Organisation of the body structures
advertisement

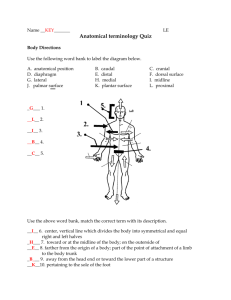
ORGANISATION OF THE BODY STRUCTURES BODY CAVITIES • It is a space within the body that contains internal organs • Group of cells that are identical in their structure and function makes up tissues • Tissues that are different in their structure and function make up an organ • Organs make up an organ system DIVISIONS OF BODY CAVITIES Major body cavities are • Ventral body cavity - one which lies in the front, derived from latin word venter (er –suffix)means – belly • Dorsal body cavity- one which lies behind or back ,derived from latin word dorsum means back (alsuffix) Subdvisions • Ventral body cavity Thoracic cavity Abdominopelvic cavity • Dorsal body cavity Cranial cavity Spinal cavity CAVITIES IN THE BODY • 1. Cranial cavity- contains brain and pituitary gland • 2. Thoracic cavity- contains lungs ,heart, oesophagus, trachea ,bronchial tubes, thymus gland, large arteries Subdivisions of thoracic cavity Pleural cavity – space surrounding lungs lined by a double folded membrane called pleura Mediastinum – central located area between two lungs that contains heart, aorta, trachea , esophagus, thymus ,bronchial tubes .lymph nodes • 3. Abdominal cavity- contains abdominal visceras like stomach, intestines, spleen, pancreas, liver , gall bladder, kidneys (abdomen = abdodere= to hide) • Covered by a double folded membrane called peritoneum except kidneys ( lies behind the peritoneum) • 4. Pelvic cavity- contains portions of intestines, rectum, urinary bladder, urethra, ureters, uterus and vagina in females. • 5. Spinal cavity- contains spinal cord. PLEURA AND PERITONEUM • Diaphragm – is a musculoaponeurotic partition that separates thoracic cavity from abdomino pelvic cavity DIVISIONS OF THE SPINAL COLUMN • It is made up of series of bones called vertebrae extending from neck to tailbone(coccyx) Cervical – 7 – in neck region Thoracic – 12- in thorax Lumbar – 5 – in the groin (hip region) Sacral- 5 – fuses to form bone of lower back Coccygeal- 4- small bones forming the tail bone • Spinal cord is present within the cavity formed by spinal column. • Spaces between each vertebrae has a disc (a pad like structure formed by cartilage) BODY SYSTEMS Group of organs make up a body system. They are Integumentary system- ( latin word - covering )includes skin, nails , hair, sweat and sebaceous glands Digestive system- includes mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach , small and large intestines, liver , gall baldder, pancreas Urinary system- includes kidneys, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra Respiratory system- includes nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tubes, lungs. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Reproductive system- includes ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina mammary glands in females and testes and its duct systems, urethra, penis , prostate in males Endocrine system(hormone secreting) – includes thyroid and parathyroid gland in neck , pituitary gland in cranial cavity, sex glands like ovaries and testes, adrenal glands, pancreas Nervous system- includes brain, spinal cord, nerves. Circulatory system- includes heart and blood vessels (arteries and veins) ,lymph vessels, spleen Musculoskeletal system- includes bones, muscles, joints ENDOCRINE GLANDS NERVOUS SYSTEM AND URINARY SYSTEM RESPIRATORY & CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BODY PLANES What is anatomical postion ? • In this postion person stands erect (standing on his feet) , facing forward, with upper limbs hanging at the side of the trunk and palms of the hand facing forwards. PLANES OF THE BODY Sagittal plane Coronal plane Transverse plane Planes of the body • Frontal ( coronal plane )- is a vertical plane dividing the body into anterior and posterior halves • Sagittal plane – is a vertical plane dividing the body into right and left halves • Transverse plane (cross sectional /axial) – is a horizontal plane dividing the body into upper and lower portions POSITIONAL AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS Anterior – front side of the body • Eg: forehead lies anterior to the body Posterior – back side of the body • Scapula lies posterior to the body Superficial – on the surface • Veins are superficial Deep – away from surface • Eg: kidney lies deep in the abdomen Proximal – towards the midline of the body • Eg: humerus is a proximal bone of the upper limb Distal – away from the midline of the body • eg: radius (bone in forearm) is distal to humerus Superior( cephalic ) – above another structure • Eg : head is superior to neck Inferior (caudal ) – below another structure • Eg : feet is inferior to the body Medial – towards the midline of the body • Eg : little finger is medial to ring finger Lateral – away from the midline of the body • Eg: thumb is lateral to index finger Supine – lying on the back • Eg:position of person while sleeping Prone – lying on the belly • Eg: position of person while sleeping with face downwards