Cost Management and Control
advertisement

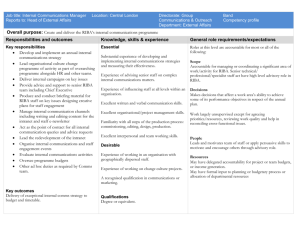
David Watkins RIBA Part 3 Course 2014 Cost Control and Management Cost Cost Management Control andand Management_dhw_2014 Control_dhw_2014 For which of you, desiring to put up a For which ofnot you,first desiring to put up a tower, does give much tower, notprice, first give thoughtdoes to the if hemuch will have thought to the price, if he will have enough to make it complete? enough to make it complete? For fear that if he makes a start and is For he with makes a start and all is not fear ablethat to goif on it to the end, not towill go on it to at thehim end, all whoable see it be with laughing who see it will be laughing at him And saying, this man made a start at And saying, man made a start building andthis is not able to make it at building completeand is not able to make it complete Luke Chapter 14 verses 28-30 Luke Chapter 14 verses 28-30 Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Buildings lie at the heart of our everyday lives Buildings cost money ……….and usually lots of it To build well you must first plan Project budgets are established for buildings to be delivered to projected cost and programme There is often a spotlight on Public Sector projects and strong emphasis on meeting the budget Financial difficulties results in public (taxpayers) and media becoming unsympathetic and vocal £10-£40m £200m £50m £827mm £110m Steelwork £414m Programme No Cost PlanContractual Disputes Poor procurement route Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 The construction industry and the environment in which it operates have changed significantly • • • • • • • • New and varied ways of buying design and construction Fragmentation of the industry with increased in specialist trade contracting Demise of direct employment Growth of labour-only and fixed term contracts Fee competition for consultancy services Introduction of partnering More conflict and less trust Clients wanting more value for money Business cycles hit peaks and lows with consultants and contractors having to cope with increasing pressure for : Faster construction Higher quality Lower costs What has not changed is the need for effective cost control from inception to completion Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Clients want : Certainty of price Projects constructed and delivered within budget Completion on time The best quality possible for the price Value for money No surprises Contractors and Consultants want : A reasonable return for the risks they take Payment on time Clients who do not keep changing their minds Satisfied clients Positive feedback, enhanced reputation and glowing references Repeat commissions and business Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 The Architect needs to have Budget and Financial Awareness SETTING COST LIMITS Why? Affordability, Profitability, Accountability and Value When? Throughout all stages RIBA Plan of Work How? Project Appraisal, Project Development and Allowances What? Budgets and Cost Plans Who? Client then Project Team and Stakeholders/External Funders Where? Project Team and Design Team Meetings BUILDING DEVELOPMENT COSTS Land/Building Costs Acquisition and Fees Construction Costs Normal and Abnormal Costs Fees Surveys and Investigations, Professional Team, Statutory Submissions Financing Costs Bank loans and interest (temporary and permanent arrangements) Financial Status VAT Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 FACTORS AFFECTING BUILDING DEVELOPMENT COSTS Forms of Procurement Traditional Design and Build Management Contracting Construction Management Method of Tendering Competitive tender Negotiated tender Risk Identify and Evaluate the risks as a Project Team Establish a Risk Register and monitor Manage the risk and use register as a dynamic document Reduce the risk Accept the risk Mitigate the risk by transfer or share Eliminate the risk Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Control and Management Risk Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 COST IMPLICATIONS OF DESIGN VARIABLES Interested parties Heritage and conservation groups, archaeological groups, local history societies, Local Authority, resident groups, ecology groups….. Site conditions Location, access, topography, infrastructure, contamination, ground bearing capacity, location and diversion of services, etc……………….…. Legislation Built environment issues to include land searches, restrictive covenants, land registration, Building Regulations, CDM, consents…… Future proofing Changes in operation and technology may necessitate requirement for alternative layout, accommodation, M&E systems which if planned for would minimise disruption. Life cycle cost exercises……… Environmental Client policies will identify attitude towards environmentally-friendly inclusions/considerations such as pollution, dirt, dust, noise, smoke, traffic, travel, chemicals, sustainability in regard to waste and energy Redundant performance and circulation areas Not primary function spaces – car parking areas, corridors, foyers, stairwells, balconies, lift shafts, plant rooms, operating plant………….. Building Shape Plan shape and the geometry created has a direct influence on the cost to construct - square, rectangular, irregular with right angles, circular Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 If each building is 5m high and 400 sqm floor area Perimeter wall areas as follows: Plan 1 Perimeter area 20 x 4 x 5 = 400sqm Plan 2 Perimeter area 40 x 2 + 10 x 2 = 100 x 5 = 500sqm Plan 3 Perimeter area 60 +10+25+10+10+10+25+10 = 160 x5 = 800sqm Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Storey Height Numbers of levels requires consideration – low rise and high rise Modulation Repetition in regard to productivity and programme Buildability Ease or complexity of physical construction Environmentally-friendly Adoption of passive measures – insulation standards, air tightness, rainwater harvesting, electrical generation, solar heating, etc………….. Life cycle costs Capital cost to install versus benefit gained through the occupational life of the building So who can prepare the costs at the appropriate stages, incorporate the various aspects and elements and monitor continually? Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost monitoring and Control Quantity Surveyor takes the lead Design Team approach – collaborative working Project Team approach – collaborative working Pre-conceived impressions ?? The Image of the Quantity Surveyor Cost planning should be perceived as a positive disciplinary process to enable a building to be constructed to a perceived amount Listen, integrate, estimate, record and view big picture By the Architect Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost monitoring and Control – Why? • Ensure employers are provided with value for money • Make employers and designers aware of the cost consequences of their desires and/or proposals • Provide advice to designers to enable them to arrive at practical and balanced designs within cost limits • Keep expenditure within cost limits approved by the employer • Provide robust cost information upon which the employer can make informed decisions - cost predictability Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost monitoring and Control – How? • Estimating and cost planning • Cost checking • Pre-tender estimate • Tender analysis • Cost control reports during the construction stage at regular intervals • Final Account and Feedback • Value Engineering Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Strategic Definition Preparation and Brief Concept Design Developed Design Technical Design Construction Handover and Close Out In Use Core Objectives Business Case And Strategic Brief Develop Project Objectives Project Brief Prepare Concept Design Final Brief Prepare Developed Design Building Co-ordination Prepare and co-ordinate all technical design Off site manufacturing and on site construction Handover of building and contract completion In use activities and feedback Cost Input Estimate(s) Estimate(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Checking Pre-tender Estimate Tender Analysis Cost Control Financial Statements Cost Control Financial Statements Final Account and Feedback RIBA Plan of Work Input at Key Development Stages – continual Cost Control and Management RIBA Plan of Work Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost monitoring and control - How Estimate Determination of possible cost of building • Floor Area Method • Functional Unit Method • Elemental Method Cost Plan Critical breakdown of the cost limit for the building (provides a statement of how the Design Team propose to distribute the available budget among the elements of the building • Elemental Method Contingency - Design/Construction/M&E Inclusion and Exclusions Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Input 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Strategic Definition Preparation and Brief Concept Design Developed Design Technical Design Construction Handover and Close Out In Use Estimate(s) Estimate(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Checking Pre-tender Estimate Tender Analysis Cost Control Financial Statements Cost Control Financial Statements Final Account and Feedback RIBA Plan of Work Input at Key Development Stages – continual Cost Control and Management RIBA Plan of Work : Strategic and Concept Stages Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Control and Management Budget Estimate Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Don’t be tempted or drawn into giving cost estimates Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost monitoring and control – Tender Analysis Pre-tender Estimate Tender Analysis and report in respect of submitted tenders Errors Obvious Mistakes in Pricing Arithmetical Errors Qualifications Make-up and breakdown of price Consistency and Competitiveness Dealing with Errors and Qualifications Cost Control and Management Budget Estimate Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Strategic Definition Preparation and Brief Concept Design Developed Design Technical Design Construction Handover and Close Out In Use Contract awarded Tenders submitted Cost Input Estimate(s) Estimate(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Checking Pre-tender Estimate Tender Analysis Cost Control Financial Statements Cost Control Financial Statements Final Account and Feedback RIBA Plan of Work Input at Key Development Stages – continual Cost Control and Management RIBA Plan of Work : Technical Design Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost monitoring and control – What? Cost Control Forecasting and anticipating final cost at regular intervals Accounting for variations Controlling and Reporting – Regularly and Comprehensively (Design Team Input) Variations Additional work Omissions Change in specification Correction of Errors in contract documents Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost monitoring and control – Why? Cost Control Variations Keep Client updated on financial situation/anticipated costs Inform to allow decisions to be taken Variations Change of mind Errors – brief/design/quantities/specification Fashion Technology Business Trends Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Input 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Strategic Definition Preparation and Brief Concept Design Developed Design Technical Design Construction Handover and Close Out In Use Estimate(s) Estimate(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Checking Pre-tender Estimate Tender Analysis Cost Control Financial Statements Cost Control Financial Statements Final Account and Feedback RIBA Plan of Work Input at Key Development Stages – continual Cost Control and Management RIBA Plan of Work : Fabrication and Construction Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Control and Management RIBA Plan of Work : Technical Design Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost monitoring and control – Final Account Final Account Adjustment of contract sum, Provisional Sums, PC Sums and loss/expense Variations Feedback Cost Control and Management Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014 Cost Input 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Strategic Definition Preparation and Brief Concept Design Developed Design Technical Design Construction Handover and Close Out In Use Estimate(s) Estimate(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Plan(s) Cost Checking Pre-tender Estimate Tender Analysis Cost Control Financial Statements Cost Control Financial Statements Final Account and Feedback RIBA Plan of Work Input at Key Development Stages – continual Cost Control and Management RIBA Plan of Work : Final Account and Feedback Cost Control and Management_dhw_2014