Kingdom Protista
advertisement

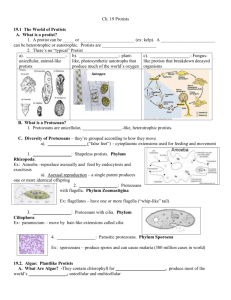
Kingdom Protista Kingdom Protista • Eukaryotic • “Catch-all” Kingdom • Contains organisms that resemble organisms in the kingdoms animalia, plantae, and fungi. • Can be autotrophs or heterotrophs. • Can be unicellular or multicellular. Animal-like Protists: Protozoans What’s a flagella???? • Phylum Zoomastigina (Zooflagellates) – Swim using one or two flagella – Absorb food through the cell membrane – Reproduce asexually (mitosis) or sexually – Live in lakes, or streams, can be parasitic A temporary Animal-like Protists: Protozoans cytoplasmic extension • Phylum Sarcodina (Sarcodines) – What is a – Move and feed by using a pseudopod. vacuole??? – Movement is called “amoeboid movement” – Contain a food vacuole. – Reproduce asexually (mitosis) – Most common example: amoeba Animal-like Protists: Protozoans • Phylum Ciliophora (Ciliates) – Small hairWhat is like conjugation?? projections ? – Feed and move using cilia – Reproduce by conjugation – Live in fresh and salt water, can be parasitic. – Common example: paramecium Animal-like Protists: Protozoans • Phylum Sporozoa (Sporozoans) – – Do not move on their own – Parasitic – Have a complex life cycle that involves more than one host. Fungus–like Protists • Heterotrophs that absorb nutrients from dead or decaying matter. • Lack chitin in cell walls. A carbohydrate • 2 types: found in the – Slime molds – Water molds cell wall of fungal organisms Plant-like Protists: Unicellular Algae • Phylum Euglenozoa (Euglenophytes) Specialized cell wall – Have two flagella – Have a pellicle – Have an eyespot that directs light to chloroplast – Reproduce asexually Plant-like Protists: Unicellular Algae • Phylum Chrysophyta (Chrysophytes) – Have gold-colored chloroplasts – Store food in the form of oil instead of starch – Reproduce sexually and asexually Plant-like Protists: Unicellular The main Algae component of • Phylum Heterokontophyta (Diatoms) glass – Have cell walls made of silicon – Shaped like two sides of a petri dish Plant-like Protists: Unicellular Algae • Phylum Dinoflagellata (Dinoflagellates) – 50% autotrophs, 50% heterotrophs – Have two flagella They glow!!! – Reproduce asexually – Many are luminescent – Can cause “red tide” Plant-like Protists: Red, Brown & Green Algae • Phylum Rhodophyta (Red Algae) – Live at great depths – Contain reddish accessory pigments called phycobillins – Mostly multicellular – Contain flagella Plant-like Protists: Red, Brown & Green Algae • Phylum Phaeophyta (Brown Algae) – Contains brown accessory pigment called fucoxanthin. – Largest and most complex algae – Multicellular – Most are marine – Largest algae – giant kelp Plant-like Protists: Red, Brown & Green Algae • Phylum Chlorophyta (Green Algae) Switch – Share many characteristics with plants between haploid and – Found in fresh and salt water diploid stages – Most live most of life as unicellularduring their life cycle – Reproduce through a process called alternation of generations Human Uses of Algae • Produce much of the Earth’s oxygen through photosynthesis • Chemicals in algae are used to treat stomach ulcers, high blood pressure and arthritis • Used to make sushi rolls, ice cream, salad dressing, pudding, candy bars, pancake syrup and eggnog • Used to make plastics, waxes, transistors, deodorants, paints, lubricants and artificial wood.