Lesson 18 Solutions
advertisement

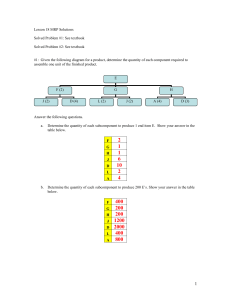
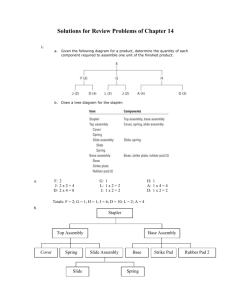
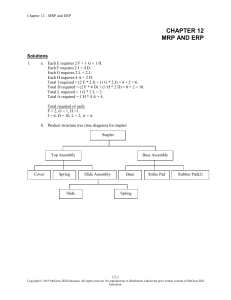
Lesson 18 MRP Solutions Solved Problem #1: See textbook Solved Problem #2: See textbook #1: Given the following diagram for a product, determine the quantity of each component required to assemble one unit of the finished product. E F (2) J (2) G D (4) L (2) H J (2) A (4) D (3) Answer the following questions. a. Determine the quantity of each subcomponent to produce 1 end item E. Show your answer in the table below. F G H J D L A b. 2 1 1 6 10 2 4 Determine the quantity of each subcomponent to produce 200 E’s. Show your answer in the table below. F G H J D L A 400 200 200 1200 2000 400 800 1 #2: Draw a product structure tree diagram for a stapler, where Item Stapler Top Assembly Slide Assembly Base Assembly Components Top Assembly, Base Assembly Cover, Spring, Slide Assembly Slide, Spring Base, Strike Plate, Rubber Pad (2) Stapler Base Assembly Top Assembly Cover Slide Assembly Spring Base Rubber Pad (2) Strike Plate Slide Spring #3: The following product structure tree shows the subcomponents for an end item. Also, the lead times and the quantity on hand are given. End Item B (2) E (2) Item LT (wk) Amount on hand C F (3) End 1 0 G (2) B 2 10 D (3) E (2) C 3 10 D 3 25 H (4) E 1 12 F 2 30 E (2) G 1 5 H 2 0 Answer the following questions. This problem must be done manually. a. If 20 units of the end item are to be assembled, how many additional units of E are needed? 138 b. A order for the end item is scheduled to be shipped at the start of week 11. What is the latest week that the order can be started and still be ready to ship on time. The beginning of week 5 2 #4: A table (T) is assembled using 3 components: wood sections (WS), braces (B) and legs (L). The product structure tree is shown below: T WS (2) B (3) L (4) The company wants to ship 100 units at the beginning of day 4, 150 units at the beginning of day 5, and 200 units at the beginning of day 7. Receipts of 100 wood sections scheduled at the beginning of day 2. There are 120 legs and 60 braces on hand. 200 legs are scheduled for receipt at the beginning of day 2. 150 braces are scheduled for receipt at the beginning of day 3. The lead times in days are as follows: assembly time for tables – 1 day; wood sections – 2 days for braces; and 1 day for legs. Prepare the material requirements plan for braces and legs as requested in the following. a. Prepare a material requirements plan for braces using lot-for-lot ordering. Complete the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number 1 2 Demand Gross requirements OH/ SR 60 Projected on hand 60 60 Net requirements Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases b. 4 300 300 150 210 90 90 450 450 600 600 0 450 450 600 0 600 600 90 450 5 6 7 8 9 Prepare a material requirements plan for legs using a lot size of 60. Complete the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number Demand Gross requirements OH/ SR 3 120 Projected on hand Net requirements Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases 1 2 3 4 400 600 400 600 5 6 7 8 9 800 800 200 120 320 320 40 40 40 20 20 20 80 560 760 120 600 780 120 600 780 3 #5: End item P is composed of three subassemblies: K, L, and W. K is assembled using 3 G’s and 4 H’s. L is made of 2 M’s and 2 N’s. W is made of 3 Z’s. On hand inventories are 20 L’s, 40 G’s, and 200 H’s. Scheduled receipts are 10 K’s at the start of week 3, 30 K’s at the start of week 6, and 200 W’s at the start of Week 3. One hundred P’s will be shipped at the start of week 6 and another 100 at the start of week 7. Lead times are two weeks for subassemblies, and one week for components, G, H, M, N and Z. Final assembly of P requires one week. a. Develop a product structure tree for P. P K L G (3) b. H (4) W M (2) N (2) Z (3) Complete the following table. Item P K L W G H M N Z Lead Time (wk) 1 2 2 20 2 1 40 1 200 1 1 1 Amount on hand c. Prepare a master schedule and MRP for P using lot-for-lot ordering by completing the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number Demand Gross requirements 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 100 100 100 100 OH/ SR Projected on hand Net requirements Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases 100 100 100 100 100 100 4 d. Prepare an MRP for K using lot-for-lot ordering by completing the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number 1 2 3 4 Demand Gross requirements 10 10 OH/ SR Projected on hand Net requirements Planned-order receipts 90 Planned-order releases e. 1 2 Gross requirements 8 9 100 100 100 100 30 10 10 30 90 70 90 70 70 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 50 50 50 50 40 Projected on hand 40 Net requirements Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases 40 40 50 50 230 160 280 210 280 210 Prepare an MRP for H using a lot size of 100 by completing the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number Demand Gross requirements OH/ SR 7 270 210 270 210 Demand f. 6 Prepare an MRP for G using a lot size of 70 by completing the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number OH/ SR 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 60 60 60 60 360 280 360 280 200 Projected on hand Net requirements Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases 200 200 200 40 60 160 240 200 300 200 300 5 #6: A company which makes electric golf carts has just received an order for 200 carts, which must be ready for delivery at the end of week 8. Information concerning the product structure, lead times, and quantities on hand are shown in the following table. There are no scheduled receipts. Parts List for Electric Golf Cart Lead Time (GC) Electric Golf Cart (T) Top (B) Base (T) Top (S) Supports (4) (CV) Cover (B) Base (M) Motor (BO) Body (SE) Seats (2) (BO) Body (F) Frame (CN) Controls (WA) Wheel Assemblies (4) Quantity on Hand 1 1 1 0 40 20 1 1 200 0 2 3 2 300 50 120 1 1 1 35 0 240 Use this information to answer the following questions. a. Develop a product structure tree for the GC. GC Electric Golf Cart T Top S (4) Supports B Base CV Cover M Motor BO Body SE (2) Seats F Frame CN Controls WA (4) Wheel Assemblies 6 b. For this problem disregard the quantities on hand, and determine the Bill of Material quantities for each subassembly and components that are required to produce 200 golf carts. Show your answers in the table below. 200 200 800 200 200 200 200 400 200 200 800 GC T S CV B M BO SE F CN WA Prepare an MRP for GC, B, BO, and WA using lot-for-lot ordering in the following questions. c. Show the MRP for GC by completing the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 200 200 Demand Gross requirements OH/ SR Projected on hand 200 200 Net requirements Planned-order receipts 200 Planned-order releases d. Show the MRP for B by completing the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 200 200 Demand Gross requirements OH/ SR 7 20 Projected on hand 20 20 20 20 20 20 Net requirements Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases 20 180 180 180 7 e. Show the MRP for BO by completing the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gross requirements 9 50 OH/ SR Projected on hand 50 50 50 50 50 50 130 130 Net requirements Planned-order receipts 130 Planned-order releases Show the MRP for WA by completing the table below. You do not need to enter values of 0. Week Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 520 520 Demand Gross requirements 240 OH/ SR Projected on hand Net requirements Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases g. 8 180 180 Demand f. 7 240 240 240 280 280 280 0 Show the assembly time chart for GC – BO – B – WA. What is the lead time for this assembly sequence? Assem blly Tim e Chart -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 WA BO B GC 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The assembly sequence GC – BO – B – WA lead time is 6 weeks. 8