Abnormal findings
advertisement

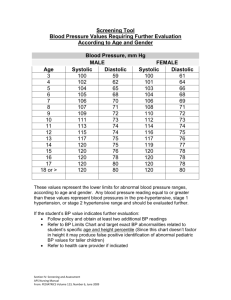
PERIPHERAL VASCULAR ASSESSMENT Preparing the Client 1. Have the client wear an examination gown and sit upright on an examination table. 2. Make sure the room has a comfortable temperature without drafts. 3. Inform the client that it will be necessary to inspect and palpate all four extremities and the groin area. Preparing the Client 4. Explain that the client can sit for examination of the arms but will need to lie down for examination of the legs and groin. 5. Explain in detail what you are doing and answer any questions the client may have. Equipment • • • • • • • • Centimeter ruler Stethoscope Doppler ultrasound device Conductivity gel Tourniquet Gauze or tissue Waterproof pen Blood pressure cuff Physical Assessment of Upper Extremities Inspection Observe arm size, venous pattern, and color; also look for edema. Abnormal findings: • Lymphedema • Prominent venous pattern • Raynaud’s disease Palpation • Palpate the client’s fingers, hands and arms, and note the temperature. Abnormal findings: • Arterial insufficiency • Raynaud’s disease Palpation • Assess capillary refill time. Abnormal findings: • Capillary refill time exceeding 2 seconds Palpation • Palpate the radial pulse. Abnormal findings: increased volume - hyperkinetic state decreased or absent pulse - partial or complete arterial occlusion Buerger’s disease or scleroderma Compartment syndrome Buerger’s Disease Scleroderma Compartment Syndrome Palpation Palpate the ulnar pulses. Abnormal finding: - non-elastic wall - arteriosclerosis Palpate the brachial pulses if arterial insufficiency is suspected. Abnormal findings: – Increased, diminished, or absent Palpation Palpate the epitrochlear lymph nodes (size, tenderness, consistency) Abnormal findings: • infection on the hand or forearm / lesion Palpation Perform the Allen test Abnormal findings: - persistence of pallor for more than 5 seconds - arterial insufficiency or occlusion of the ulnar / radial artery Physical Assessment of Lower Extremities Inspection • Observe skin color while inspecting both legs from the toes to the groin Abnormal findings: • arterial insufficiency (pallor) • venous insufficiency (cyanosis & brownish pigmentation) Inspection • Inspect distribution of hair – Abnormal findings: • arterial insufficiency (Hair Loss) Inspection Inspect for lesions or ulcers – Abnormal findings: • arterial insufficiency (smooth, even margins that occur at pressure areas) • venous insufficiency (irregular edges, bleeding and possible bacterial infection that occur in the medial ankle) Inspection • Inspect for edema – Abnormal findings: • Bilateral and Unilateral edema Palpation • Palpate edema – Abnormal findings: • CHF or hepatic cirrhosis Palpation Palpate bilaterally for temperature of the feet and legs Abnormal findings: • generalized coolness in one leg or change in temperature from warm to cool as you move down the leg • increased warmth Palpation • Palpate the superficial inguinal lymph nodes – Abnormal findings: • local infection • Palpate the femoral pulses – Abnormal findings: • partial or complete arterial occlusion Palpation • Auscultate the femoral pulses – Abnormal findings: • Bruit Palpation • Palpate the popliteal pulses Palpation • Palpate the dorsalis pedis pulses Palpation • Palpate the posterior tibial pulses – Abnormal findings: • partial or complete arterial occlusion Inspection • Inspect for varicosities and thrombophlebitis – Abnormal findings: • Varicose veins Palpation • Check for Homan’s sign – Abnormal findings: • CHF or hepatic cirrhosis Special Tests for Arterial or Venous Insufficiency • Perform position change arterial insufficiency test for – Abnormal findings: • pallor with legs elevated • return of pink color that takes longer than 10 seconds and superficial veins that take longer than 15 seconds to fill • persistent rubor • Use ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI) – Abnormal findings: • an ABPI of 0.5 to 0.95 indicates mild to moderate arterial insufficiency • an ABPI of 0.25 or lower indicates severe stenosis • Manual compression test – Abnormal findings: • you will feel a pulsation with your upper fingers if the valves in the veins are incompetent • Trendelenburg test – Abnormal findings: • filling from above with the tourniquet in place and the client standing • rapid filling of the superficial varicose veins from above after the tourniquet has been removed Documentation of Objective Data • arms are equal in size, no swelling, pinkish skin tone • no clubbing of fingertips, warm bilaterally • capillary refill time less than 2 seconds • radial and brachial pulses strong bilaterally • no epitrochlear lymph nodes palpated • legs are pink from toes to groin bilaterally, normal distribution of hair, no ulcers or edema • legs are warm bilaterally • 1-cm nontender inguinal lymph nodes palpated • femoral, popliteal, dorsalis pedis, and posterior tibial pulses strongly palpated bilaterally • no apparent varicosities or superficial thrombophlebitis Nursing Diagnosis Wellness Diagnoses – Readiness extremities for enhanced circulation to – Health-Seeking Behavior. Requests information on regular monitoring of pulse, blood pressure, cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Regular exercise, and smoking cessation Nursing Diagnosis Risk Diagnoses – Risk for Ineffective Management Therapeutic Regimen – Risk for Infection – Risk for Injury – Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity – Risk for Activity Intolerance – Risk for Peripheral Neurovascular Dysfunction Nursing Diagnosis Actual Diagnoses – Ineffective Tissue Perfusion – Impaired Skin Integrity – Pain – Fear of loss of extremities – Disturbed Body Image END