was removed. Temperature (degrees C) Temperature vs. Time 55 50 45 40 35 30 0 100 200 300 400 Time (s) 500 600 If possible write the period(s) of time (e.g. 175 – 225s and 350 – 600s) where each of the following occur, if it doesn’t occur on the graph write “NA” for not applicable. 0 – 50s and 450-600s b. Substance is a liquid: 150s -300s (150s to 200s and 200s-300s) c. Substance is a gas: N/A d. Substance is melting: 50s – 150s e. Substance is vaporizing: N/A f. Substance is condensing: N/A g. Substance is freezing: 300s – 450s 11. At what time was the burner removed? 200s What state of matter is the substance in at that point? Liquid a. Substance is a solid: 12. If possible list the following temperatures, if it can’t be determined, write “can’t determine” a. Melting point b. Boiling point c. Condensation point: d. Freezing point: 43°C can’t determine can’t determine 43°C