Kingdom Protista
advertisement
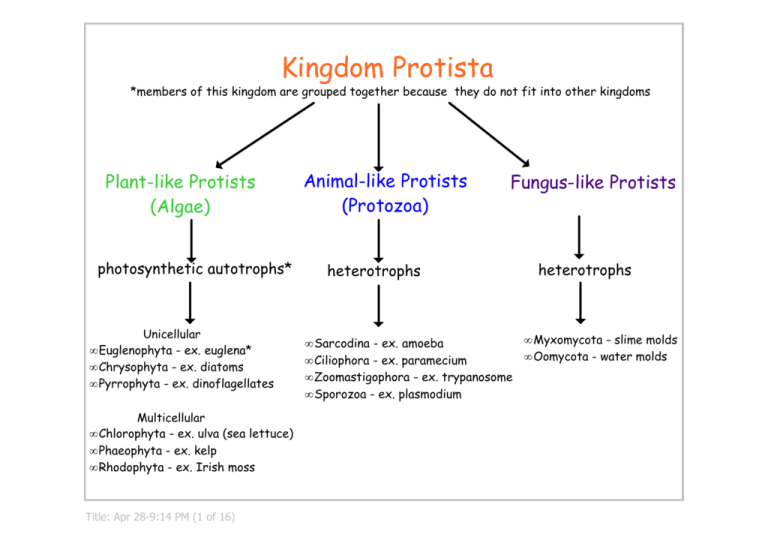
Kingdom Protista *members of this kingdom are grouped together because they do not fit into other kingdoms Plant-like Protists (Algae) Animal-like Protists (Protozoa) photosynthetic autotrophs* Unicellular • Euglenophyta - ex. euglena* • Chrysophyta - ex. diatoms • Pyrrophyta - ex. dinoflagellates Multicellular • Chlorophyta - ex. ulva (sea lettuce) • Phaeophyta - ex. kelp • Rhodophyta - ex. Irish moss Title: Apr 28­9:14 PM (1 of 16) heterotrophs • • • • Fungus-like Protists heterotrophs • Myxomycota - slime molds Sarcodina - ex. amoeba • Oomycota - water molds Ciliophora - ex. paramecium Zoomastigophora - ex. trypanosome Sporozoa - ex. plasmodium Plant-like Protists (Algae) Unicellular Title: Apr 29­9:33 PM (2 of 16) Phylum Euglenophyta Representative: Euglena General Features: • rounded anterior, pointed posterior • hard outside covering called pellicle • cytoplasm: clear ectoplasm, dense endoplasm • live in fresh water • contractile vacuole to remove excess water Food Getting: • have chloroplasts for photosynthesis • also absorb nutrients by diffusion Title: Apr 29­6:26 AM (3 of 16) Movement: • flagellum in front to draw through water • euglenoid mvmt: shorten and extend body Reproduction: • asexually by binary fission • form dormant cyst in unfavorable conditions Response to Stimuli: • light: eyespot detects light, move twds it • water: if pond dries up, forms cyst pond sample euglenoid movement binary fission http://www.btinternet.com/~stephen.durr/euglena.html Title: Apr 29­6:44 AM (4 of 16) cysts Phylum Chrysophyta Representative: Diatoms General Features: • fresh water and salt water • most imp/abundant primary producers in aquatic env • body structure: two halves called valves • valves fit like top and bottom of shoe box • valves are made of silica (sand, glass component) • mined and used as abrasive in polishes, toothpaste... Food Getting: • have chromoplasts for photosynthesis • also absorb nutrients by diffusion Title: Apr 29­6:26 AM (5 of 16) Movement: • do not move on own; flow with currents Reproduction: • asexually by binary fission til too small • valves separate, each forms new one inside • sexually by release and union of gametes • gametes have two flagella so swim + unite • zygote (fert. egg) that forms devs into adult Phylum Pyrrophyta Representative: dinoflagellates General Features: • another imp food source for aquatic animals • protective coat of cellulose plates • phosphorescent - release a small amt light • in high numbers, appear as "red tide" • can produce toxins ~ kill shellfish / poison people Food Getting: • have chloroplasts for photosynthesis • also absorb nutrients by diffusion Title: Apr 29­6:26 AM (6 of 16) Movement: • two flagella - one spins it, one a rudder Reproduction: • mainly asexually by binary fission • sexually in certain circumstances Plant-like Protists (Algae) Seaweeds - Multicellular Title: Apr 29­10:55 PM (7 of 16) Phylum Chlorophyta (Green Algae) Representatives: volvox spirogyra ulva (sea lettuce) General Features: • the most plant-like algae • same chlorophyll, cell walls of cellulose, store starch Movement: • most live in fresh water and are multicellular • depends on form: ulva floats, volvox flagella • leaf like part called thallus (if multicellular) • show alteration of generations (sexual + asexual stages) Food Getting: • have chloroplasts for photosynthesis • also absorb nutrients by diffusion Title: Apr 29­6:26 AM (8 of 16) Reproduction: • asexually by fragmentation, spores, cell division • sexually if unfavorable to form zygospore Phylum Phaeophyta (Brown Algae) Phylum Rhodophyta (Red Algae) ex. Irish moss, dulse ex. kelp, rockweed Note: most imp economically - source of agar, carrageen What do they have in common? • multicellular algae • photosynthetic autotrophs • aquatic • leaflike part called thallus • anchored to rocks by "root-like" holdfast • show alternation of generations (asexual and sexual stages in life cycle) • harvested for use as fertilizer Title: Apr 29­7:18 AM (9 of 16) Animal-like Protists (Protozoa) * separated into phyla based primarily on method of locomotion Title: Apr 29­7:18 AM (10 of 16) Phylum Sarcodina Representative: Amoeba General Features: • no cell wall or pellicle; no fixed shape • cytoplasm: clear ectoplasm, dense endoplasm • finger-like projections called pseudopods • live at bottom of fresh water bodies • contractile vacuole to remove excess water Food Getting: • phagocytosis; pseudopods engulf food ~ vacuole • lysosomes fuse with vacuole, enzymes digest food Title: Apr 29­6:26 AM (11 of 16) Movement: • extends pseudopods in direction wishes to go • "amoeboid movement" Reproduction: • asexually by binary fission Response to Stimuli: • light: do not like light, move to pond bottom Phylum Ciliophora - "Ciliated Protozoa" Representative: Paramecium General Features: • most highly advanced of animal-like protists • have stiff pellicle, fixed slipper shape • cytoplasm: clear ectoplasm, dense endoplasm • definite mouth on oral side • indent called oral groove (mouth at end of groove) • contractile vacuole to expel excess water Movement: • surface covered with cilia; beat to move • speed > euglena which > amoeba Reproduction: • asexually by binary fission • sexually by conjugation Food Getting: • predators - go out in search for food Response to Stimuli: • shoot dart-like trichocysts to paralyze prey (+ defence) • light: no preference (all water levels) • use cilia to sweep food into oral groove + mouth • touch: trichocysts shoot out ~ touch • food passes through short gullet into food vacuole • lysosomes fuse with vacuole and enzymes digest food • undigested material out anal spot Title: Apr 29­6:26 AM (12 of 16) Phylum Zoomastigophora - "Flagellated Protozoa" Representative: trypanosome General Features: • aquatic • picked up by biting insects and spreads disease • causes African Sleeping Sickness ~ tsetse fly Title: Apr 29­6:26 AM (13 of 16) Movement: • flagellum • undulating membrane Phylum Sporozoa Representative: plasmodium General Features: • parasites • complex life cycles with sporozoite stage • picked up by biting insects and spread disease • causes malaria ~ mosquito Title: Apr 29­6:26 AM (14 of 16) Movement: • flagellum Fungus-like Protists Phylum Myxomycota - Slime Molds Phylum Oomycota - Water Molds General Features: • tiny slug-like organisms • creep over damp, decaying plant material • "streaming blob" • cytoplasm streams through skeleton-like tubules • appear ______________ so resemble fungi in this way Food Getting: • most are _____________ (feed on dead organic matter) • engulf food by phagocytosis Reproduction: • sexually by formation of _________ (like some fungi) • these produce haploid spores ~ dry conditions • unite to form zygote when damp again Title: Apr 29­7:18 AM (15 of 16) Book Questions: 7, 9, 11-13, 15, 18-20 Q1: Describe what a slime mold is, why it is named that, and why it is considered a member of Kingdom Protista. Q2: List some ways in which the paramecium is more advanced than other protists. Title: Apr 29­11:00 PM (16 of 16)






