Interconnection Devices Interconnection Devices
advertisement
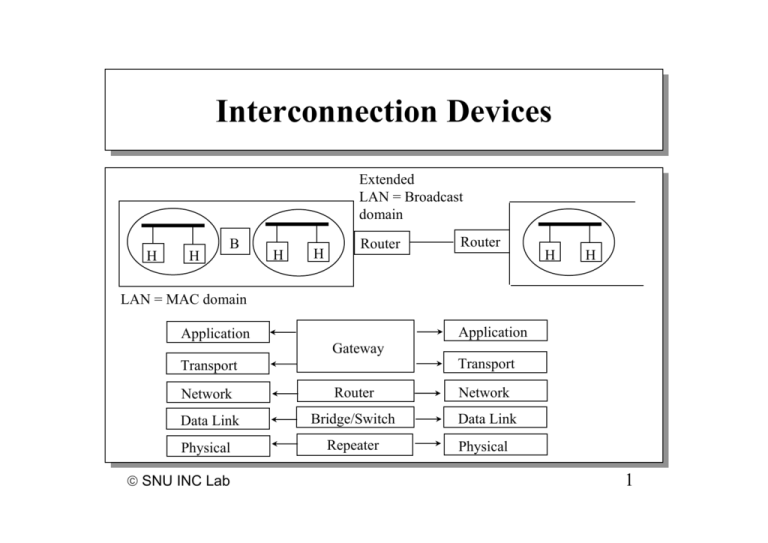
Interconnection Interconnection Devices Devices Extended LAN = Broadcast domain H H B H H Router Router H H LAN = MAC domain Application Application Gateway Transport Transport Network Router Network Data Link Bridge/Switch Data Link Physical Repeater Physical SNU INC Lab 1 Interconnection Interconnection Devices Devices ØØ Repeater Repeater §§ Physical Physicallayer layerdevice devicethat thatrestores restoresand andrelays relayssignals signalssignals signals ØØ Limitation Limitationof ofrepeaters repeaters §§ Collision Collisiondomain domain §§ Physical Physicallimitations limitations ØØ Hub Hub •• Ethernet Ethernet––2500 2500meter metermax. max.distance distance §§ Multiport Multiportrepeater repeater++Fault Faultdetection detection&&recovery recovery ØØ Bridge Bridge §§ §§ §§ §§ Data Datalink linklayer layerdevice device Store Storeand andforward: forward:forwards forwardsaccording accordingto toMAC MAC Extended ExtendedLAN LAN Propagate PropagateMAC MACmulticast multicastframe frame SNU INC Lab 2 Quick Quick Notice Notice Ø Ø Office OfficeHours Hours §§ Tue Tue&&Thur Thur9:30~10:30, 9:30~10:30,13:00 13:00~~16:00 16:00 Ø Ø Class Classon onSep. Sep. 20 20 §§ Just 추석 Justafter afterthe the추석 SNU INC Lab 3 Interconnection Interconnection Devices Devices Ø Ø Router Router §§ Network Networklayer layerdevice device §§ Does Doesnot notpropagate propagateMAC MACmulticast multicast Ø Ø Switch Switch(layer (layer 2) 2) Ø Ø Ø Ø §§ Multiport Multiportbridge bridgewith withparallel parallelpaths paths Layer Layer NNswitch switch Gateway Gateway §§ Transport Transport&&upper upperlayer layerdevices devices SNU INC Lab 4 Network Network Layer Layer Ø Functions § § Construction of a logical network connecting multiple physical networks • internetwork, internet End-to-end packet delivery (internetwork, internet) Logical Network Network Physical Network Router (Gateway) - Routing -Arbitrate difference between two physical networks SNU INC Lab 5 Internetworking Internetworking with with IP IP Ethernet Ethernet Y X Point-topoint A Z B FDDI TCP TCP IP ETH IP ETH SNU INC Lab IP FDDI FDDI IP P2P P2P IP ETH ETH 6 IP IP Packet Packet Delivery Delivery Model Model Ø Ø Datagram Datagram §§ No Noconnection connectionsetup setup Ø Ø Best-effort Best-effort §§ §§ §§ §§ §§ Lost Lostpackets packets Out-of-order Out-of-orderdelivery delivery Packet Packetduplication duplication Delayed Delayeddelivery delivery Higher Higherlayers layersmay mayprovide providereliable reliableservice service Ø Ø IP IPcan canaccommodate accommodate(almost) (almost) any anyhardware hardware technologies technologies SNU INC Lab 7 IP IP Address Address Ø Ø Each EachInternet Internet host hosthas hasaauniversally universallyunique uniqueIP IP address address Ø Ø Format Format §§ 44bytes bytes §§ Hierarchical Hierarchical--Class Class Net ID Host ID InterNIC (or local authority or ISP) assigns a Net ID to an AS (or large customer) AS(Autonomous System) assigns Host ID for each host SNU INC Lab 8 IP IP Address Address Notations Notations Ø Ø Binary Binary -- 11000000 11000000 00000101 0000010100110000 0011000000000011 00000011 Ø Ø Dotted Dotteddecimal decimal -- 192.5.48.3 192.5.48.3 SNU INC Lab 9 IP IP Address Address Classes Classes 0 Net ID 10 Net ID 1 10 Host ID Net ID 1 11 0 SNU INC Lab Class A Host ID Multicast Address Class Range (First Byte) A B C D E 0 - 127 128 - 191 192 - 223 224 - 239 240 - 255 Host ID Class B Class C Class D 10 Special IP Addresses Ø All-0 host suffix § Network address Ø All-0s § This host Ø All-1 host suffix § § All hosts in the specified net Directed broadcast Ø All-1s § § All hosts on this net Limited broadcast Ø 127.*.*.* § Loopback through IP layer SNU INC Lab 11 IP IP Addressing Addressing Ø Ø All Allhosts hostson onaasame samephysical physical network networkhave havethe the same samenetwork networkprefix prefix 128.211 128.10 128.211.6.5 128.10.0.1 128.10.0.2 10 10.0.0.37 SNU INC Lab 192.5.48.3 192.5.48 10.0.0.49 12 Multi-homing Multi-homing Ø Host may connect more than one networks § § Each interface has its own IP address An IP address is assigned to an interface not to a host Ethernet Token Ring 223.240.129 131.108 131.108.99.5 223.240.129.2 223.240.129.17 WAN 78 78.0.0.17 SNU INC Lab 13 IP Routing Ø Direct and Indirect delivery §Direct – Destination is in the same physical network §Indirect – Destination is on other physical network Case 1: Host a --> Host b Host a knows that host b is in the same physical network How? Case 2: Host a --> Host c Host a relay datagram to router A or B a c B E C b A SNU INC Lab F D d 14 Forwarding Forwarding Table Table Ø Format § § <Destination ID, next hop> Destination ID is the network prefix of an IP address Ø Hop by hop forwarding § A forwarding table indicates the next hop router (or direct delivery) toward the final destination Forwarding table at node a SNU INC Lab Destination ID Net.1 Net 2 Net 3 Net 4 Net 5 Next hop Direct delivery Router B Router A Router B Router A 15 Forwarding Forwarding Table Table Reduction Reduction Ø Ø Ø Ø Network Networkbased basedrouting routing Default Default route route Destination ID Net.1 Net 2 Net 4 Deafult Next hop Direct delivery Router B Router B Router A Ø Ø Search Searchsequence sequenceis isimportant important §§ From Fromspecific specificto togeneral general SNU INC Lab 16 Example Example 10.0.0.1 20.0.0.0 a c B 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.5 b A 10.0.0.7 30.0.0.4 E 40.0.0.0 40.0.0.0 C 30.0.0.0 40.0.0.5 F D 50.0.0.0 50.0.0.0 d 50.0.0.1 A 10.0.0.4 20.0.0.3 B 20.0.0.1 30.0.0.1 C 30.0.0.6 50.0.0.2 D SNU INC Lab 17 Physical/Logical Network Interaction Host a (10.0.0.1) sends a datagram to Host c (40.0.0.5) Assume that it takes the following path 20.0.0.3 = 389 a 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.1 = 077 10.0.0.4 = 104 B 20.0.0.5 = 300 20.0.0.0 E 40.0.0.0 40.0.0.1 = 548 c 40.0.0.5 = 731 End-to-end delivery over a logical network is realized by - Repetitive hardware routing within a series of physical networks - Network layer routing at intermediate routers SNU INC Lab 18 ARP ARP (Address (Address Resolution Resolution protocol) protocol) Ø Ø Problem Problem §§ Each Eachhost hosthas hastwo twodifferent differentaddresses addresses §§ Physical Physicaladdress address(Hardware (Hardwareaddress) address) §§ Logical Logicaladdress address(Protocol (Protocoladdress, address,IP IPaddress) address) D B A C SNU INC Lab F Assumption: Every host knows its own logical & Physical addresses Suppose A wants to send a packet to C E 19 ARP ARP –– Basic Basic Ø Ø Use Useaatable tablethat that maps mapsIP IPaddress address––MAC MACaddress address pairs pairs IP address MAC address 197.15.3.1 197.15.3.2 197.15.3.3 197.15.3.4 197.15.3.5 0A:4B:00:00:07:08 0B:4B:00:00:07:00 0A:5B:00:01:01:03 04:06:07:08:09:10 06:07:09:08:03:01 Ø Ø How How and andwho whomanages managesthe thetable table?? SNU INC Lab 20 ARP ARP –– Two Two Methods Methods Ø Ø Two Twotypes types of ofnetwork network §§ Broadcast Broadcastnetwork: network:LANs LANs(Ethernert, (Ethernert,Token Tokenring, ring,…) …) §§ NBMA NBMA(Non-Broadcast (Non-BroadcastMultiple MultipleAccess) Access) •• Example: Example:ATM, ATM,X.25 X.25 Ø Ø Two TwoARP ARPapproaches approaches §§ Distributed Distributed •• •• Each Eachhost hostbuilds buildsthe themapping mappingtable table Get Getmapping mappinginformation informationasking askingto tothe thetarget target •• •• Only Onlyspecialized specializedARP ARPserver serverhave havethe thetable table Usually, Usually,each eachhost hostperiodically periodicallyreports reportsits itsown ownmapping mapping information to the servers information to the servers §§ Centralized Centralized SNU INC Lab 21 ARP - Distributed Broadcast Network A B C D E Suppose host A wants to send a packet to host C First, host A looks up its ARP cache for C’s mapping information If the inf. does not exist, Host A broadcasts request packet ==> Everyone receives the request Host C sends back a response message How do you design a protocol ?? SNU INC Lab 22 ARP ARP Packet Packet Format Format Ø Ø IP-Ethernet IP-Ethernet HW Type HLEN PLEN Protocol Type Operation Sender HA (Octets 0-3) Sender HA (octets 4,5) Sender IP (Octet 0,1) Sender IP (octets 2,3) Target HA (Octet 0,1) Target HA (Octets 2-5) Target IP (Octets 0-3) SNU INC Lab 23 ARP ARP Processing Processing Ø Ø ARP responses are cached Entry replaced (or purged) when § Cache table overflow • Policy? § After timeout • E.G. 20 min Ø How do you reduce ARP traffic ?? § § Ø Proxy ARP § Ø Cache inf. In the request Cache inf. In the response A server (usually a router) may act as a proxy for many IP address Gratuitous ARP SNU INC Lab 24 Reverse Reverse ARP ARP (RARP) (RARP) Ø Ø AAhost host may maynot not know knowits itsIP IPaddress address §§ Knows Knowsits itshardware hardwareaddress address Ø Ø Problem Problem §§ What Whatisisthe theIP IPaddress addressof ofaagiven givenh/w h/waddress? address? §§ RARP RARPserver server Ø Ø BOOTP BOOTP §§ To Tolease leasean anIP IPaddress addresstemporarily temporarily Ø Ø DHCP(Dynamic DHCP(DynamicHost HostConfiguration ConfigurationProtocol) Protocol) §§ Advanced AdvancedBOOTP BOOTP SNU INC Lab 25 DHCP Ø To join the Internet, a host needs § § § Ø Unique IP address Forwarding table – Default router DNS server DHCP § § A protocol to auto-configure IP address, default router & DNS server DHCP server has information • A pool of available IP addresses • Default routes & DNS server inf. DHCPDISCOVER Reply SNU INC Lab 26 DHCP DHCP Packet Packet Format Format Operation Operation HT ype HT ype HLen HLen Hops Hops Xid Xid Secs Secs Flags Flags ciaddr ciaddr yiaddr yiaddr siaddr siaddr giaddr giaddr chaddr chaddr(16 (16bytes) bytes) sname sname(64 (64bytes) bytes) file file(128 (128bytes) bytes) SNU INC Lab options options 27 DHCP DHCP Relay Relay Ø Ø DHCP DHCPserver server for for each eachnetwork network §§ Management Managementoverhead overhead Ø Ø Relay Relay Unicast to server Broadcast DHCP relay Other networks DHCP server Host SNU INC Lab 28 DHCP DHCP Ref. Ref. nd Ø Ø R. R. Droms, Droms,“The “TheDHCP DHCPHandbook”, Handbook”, 22ndEd., Ed., SAMS SAMS Ø Ø RFC RFC2131, 2131, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2131.txt http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2131.txt SNU INC Lab 29 IP IP Datagram Datagram Format Format VERS HLEN Service Type ID TTL Total Length Flags Protocol Fragment Offset Header Checksum SA DA IP Options (If Any) Padding Data * IETF has finished IPv6 called IPng SNU INC Lab 30 IP IP Datagram Datagram Format Format Ø Version § § Ø Type of service § § § Ø Ø Ø Currently 4 New version = 6 Reliability Delay Throughput Total length § Header + data in bytes (Max = 64 KB) § § Uniquely identify a datagram during its lifetime For fragment reassembly ID Flags § § M (More flag) Do-not-fragment SNU INC Lab 31 IP IP Datagram Datagram Format Format Ø TTL (Time To Live) § In hop count Ø Protocol § Next layer protocol to receive the data SNU INC Lab Decimal Protocol 0 1 2 4 5 8 9 17 Reserved ICMP IGMP ST (Stream protocol) TCP EGP IGP UDP 32 IP IP Datagram Datagram Format Format Ø Ø Header Header checksum checksum §§ 1’s 1’scomplement complementsum sumof ofall all16-bit 16-bitwords wordsininthe theheader header Ø Ø Source Source&&destination destinationaddresses addresses §§ Original Originalsource source&&destination destination §§ Invariable Invariable Ø Ø Options Options §§ §§ §§ §§ Security Security Source Sourceroute route Record Recordroute route Stream StreamID IDfor forreserved reservedresource resource •• For Forvoice voice §§ Timestamp Timestamp SNU INC Lab 33 IP Options Coding Ø TLV Format Type 1B Flag Copy 1b Length 1B Class 2b Value nB Number 5b Flag Copy 0: Copy the option only into the first fragment 1: Copy into all fragments Class 0: User or control 1: Reserved 2: Diagnostics 3: Reserved SNU INC Lab 34 IP IP Options Options Ø Ø .. Class Number Length Description 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 2 3 7 8 9 4 End of Options No Op Security Loose Source Routing Record Route Stream ID (Obsolete) Strict Source Routing Internet Timestamp SNU INC Lab 0 0 11 Var Var 4 Var Var 35 Fragmentation Fragmentation & & Reassembly Reassembly Ø MTU (Maximum Transfer Unit) § § Maximum frame size that a physical network can transmit Different physical networks have different MTUs • Ethernet - 1500 Byte • FDDI - 4500 Byte, TR - 8000 Byte Ethernet Router Router 8000 Byte SNU INC Lab 36 Fragmentation Fragmentation & & Reassembly Reassembly Ø Fragmentation § § Partitioning of a datagram into multiple smaller fragments Sizes <= MTU of next physical network Ø Reassembly § § Concatenation of fragments into the original datagram Protocol principle SNU INC Lab 37 Fragmentation Fragmentation & & Reassembly Reassembly MTU = 2000 MTU = 820 MTU = 2000 Original = 2000 Byte Fragments = 820 Byte Fragments = 400 Byte SNU INC Lab Information for reassembly ID Offset Total length Flag 38