Enzyme-Controlled Reactions Virtual Lab
advertisement

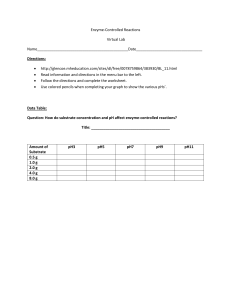
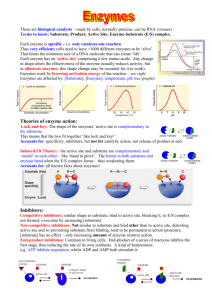
Enzyme-Controlled Reactions Virtual Lab http://novella.mhhe.com/sites/dl/free/0078695104/383930/BL_11.html Background Information Describe the function of enzymes. List 5 enzymes found in the human body, where they are found specifically, and describe the reaction they catalyze. Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to investigate how pH, temperature, and substrate concentration effect enzyme-controlled activity. Part A: The Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme-controlled Reactions Directions and Procedure 1. Follow the directions on the side bar menu. 2. Do 1 to 2 different trials….changing concentration on the enzyme. If access to a printer, click on the table that is on your virtual lab computer. Record your data in the charts and graphs. If not, record and draw by hand. Part B: The Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme-controlled Reactions 1. Follow the directions on the side bar menu. 2. Do 1 to 2 different trials….changing pH or changing both concentration and pH. If access to a printer, click on the table that is on your virtual lab computer. Record your data in the charts and graphs. If not, record and draw by hand. Part C: The Effect of Temperature on Enzyme-controlled Reactions Directions and Procedure Read and interpret the following graphs showing the general rate of enzymatic activity at different temperatures. 1. Describe the pattern of the graphs. 2. Explain the changes to the rate of reaction as temperature increases. 3. How can you tell from the graphs what the optimum (best) conditions are for each variable in this simulation? 4. What temperature is optimal for the rate of photosynthesis? Conclusion Questions 1. Describe the relationship between substrate concentration and the initial reaction rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Is this a linear relationship? What happens to the initial reaction rate as substrate concentration increases? 2. What is the maximum initial reaction rate for this enzyme at pH 7? 3. Explain why the maximum initial reaction rate cannot be reached at low substrate concentrations. 4. What does your data indicate about the optimum pH level for this enzyme-catalyzed reaction? 5. Enzymes function most efficiently at the temperature of a typical cell, which is 37 degrees Celsius. Increases or decreases in temperature can significantly lower the reaction rate. What does this suggest about the importance of temperature-regulating mechanisms in organisms? Explain.