http://multimedia.mcb.harvard.edu
advertisement

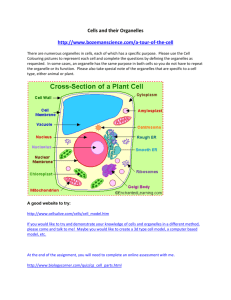
HB The Human Cell http://multimedia.mcb.harvard.edu Pre Test! 1. How many cells do we have in our bodies? 2. How many specialized cells do we have in our bodies? 3. What is the outermost part of a human cell? 4. Where is the genetic information found within a cell? 5. What molecule contains all of our genetic information? 6. What is an organelle? 7. Name 5 organelles. 8. What do cells sit around and do all day long? 9. How long do cells live? 10. Groups of cells that perform a similar function are called tissues. Name the 4 types of tissues found in the human body. Levels of Organization: Atoms, Compounds, Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ systems, Organism Chapter 3: The Cell I. Introductory Facts A. 70,000,000,000,000 B. 200 http://multimedia.mcb.harvard.edu/ Neurons Red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets Cardiac muscle cells, Capillary, Purkinje Fibers Skeletal Muscle Sarcomeres & Mitochondria Chapter 3: The Cell I. Introductory Facts (continued) C. Cell specialization D. Interdepencence E. Eukaryotic http://multimedia.mcb.harvard.edu/ We Are Eukaryotic! I. Introductory Facts (continued) E. Heterotrophic Draw & Label the parts of a human cell. Cell membrane Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear membrane with pores Chromatin Cytoskeleton Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Mitochondria Cilia Flagella Centrioles Vacuoles II. Cellular Processes A. Nutrition II. Cellular Processes (continued) B. Digestion II. Cellular Processes (continued) C. Absorption II. Cellular Processes D. Biosynthesis (continued) II. Cellular Processes (continued) E. Cellular Respiration II. Cellular Processes (continued) F. Excretion II. Cellular Processes (continued) G. Secretion Mucus (brown) is secreted by mucous cells and whisked away by cilia in respiratory tract. It traps dust, pathogens, etc. and keeps them from entering respiratory system. II. Cellular Processes (cont.) H. Response Macrophage and Erythrocyte (RBC) Macrophage destroying cancer cell! II. Cellular Processes (continued) I. Cellular Reproduction Amoeba Amoeba Bacteria Paramecia Human Leucocytes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rgLJrvoX_qo&NR=1 II. Cellular Processes (continued) I. Cellular Reproduction 1. Mitosis II. Cellular Processes (continued) I. Cellular Reproduction 2. Meiosis Zygote Two Cells http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=cd4d9aa2-39a6-4450-bb56-6d40f694e617 Chick Embryo, 40 Days III. Cell Membrane A. Structure of Cell Membrane 1. Lipid bilayer 2. Proteins 3. Sugars III. Cell Membrane (continued) B. Function of Cell Membrane 1. Separates cell from environment 2. Regulates what enters and exits cell 3. Supports organelles http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q530H1WxtOw IV. Miscellaneous A. Cytoskeleton Microtubules (green), actin filaments (red), and the nucleus (blue) V. Organelles V. Organelles A. Nucleus 1. Nuclear membrane/ pores 2. Nucleolus 3. DNA a. Chromatin V. Organelles A. Nucleus (continued) 3. DNA b. Chromosomes V. Organelles (continued) B. Endoplasmic Reticulum 1. Rough ER 2. Smooth ER V. Organelles (continued) C. Ribosomes V. Organelles (continued) D. Golgi Apparatus V.Organelles (continued) E. Vesicles V.Organelles (continued) F. Lysosomes V.Organelles (continued) G. Mitochondria http://multimedia.mcb.harvard.edu/ V.Organelles (continued) I. Centrioles V. Organelles (continued) I. Centrioles 1. Centrosome Spindles V.Organelles (continued) J. Cilia Nasopharynx epithelial cells with Cilia 3. Sinus Mucousa Auditory Ear Cells With Cilia Auditory Ear Cells 4. Microtubules 5. Microvili Mucus (brown) is secreted by mucous cells and whisked away by cilia in respiratory tract. It traps dust, pathogens, etc. and keeps them from entering respiratory system. V.Organelles (continued) K. Flagella Sperm & Egg V. Organelles (continued) L. Vacuole Vacuole in Muscle Cell VI. Cytoplasm A. Cytosol 1. Fluid 2. Inclusions B. Organelles http://multimedia.mcb.harvard.edu/ I. Introductory Facts (cont.) F. 4 Types of Tissues 1. Muscular 2. Nervous 3. Connective 4. Epithelial http://multimedia.mcb.harvard.edu/ Neuron cell body (purple) with numerous synapses (blue). Communication from one neuron flows to another neuron across a synapse, the small gap separating neurons. SEM X80,000.