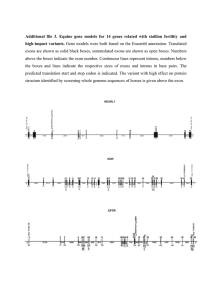
The entire human genome consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes
advertisement
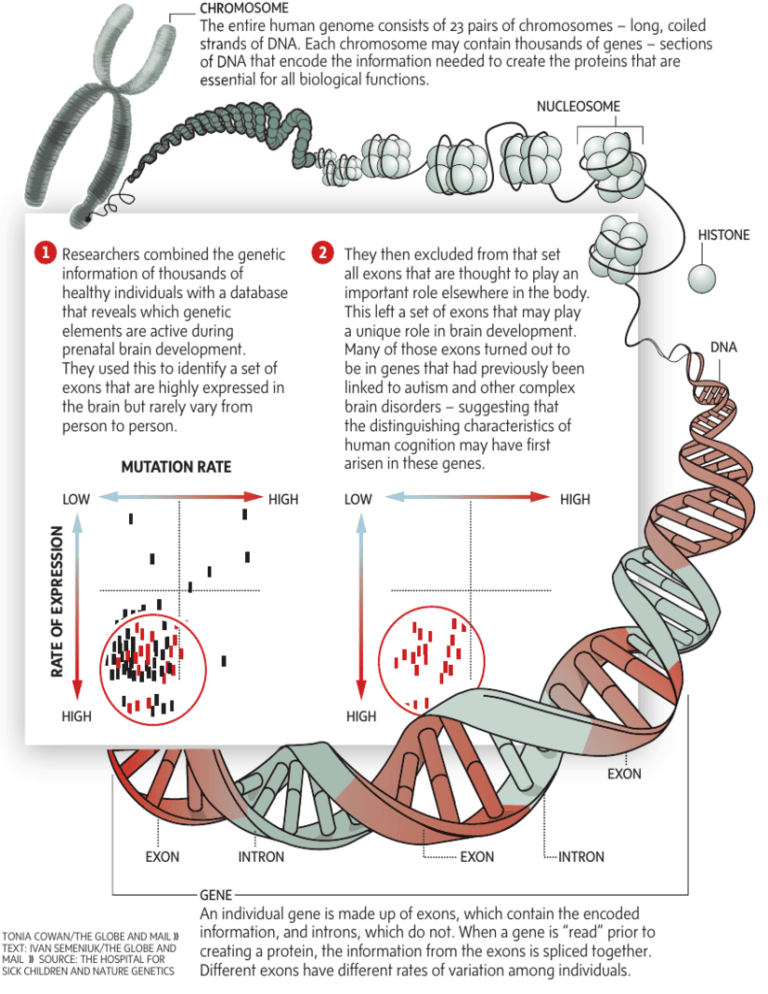
CHROMOSOME The entire human genome consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes – long, coiled strands of DNA. Each chromosome may contain thousands of genes – sections of DNA that encode the information needed to create the proteins that are essential for all biological functions. NUCLEOSOME 1 Researchers combined the genetic information of thousands of healthy individuals with a database that reveals which genetic elements are active during prenatal brain development. They used this to identify a set of exons that are highly expressed in the brain but rarely vary from person to person. MUTATION RATE HIGH HISTONE They then excluded from that set all exons that are thought to play an important role elsewhere in the body. This left a set of exons that may play a unique role in brain development. Many of those exons turned out to be in genes that had previously been linked to autism and other complex brain disorders – suggesting that the distinguishing characteristics of human cognition may have first arisen in these genes. LOW DNA HIGH RATE OF EXPRESSION LOW 2 HIGH HIGH EXON EXON INTRON EXON INTRON GENE TONIA COWAN/THE GLOBE AND MAIL 66 TEXT: IVAN SEMENIUK/THE GLOBE AND MAIL 66 SOURCE: THE HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN AND NATURE GENETICS An individual gene is made up of exons, which contain the encoded information, and introns, which do not. When a gene is “read” prior to creating a protein, the information from the exons is spliced together. Different exons have different rates of variation among individuals.