Managing Human Resources
Training and Development,
Performance Management,
Rewards and Compensation, Health
& safety and Grievance
By
Rajitha Silva MBA (AUS), PG Dip.(UK), BBA (COL)
grpriyankara@gmail.com
The Scope of Training
• Training
– Effort initiated by an organization to foster
learning among its members.
– Tends to be narrowly focused and oriented toward
short-term performance concerns.
• Development
– Effort that is oriented more toward broadening an
individual’s skills for the future responsibilities.
Systems Model of Training
Phase 1: Conducting the Needs
Assessment
• Organization Analysis
– An examination of the environment, strategies, and
resources of the organization to determine where
training emphasis should be placed.
• Task Analysis
– The process of determining what the content of a
training program should be on the basis of a study of
the tasks and duties involved in the job.
• Person Analysis
– A determination of the specific individuals who need
training.
Phase 2: Designing the Training
Program
• Instructional Objectives
– Represent the desired outcomes of a training
program
• Performance-centered objectives
– Provide a basis for choosing methods
and materials and for selecting
the means for assessing
whether the instruction
will be successful.
Principles of Learning
Phase 3: Implementing the Training
Program
Choosing the instructional method
Nature of training
Type of trainees
Organizational extent of training
Importance of training outcomes
Training Methods for Nonmanagerial Employees
• On-the-Job Training (OJT)
• Apprenticeship Training
• Cooperative Training,
Internships, and Governmental
Training
• Classroom Instruction
• Programmed Instruction
• Audiovisual Methods
• Computer-based Training and ELearning
• Simulation Method
Training Methods for Management
Development
•
•
•
•
•
•
On-the-Job Experiences
Seminars and Conferences
Case Studies
Management Games
Role Playing
Behavior Modeling
On-the-Job Experiences
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Coaching
Understudy Assignment
Job Rotation
Lateral Transfer
Special Projects
Action Learning
Staff Meetings
Planned Career
Progressions
Behavior Modeling
• Behavior Modeling
– An approach that demonstrates desired behavior
and gives trainees the chance to practice and roleplay those behaviors and receive feedback.
– Involves four basic components:
• Learning points
• Model
• Practice and role play
• Feedback and reinforcement
Phase 4: Evaluating the Training
Program
Measuring program effectiveness
Criterion 1: Trainee reactions
Criterion 2: Extent of learning
Criterion 3: Learning transfer to job
Criterion 4: Results assessment
Criteria for Evaluating Training
Deming’s Benchmarking Model
1. Plan: conduct a self-audit to identify areas for
benchmarking.
2. Do: collect data about activities.
3. Check: Analyze data.
4. Act: Establish goals, implement changes,
monitor progress, and redefine benchmarks.
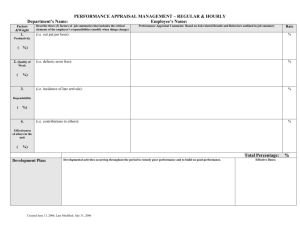
Performance Appraisal Programs
• Performance Appraisal
– A process, typically performed annually by a
supervisor for a subordinate, designed to help
employees understand their roles, objectives,
expectations, and performance success.
• Performance management
– The process of creating a work environment in
which people can perform to the best of their
abilities.
Performance Appraisal
Appraisal Programs
Administrative
Developmental
Compensation
Ind. Evaluation
Job Evaluation
Training
EEO/AA Support
Career Planning
Reasons Appraisal Programs
Sometimes Fail
• Lack of top-management
information and support
• Unclear performance standards
• Rater bias
• Too many forms to complete
• Use of the appraisal program for
conflicting (political) purposes.
Performance Standards
Characteristics
Strategic
Relevance
Individual standards directly relate
to strategic goals.
Criterion
Deficiency
Standards capture all of an
individual’s contributions.
Criterion
Contamination
Performance capability is not
reduced by external factors.
Reliability
(Consistency)
Standards are quantifiable,
measurable, and stable.
Alternative Sources of Appraisal
360-Degree Performance Appraisal
System Integrity Safeguards
•
•
•
•
•
Assure anonymity.
Make respondents accountable.
Prevent “gaming” of the system.
Use statistical procedures.
Identify and quantify biases.
Training Performance Appraisers
Common rater-related errors
Error of central tendency
Leniency or strictness errors
Similar-to-me errors
Recency errors
Contrast and halo errors
Rater Errors
• Error of Central Tendency
– A rating error in which all employees are rated about
average.
• Leniency or Strictness Error
– A rating error in which the appraiser tends to give all
employees either unusually high or unusually low
ratings.
• Recency Error
– A rating error in which appraisal is based largely on an
employee’s most recent behavior rather than on
behavior throughout the appraisal period.
Rater Errors
• Contrast Error
– A rating error in which an employee’s evaluation is
biased either upward or downward because of
comparison with another employee just
previously evaluated.
• Similar-to-Me Error
– An error in which an appraiser inflates the
evaluation of an employee because of a mutual
personal connection.
Performance Appraisal Methods
Graphic Rating
Scale
Trait
Methods
Mixed Standard
Scale
Forced-Choice
Essay
Trait Methods
• Graphic Rating-Scale Method
– A trait approach to performance appraisal
whereby each employee is rated according to a
scale of individual characteristics.
• Mixed-Standard Scale Method
– An approach to performance appraisal similar to
other scale methods but based on comparison
with (better than, equal to, or worse than) a
standard.
Highlights in HRM 2
Graphic Rating
Scale with
Provision for
Comments
Trait Methods
• Forced-Choice Method
– Requires the rater to choose from statements
designed to distinguish between successful and
unsuccessful performance.
– 1. ______ a) Works hard
_____ b) Works quickly
– 2. ______ a) Shows initiative
_____ b) Is responsive to customers
– 3. ______ a) Produces poor quality _____ b) Lacks good work habits
• Essay Method
– Requires the rater to compose a statement
describing employee behavior.
Behavioral Methods
Critical Incident
Behavioral Checklist
Behavioral
Methods
Behaviorally Anchored Rating
Scale (BARS)
Behavior Observation Scale
(BOS)
Behavioral Methods
• Critical Incident Method
– Critical incident
• An unusual event that denotes superior or inferior employee
performance in some part of the job
– The manager keeps a log or diary for each employee
throughout the appraisal period and notes specific
critical incidents related to how well they perform.
• Behavioral Checklist Method
– The rater checks statements on a list that the rater
believes are characteristic of the employee’s
performance or behavior.
Behavioral Methods
• Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scale (BARS)
– Consists of a series of vertical scales, one for each
dimension of job performance; typically developed by
a committee that includes both subordinates and
managers.
• Behavior Observation Scale (BOS)
– A performance appraisal that measures the frequency
of observed behavior (critical incidents).
– Preferred over BARS for maintaining objectivity,
distinguishing good performers from poor performers,
providing feedback, and identifying training needs.
© 2007 Thomson/SouthWestern. All rights reserved.
8–30
Results Methods
• Productivity Measures
– Appraisals based on quantitative measures (e.g., sales
volume) that directly link what employees accomplish
to results beneficial to the organization.
• Criterion contamination
• Focus on short-term results
• Management by Objectives (MBO)
– A philosophy of management that rates performance
on the basis of employee achievement of goals set by
mutual agreement of employee and manager.
The Balanced Scorecard
• The appraisal focuses on four related categories
– Financial, customer, processes, and learning
• Ensuring the method’s success
Translate strategy into a scorecard of clear objectives.
Attach measures to each objective.
Cascade scorecards to the front line.
Provide performance feedback based on measures.
Empower employees to make performance
improvements.
Reassess strategy.
Definition-Compensation/ Reward
“Salary or wage is a form of compensation
paid to an employee for the contribution
made by him through the process of offering
his service to the organization’.
33
Compensation
This refers to all form of financial returns, tangible
services & benefits employee receives as a part of an
employment relationship. It covers
• Internal equity – Within the organization
• External equity – Within the industry
• Individual equity – Unique individual
commitments
34
Definition – Reward/Incentive
“An incentive scheme is a plan or program to
motivate individual or group performance. An
incentive program is also frequently built on
monitory rewards (Incentive pay or monitory
bonus), but may also include a variety of non
monitory rewards or prizes”.
35
Reward Management Alignment
Organizational
Values &
anticipated
business outcome
Market Situation
Organizational
Rewarding Policy
36
“7 Criteria” for effectiveness in
Compensation
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Adequate
Equitable – For efforts
Balance – Reasonable
Cost effective
Incentive providing
Acceptable to employees
Secure or stable
37
Basic objectives of Sound Reward System
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Attract competent employees
Retain employees
Motivate employees
Inspiring employees
Job satisfaction
Rewarding employees
Industrial relation
38
Job Evaluation - Definition
“Job evaluation is a process of systematic
determination of the relative worth of a
specific job within a plant or the organization”.
39
Model of Total Reward
(Towers Perrin Model)
PAY
BENEFITS
* Base pay
* Pensions
* Contingent Pay
* Holidays
* Cash Bonus
* Healthcare
* long-term incentives
* Other perks
* Shares
* Flexibility
* Profit Sharing
LEARNING &
DEVELOPMENT
* Work Place Learning and
Development
* Training
* Performance Management
* Career Development
WORK ENVIRONMENT
* Core Values of the Organization
* Leadership
* Employee voice
* Recognition
* Achievement
* Job Design and Role Development
* Quality of working life
* Work-Life Balance
* Talent Management
40
Employee Benefits
Statutory Benefits
◦ Unemployment ( ETF)
◦ Workers' compensation ( Compensation Formula)
◦ Social Security ( EPF)
◦ Disability (occupational) (Workmen Compensation Act)
Company Benefits
◦ Medical
◦ Savings
◦ Allowances
Pay for Time Not Worked -- These programs are designed to protect
the employee's income flow when not actively engaged at work.
Away from work (vacation, company holidays, personal days).
41
Types of Incentive Plan
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Measured day work
Piece work
Standard hour plan
Gain sharing plan
Group incentive plan
Employee stock ownership
Profit sharing plan
42
Regulations of Compensation
Wages boards Ordinance
Shop and Office Employees’ Act
Maternity Benefits ordinance
Employees’ Provident Fund Act
Workman’s Compensation Ordinance
Termination of Employment ( Special
provisions)
43
Health and Safety
• Health
A state where physical and mental
problems, which impair general & special
activities of a n employee.
• Safety
Protection of employees’ physical health
from the danger of accident.
Occupational Hazards
•
•
•
•
•
“Hazard is the potential for harm”.
Health Hazard
Physical (Noise , Vibration , heat , Radiation ,poor
lighting , Poor Ventilation )
Chemical ( Dust ,Fumes , Gases , Poison , Toxic )
Biological (Bacteria, Fungus , insects )
Psychological (Boredom, Monotony , Frustration
, Stress )
Occupational Hazards
• Safety Hazard
–
–
–
–
Electricity
Fire
Chemical
Uncovered machinery
• Occupational diseases
–
–
–
–
–
–
Skin diseases
Lung diseases
Respiratory diseases
Poisoning
Eye fatigue
Asthma
Uses of Health and Safety
To protect employee.
To improve the Productivity.
To Comply with the Country law.
To improve Goodwill.
To Satisfy the Customer / buyers
Requirements.
• To impact on effectiveness.
•
•
•
•
•
Health and Safety Policy
This contains own statement of general policy
on health and safety at work and the
organization and arrangements in place for
putting that policy into practice.
Industrial Accidents
• An unplanned, unexpected event that
interferes with or interrupts normal activity
& potentially leads to personal injury or
equipment damage.
• Near Misses
An undesired event which under slightly
different circumstances could have resulted in
harm to people, environment, damage to
property or loss to process
Unsafe Acts
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Operating without authority
Working on moving machinery
Working on machinery without guards
Working without personnel protective
equipments
Wearing dangling cloths
Horse play
Unsafe lifting carrying, moving and placing
Using hand
Unsafe Condition
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Unguarded machinery
Defective machinery
Inadequately guarded machinery
Bad house keeping
Inadequate illumination
Inadequate ventilation
Heat
Bad design
Relevant Legislations
Factories Ordinance Workman Compensation Ordinance Shop & office employee act Wagers Board ordinance Maternity benefit ordinance Employment of woman & young person and
children • National Institute of Occupational Safety &
Health Act •
•
•
•
•
•
Grievance
“Sense of injustice”
“If there is any discontentment or sense of
injustice, expressed or implied felt by the
employee in connection with his employment
in the organization”.
53
Reasons for grievances
Perception
Communication
Unintentional mistakes
Purposive
discrimination
• Legitimate rational
action
•
•
•
•
Identification of
Grievances
- Employee behavior
- Job outcome
- Industrial Accident Wastage
- Employee
satisfaction
54
Handling Grievances
•
•
•
•
Open door policy
Ombudsman
Inspector general method
Grievance committee
55
Disciplinary Procedure
• Pre-show cause stage (Primary inquiry)- There
should be a complain in written & need to
prepare statements of witnesses
(To check nature of prima-facie)
• Issue of show cause letter & suspension
• Acceptance of letter of explanation
• Disciplinary inquiry
• Action
56
Types of Punishment
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Suspension
Dismissal
Deferments of increment
Stoppage of increment
Suspension of increment
Fine
Demotion
Transfers
Reduction /cancellation of bonus
57
Discussion !!!
Thank you
58