PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEM
advertisement

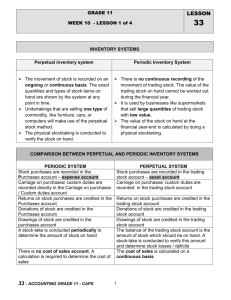
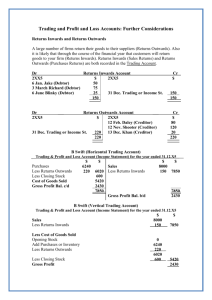
PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEM In the periodic inventory system, there is no continuous recording of the trading stock movements. Cost of Sales is NOT recorded, and the only way to determine stock on hand is by doing a stock take (physical stock count). The following takes place at year-end: 1. Adjustment Given: The value of stock on hand at year end according to the physical stock take is R 500. LEDGER ACCOUNTS FOR PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEM Accounts for: Opening Stock Purchases - General Journal entry: Trading Stock dr. Closing Stock cr. opening balance of stock to record any stock purchased during the year. Donations and drawings of stock are deducted from the purchases account. - 500 General Ledger: Trading Stock Carriage on purchases - carriage that is paid on any stock during the year. Creditors Allowances 500 Closing Stock 500 500 stock that id returned to the supplier during the year. closed off to Purchases at year end, to determine net purchases. 2. Closing Stock - closing balance of stock, on hand at year-end. Trading Stock - only use on 1 day and last day of the financial year, to reflect stock on hand in the balance sheet. Closing Transfers General Journal Entries: st (a) CALCULATIONS The only way of finding the cost of sales figure is to calculate it: Calculation for Cost of Sales ! + + = = J Cansfield Opening Stock Net Purchases (Purchases – Creditors Allowances) Carriage on Purchases Goods available for sale Closing Stock COST OF SALES (b) (c) Trading Account 2400 Opening Stock Purchases (net) Carriage on Purchases 400 1900 100 Sales Closing Stock Trading Account 4600 500 5100 Trading Account Profit and loss (transfer of Gross profit) 2700 2700 Check by: EXAMPLE: Perpetual vs periodic. 1. Draw rough T’s for the transactions if Baker uses the Perpetual inventory system. 2. Draw rough T’s for the transactions if Baker users the Periodic inventory system. 3. Analyse the following transactions of Bakers , under the headings account Debit; account Credit and amount. If Bakers Corner Store uses the periodic inventory system. 1.Calculating Cost of Sales: + + O/S Purchases Carriage = C/S Cost of Sales 400 1900 100 2400 500 1900 Baker stores had stock on hand at the beginning of the year, valued at R1000. 2.Find Gross Profit: = Sales Cost of Sales Gross Profit Transactions: 1. 4600 1900 2700 Purchased merchandise and paid by cheque, R600. 2. Issued R100 worth of stock as a donation to the Help the Poor Club. 3. Sold goods on credit to K. Watson, R150. 4. K. Watson returned damaged goods. Issued a credit note for R30 to him. 5. The owner, J. Baker, took stock for personal use, R300. 6. Cash sales for the day as per cash register roll, 7. Issued a cheque to J. Carter for carriage on purchases, R195. 8. J. Morris paid his account of R240 by cheque, R230. Allowed him R10 cash discount. EXERCISE 6. Complete the following. Opening Stock (1/3/94) Purchases Carriage on Purchases Cost of goods available for sale Closing Stock (28/2/95) Cost of Sales Gross Profit Sales J Cansfield (a) 760 (i) 210 4 460 1 230 (ii) (iii) 4 030 (b) Nil 5 060 (i) 5 180 Nil (ii) 4 540 (iii) (c) Nil (i) Nil 1 805 (ii) 1 340 (iii) 2 900 The value of stock on had as per physical stock take was, R… R2 500. Example: Bakers : Periodic System No Account Debit Account Credit A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 FINANCIAL STATEMENTS FOR PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEM Income Statement for the year ended _________________________ Notes Sales Cost of Sales R ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Gross Profit Other Operating Income … … Gross Operating Income Operating Expenses … … Operating Profit (Loss) Interest Income 1 Profit (Loss) before interest expense Interest Expense 2 Net Profit (Loss) for the year/ period 7 CALCULATION FOR COST OF SALES Opening Stock Net Purchases Carriage Closing Stock Notes to Financial Statements 4 INVENTORIES Trading Inventory Consumable Stores on Hand This is your closing stock amount J Cansfield O L